Augmented Reality in Healthcare is Revolutionizing Medicine
Imagine a surgeon performing a complex brain operation, relying on experience and intuition and seeing a real-time 3D hologram of the patient’s anatomy overlaid directly onto the surgical field. This isn’t science fiction – it’s the transformative power of Augmented Reality (AR) in healthcare.

AR is a technology that seamlessly integrates digital information with the physical world. Think of it as a pair of invisible glasses that overlays computer-generated graphics onto your real-time vision. In the context of medicine, this translates to a revolutionary new approach to diagnosis, treatment, and education. From guiding surgeons with intricate anatomical overlays to enabling remote consultations with 3D visualizations, AR is rapidly transforming the way we deliver and experience healthcare. Enhance patient care with augmented reality in healthcare. Explore the benefits and prospects of AR in medical training. Stay informed.
Understanding What is Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays computer-generated information in the real world in real-time. Unlike virtual reality (VR) which creates a completely immersive and simulated environment, AR enhances our perception of the physical world by adding a digital layer.
Here’s a deeper dive into AR and its core components:
Definition and Key Components:
AR seamlessly blends the physical and digital worlds, providing a view of the real environment enriched with computer-generated elements like 3D models, graphics, and data visualizations.
Three key components are essential for an AR experience:
Hardware: Devices like smartphones, tablets, or specialized AR glasses project digital information into the real world.
Software: AR applications and platforms process user input and real-world data to generate the appropriate digital overlays.
Markers: In some cases, physical markers or QR codes might be used to trigger the AR experience, providing a specific location or reference point for the digital information to be overlaid.
How AR Differs from Virtual Reality (VR):
VR and AR, while both utilizing computer-generated elements, offer distinct experiences:
VR: VR immerses the user completely in a simulated environment, shutting out the physical world entirely. This is often achieved through VR headsets that provide a panoramic visual and auditory experience. VR is used in common applications like virtual tours, training simulations, and gaming.
AR: AR, on the other hand, keeps the user connected to the physical world while adding a digital layer of information. Imagine a surgeon viewing real-time patient data overlaid directly onto the surgical field through AR glasses – that’s the essence of augmented reality.
How AR Works:
Augmented Reality technology is based on a combination of software and hardware:
Hardware: Smartphones and tablets equipped with cameras and sensors are readily available platforms for AR experiences. However, specialized AR glasses offer a hands-free and more immersive experience. These glasses contain tiny projectors or displays that overlay the digital information onto the user’s field of view.
Software: AR applications and platforms play a crucial role. These apps access real-world data through the device’s camera and sensors and then process this information to generate the appropriate digital overlays. For instance, an AR app designed for anatomy visualization might use the camera to track the user’s movements and overlay a 3D model of a heart onto a physical model or even directly onto a patient’s body.
Examples of  :
:
The healthcare field is rapidly embracing AR, with numerous platforms and tools emerging:
Anatomy Visualization Apps: These AR applications allow medical students and professionals to explore detailed 3D models of human anatomy interactively. Imagine a student holding up a textbook illustration of the heart and seeing a 3D holographic model come alive with labels and animations, explaining its structure and function in detail.
Surgical Guidance Systems: AR is being integrated into surgical navigation systems, providing surgeons with real-time overlays of patient data directly onto the surgical field. This can include 3D models of organs, blood vessels, and tumors, enhancing precision and reducing complications during surgery.
Remote Consultation and Training: AR can facilitate remote consultations with specialists. Imagine a doctor in a remote location examining a patient through a video call while simultaneously viewing real-time AR overlays of diagnostic data or anatomical models, enabling a more comprehensive evaluation.
These are just a few examples, and the potential applications of AR in healthcare are constantly evolving. As AR technology continues to mature, we can expect even more innovative tools and platforms to emerge, transforming the way we diagnose, treat, and educate in the medical field.
Applications of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, offering innovative solutions across various domains. Let’s delve into some of the most impactful applications of AR in medicine:
AR in Medical Training and Education
From Textbooks to Holographic Dissections: AR is revolutionizing medical education by enabling students to interact with 3D models of organs, bones, and even entire anatomical systems. Imagine medical students dissecting a virtual cadaver layered over a real anatomical model, allowing for a detailed exploration of structures and their relationships in a risk-free environment.
Simulating Procedures with AR: AR can create realistic simulations of surgical procedures and medical interventions. Students can practice suturing techniques, catheter placements, or even complex laparoscopic procedures using AR-powered simulators, gaining valuable experience before stepping into an operating room.
Case Study: Practicing Precision with AR
A recent study at Stanford University investigated the use of AR simulations for laparoscopic surgery training. Medical students who trained using AR simulators demonstrated significantly higher proficiency and efficiency compared to those who used traditional methods. This highlights the immense potential of AR in enhancing surgical skills and improving patient outcomes.
Surgical Assistance: A Surgeon’s Augmented Vision
AR is making its way into operating rooms, providing surgeons with real-time data visualizations and 3D overlays to enhance precision and decision-making during critical procedures:
X-Ray Vision with AR: Imagine a surgeon performing brain surgery and being able to see a real-time 3D hologram of the patient’s brain, overlaid directly onto the surgical field. This can include vital information like blood vessels, tumors, and critical structures, allowing for a more targeted and minimally invasive approach.
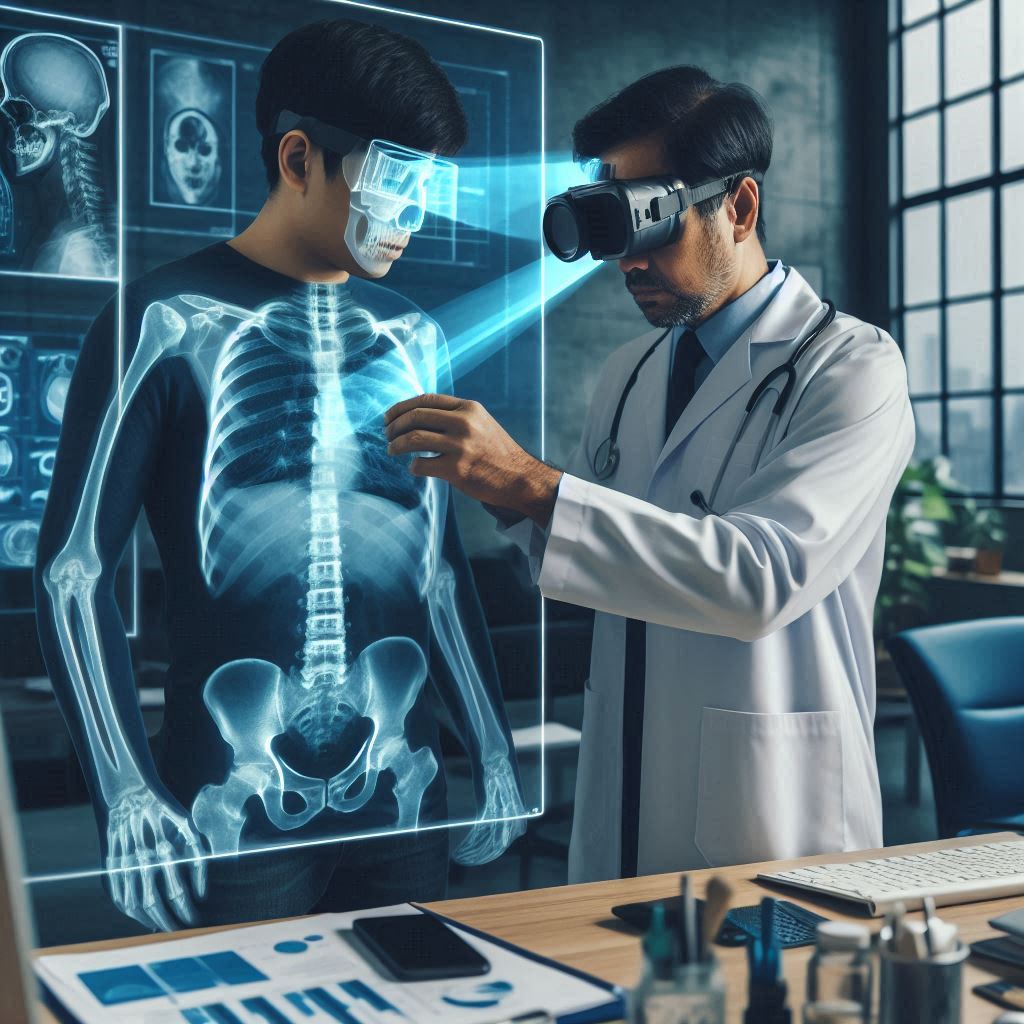

AR for Minimally Invasive Surgery: For complex laparoscopic procedures, AR can project a 3D model of the patient’s internal anatomy onto a monitor, guiding the surgeon’s movements with greater accuracy. This reduces the need for large incisions and offers faster recovery times for patients.
Example: AR-Assisted Tumor Removal
A recent news article reported on the successful removal of a brain tumor using AR guidance. The surgeons utilized an AR system that projected a 3D map of the patient’s brain onto their headsets, allowing them to target the tumor while minimizing damage to healthy tissue precisely. This exemplifies the life-saving potential of AR in surgery.
Patient Care and Treatment: Empowering Patients and Providers
AR isn’t just for surgeons; it’s empowering patients and healthcare providers alike:
Visualizing Conditions and Treatment Plans: AR can be used to educate patients about their medical conditions. Imagine a doctor explaining a complex heart condition by overlaying a 3D animated model of a healthy heart versus a diseased one, along with the proposed treatment plan. This can improve patient understanding and facilitate informed decision-making.
AR in Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: AR-powered apps can guide patients through physical therapy exercises by displaying proper form and range of motion via 3D overlays. This can enhance patient engagement and adherence to therapy protocols, leading to faster recovery times.
Remote Collaboration and Telemedicine: Bridging the Gap in Healthcare Delivery
AR is breaking down geographical barriers in healthcare by facilitating remote consultations and collaboration:
Virtual Rounds with AR Overlays: Imagine a specialist in a remote location participating in virtual rounds with a local doctor examining a patient. AR can overlay real-time diagnostic data or 3D anatomical models onto the patient’s image, enabling a more comprehensive evaluation and collaborative decision-making between healthcare providers.
Enhancing Telemedicine with AR: AR can revolutionize telemedicine consultations by allowing doctors to examine patients and visualize their conditions in greater detail remotely. For instance, a dermatologist examining a skin condition can utilize AR to magnify the area and view it from different angles, improving diagnostic accuracy during remote consultations.
These are just a few examples of how AR is transforming healthcare. As the technology continues to evolve and become more sophisticated, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications to emerge, shaping a future where AR becomes an indispensable tool for medical professionals, students, and patients alike.
Benefits of AR in Healthcare
Enhanced Visualization
Imagine a world where medical professionals wield the power of augmented reality (AR) to see beyond the limitations of the human eye. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the transformative power of AR in healthcare, ushering in an era of enhanced visualization that promises to revolutionize the way we diagnose, treat, and train in medicine. Here’s how AR is illuminating the path forward:
Demystifying the Complex: AR empowers healthcare professionals to delve deeper into intricate medical conditions. Imagine a doctor examining a patient’s X-ray and simultaneously viewing a 3D holographic model of the affected organ, complete with detailed annotations and interactive features. This enhanced visualization allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying pathology, leading to more informed diagnoses and treatment plans.
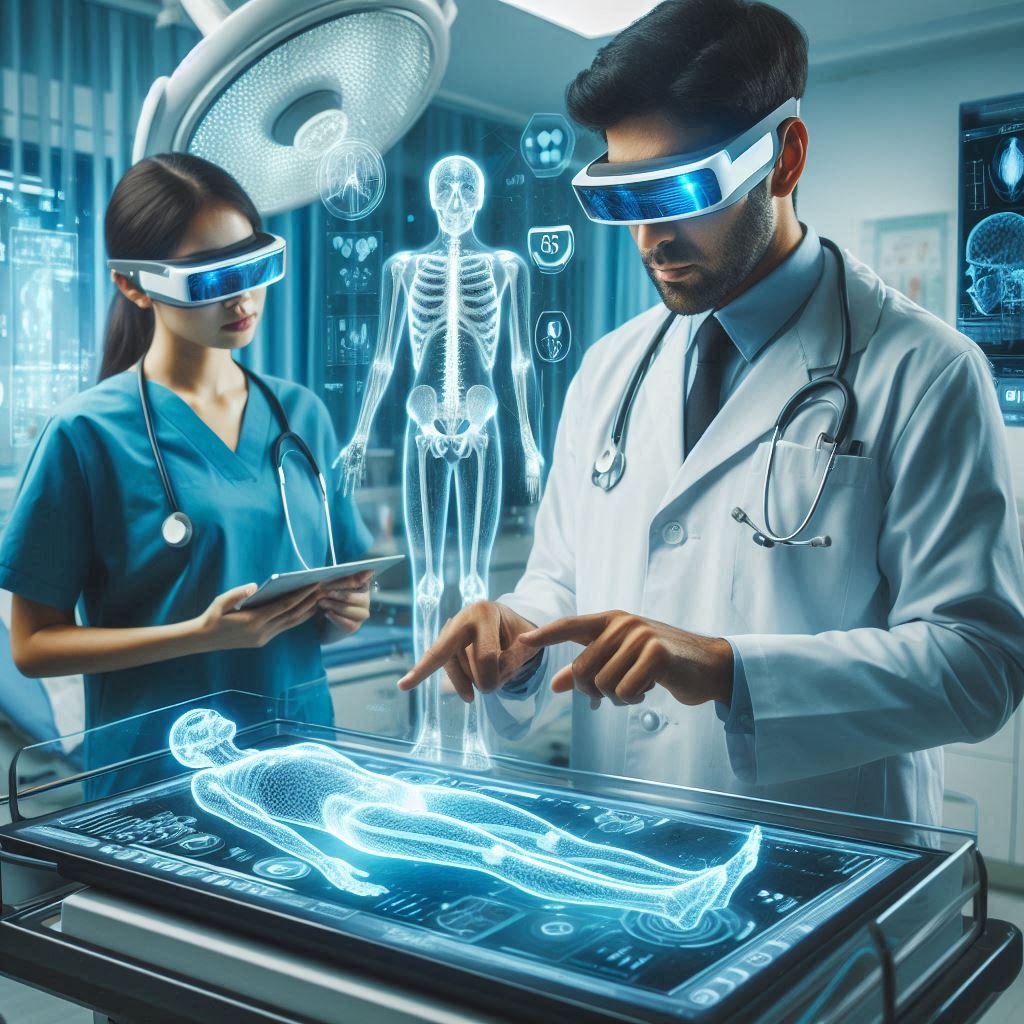

Surgical Precision Redefined: AR is poised to transform the operating room into a hub of augmented vision. Surgeons can leverage real-time data overlays and 3D anatomical models projected directly onto the surgical field. Think of a surgeon performing a delicate brain operation, able to see a virtual map of the patient’s neural pathways overlaid onto the brain itself. This augmented view enhances surgical precision, minimizes risks, and paves the way for more successful outcomes.
Increased Training Effectiveness: Learning by Doing, Virtually
AR is revolutionizing medical education by offering a safe and immersive learning environment:
Hands-on Without Harm: Traditionally, medical students honed their skills through cadaver dissection and simulated procedures. AR offers a virtual alternative, allowing students to interact with 3D models of organs and practice complex procedures in a risk-free environment. Imagine a student practicing a laparoscopic surgery on a virtual patient, receiving real-time feedback on their technique. This hands-on experience, without the risk of harming a real patient, significantly enhances learning effectiveness.
Repetition is Key: AR allows for limitless repetition in a controlled environment. Students can practice intricate surgical procedures or medical interventions repeatedly, refining their skills and gaining valuable muscle memory before stepping into a real-world setting. This ensures they are well-prepared for the challenges they will face as medical professionals.
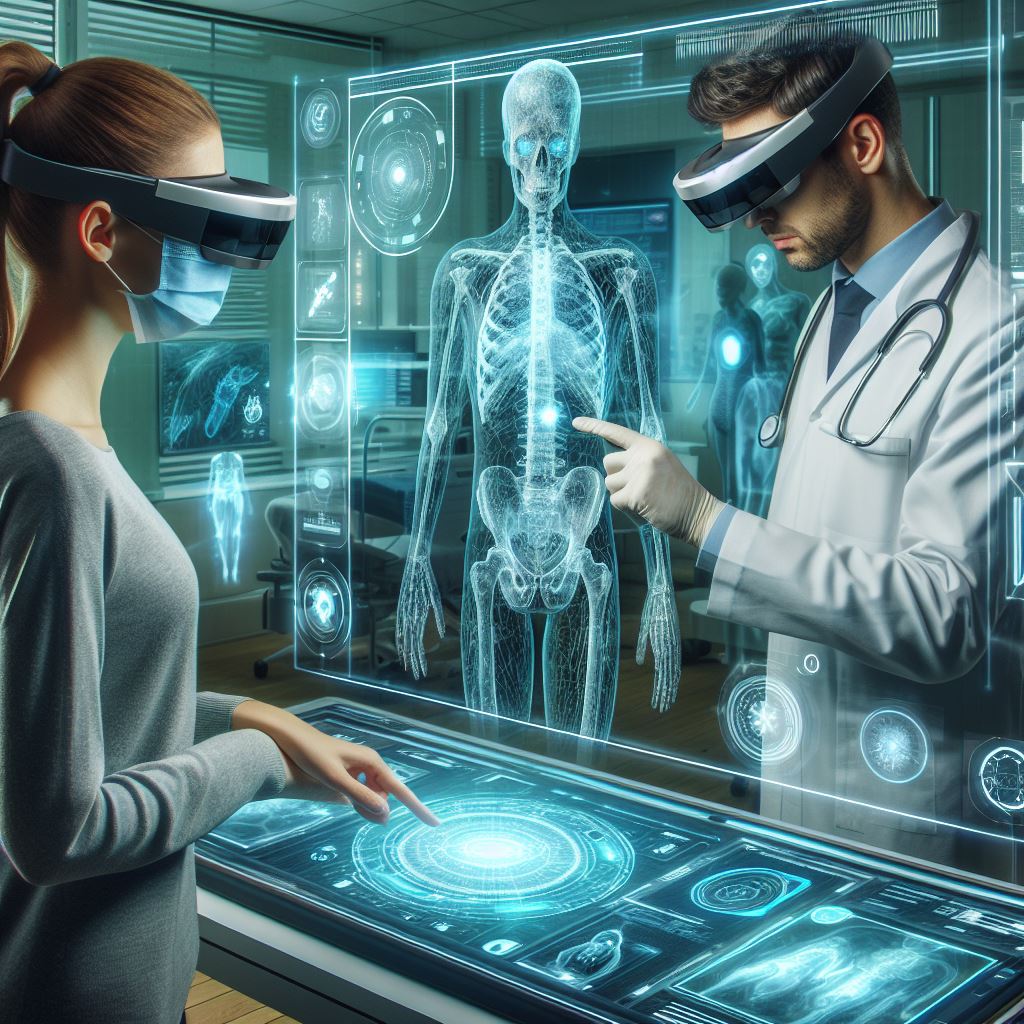

Improved Patient Outcomes:
The benefits of AR extend beyond the realm of training and directly impact patient care:
More Accurate Procedures: Enhanced visualization during surgery translates to improved precision and efficiency. This minimizes complications, reduces recovery times, and ultimately leads to better patient outcomes.
Personalized Plans, Engaged Patients: AR can be used to explain complex medical conditions and treatment plans to patients clearly and interactively. Imagine a patient viewing a 3D model of their heart and understanding the proposed surgery through interactive animations. This fosters better patient understanding, promotes informed decision-making, and increases patient engagement in their own healthcare journey.
Cost Efficiency:
The transformative power of AR extends to healthcare economics:
Optimizing Training Costs: AR-powered training simulations can significantly reduce the need for expensive resources like cadavers and specialized training facilities. This translates to cost savings for medical institutions and educators.
Minimizing Surgical Errors: Improved surgical precision brought about by AR can lead to a reduction in surgical errors. This not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the associated healthcare costs of treating complications.
By harnessing the power of enhanced visualization, AR is poised to revolutionize the healthcare landscape. From empowering medical professionals with a surgeon’s eye to fostering a more collaborative approach to patient care, AR holds immense potential to improve training, enhance procedures, and ultimately deliver better outcomes for patients worldwide.
Challenges and Limitations
The transformative potential of AR in healthcare is undeniable. However, like any emerging technology, AR faces certain challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its widespread adoption and successful integration into the medical field.
Technical Challenges: Bridging the Gap Between Promise and Reality
Several technical hurdles need to be overcome for AR to reach its full potential:
Hardware Hurdles: Current AR hardware, particularly smart glasses, can be bulky, uncomfortable for extended use, and have limited processing power. Advancements in miniaturization, display technology, and battery life are crucial for user acceptance and widespread adoption.
Cost Considerations: Implementing and maintaining AR technology can be expensive, encompassing not just the AR hardware but also the development and integration of AR software with existing medical systems. Finding cost-effective solutions is essential for ensuring equitable access to this transformative technology.
Privacy and Security: Protecting Sensitive Information
The integration of AR with healthcare necessitates a robust framework for data security and privacy:
Patient Data in the Augmented World: AR applications often rely on patient data to generate visualizations and overlays. Ensuring the security of this sensitive information throughout the AR experience is paramount. To ensure security, it is essential to make clear data governance policies and strong cybersecurity measures.
Navigating Regulations: The use of AR in healthcare falls under the purview of various data privacy regulations. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU needs to be carefully considered when developing and deploying AR applications in healthcare settings.
User Adoption and Training:
Encouraging widespread adoption of AR technology requires addressing user concerns and providing adequate training:
Overcoming Resistance to Change: Some healthcare professionals might hesitate to embrace new technology. Addressing these concerns through education, demonstrations of the benefits of AR, and fostering a culture of innovation within healthcare institutions is crucial.

Training for the Augmented Age: Effectively utilizing AR tools requires proper training. Healthcare professionals must be equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to integrate AR seamlessly into their workflows. This highlights the importance of developing user-friendly AR interfaces and comprehensive training programs.
By acknowledging these challenges and working towards solutions, we can pave the way for a future where AR flourishes in healthcare. Collaboration between technology developers, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and regulatory bodies is essential to ensure that AR reaches its full potential, transforming the way we diagnose, treat, and train in medicine.
Future of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
The future of Augmented Reality in healthcare is brimming with exciting possibilities. As research and innovation continue, we can expect to see the emergence of groundbreaking AR technologies that will further revolutionize the medical field. Let’s delve into the exciting landscape that lies ahead:
Ongoing Research and Innovations: Pushing the Boundaries
The future of Augmented Reality in healthcare is being actively shaped by ongoing research projects and pilot programs:
Haptic Feedback and Gesture Recognition: Imagine surgeons feeling the virtual texture of organs during AR-guided procedures or manipulating 3D holographic models with intuitive hand gestures. Advancements in haptic technology and gesture recognition will create a more immersive and interactive AR experience in surgery.
AI-powered AR Applications: Integrating artificial intelligence with AR holds immense potential. Imagine AI analyzing patient data in real time and providing AR overlays with personalized treatment recommendations or risk assessments during surgery.
A Pioneering Project: AR for Cancer Treatment
A recent research project at the Mayo Clinic explores AR use during liver cancer surgery. Surgeons utilize AR glasses to visualize tumor margins overlaid on the patient’s liver, allowing for a more precise and minimally invasive approach. This exemplifies the potential of AR to improve surgical outcomes in cancer treatment.
Predicted Trends: Shaping the Healthcare Landscape
As AR technology matures, several trends are likely to dominate the future of healthcare:
Personalized Medicine with AR: AR can play a crucial role in personalized medicine by enabling the creation of patient-specific treatment plans. Imagine a doctor using AR to create a 3D model of a patient’s tumor and simulate different treatment options in an augmented reality environment.
Expansion of AR Applications: The applications of AR in healthcare are expected to expand beyond surgery. Imagine AR-powered physical therapy programs with interactive exercise routines or AR apps that help patients manage chronic conditions by visualizing medication schedules and tracking vital signs.
Industry Growth: A Flourishing Market
The AR healthcare market is poised for significant growth:
Market Predictions: According to research by MarketsandMarkets, the global AR healthcare market is expected to reach a staggering USD 5.2 billion by 2027, reflecting the immense potential and increasing adoption of AR in the medical field.
Investment and Key Players: Major tech companies, healthcare institutions, and startups are actively investing in AR healthcare technology. Companies like Google, Microsoft, and Apple are developing AR platforms with healthcare applications in mind. Additionally, innovative startups like SurgicalAR and Augmedix are creating specialized AR solutions for surgery and remote patient monitoring.
The future of AR in healthcare is a collaborative one. As researchers, technologists, and healthcare professionals join forces, AR has the potential to transform the way we deliver and experience medicine, creating a future where AR becomes an indispensable tool for improving diagnosis, treatment, and patient care on a global scale.
Conclusion
The future of Augmented Reality in healthcare isn’t just promising, it’s beckoning us toward a paradigm shift. To unlock its full potential, a collaborative effort is crucial. Healthcare professionals, patients, and the public can stay informed by following industry publications, attending conferences, and engaging in open discussions. This fosters understanding and fuels widespread adoption. Healthcare institutions can take a proactive approach by exploring pilot programs and research collaborations with technology developers. Imagine co-creating AR solutions tailored to specific needs – a surgeon overlaying vital signs onto a patient in real-time, or a student practicing a procedure on a holographic model. By embracing AR and fostering a culture of innovation, we can transform healthcare delivery. This future holds immense potential: empowered medical professionals, enhanced patient care, and ultimately, a healthier world. Let’s work together to turn AR’s promise into a reality, ensuring this transformative technology benefits everyone.
Want to experience the world in a whole new way? Head over to my other post.