A Spoonful of Innovation: How Vertical Farming is Revolutionizing Food Production
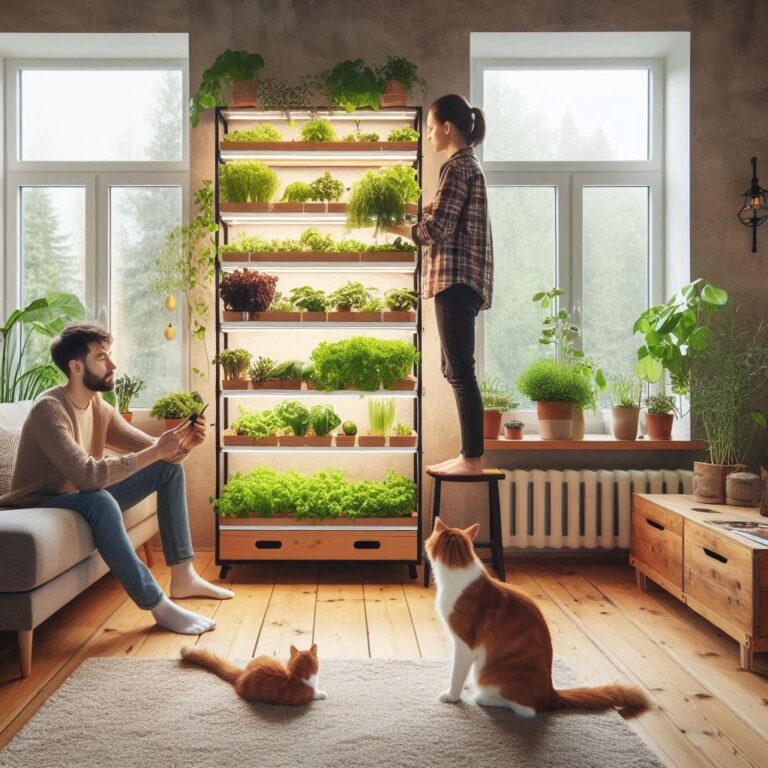
Imagine a world where towering structures aren’t just office buildings or apartment complexes, but vibrant ecosystems cultivating fresh, local produce year-round. This is the exciting vision that vertical farming promises. As our planet faces growing challenges – a rising population, resource scarcity, and unpredictable weather patterns – traditional agriculture is struggling to keep pace. Vertical farming emerges as a potential game-changer, offering a unique and innovative approach to food production. Let’s delve into the top 10 benefits of vertical farming and explore how it can revolutionize the way we grow our food.

Top 10 Benefits of Vertical Farming:
Why vertical farming is important
1. Land Efficiency: Redefining “Yield” in a Space-Constrained World
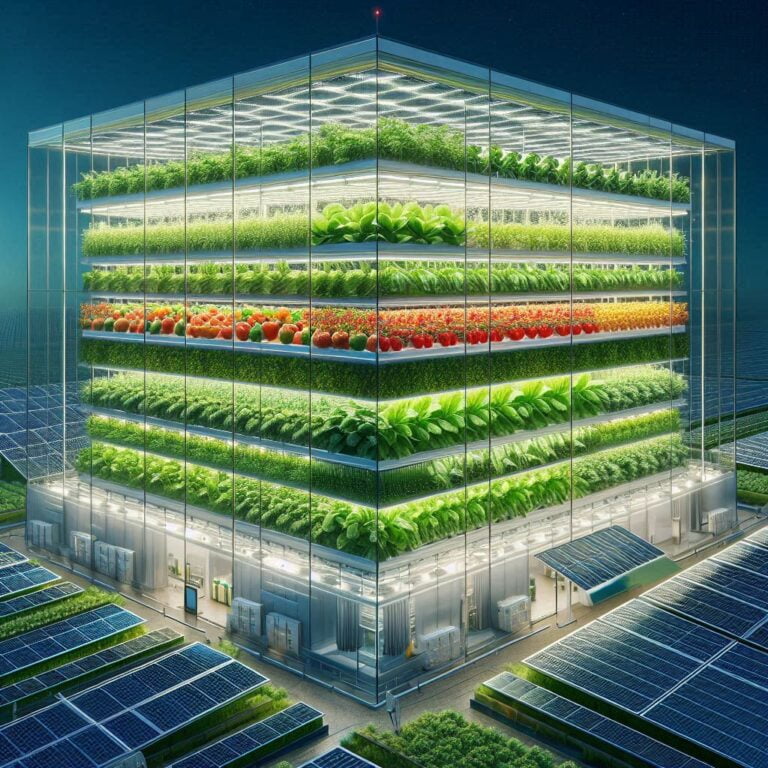
By 2050, the population of the world is projected to reach nearly 10 billion. We need to find smarter ways to utilize our limited land resources to feed this growing population. Traditional agriculture relies on vast expanses of arable land, a resource that is becoming increasingly scarce. Enter vertical farming, a revolutionary approach that challenges the traditional notion of “yield.” Vertical farms maximize crop production on a minimal footprint by stacking growing layers. Imagine a skyscraper dedicated not to offices, but to cultivating fresh greens! This vertical approach can potentially yield 50 to 100 times more produce per square foot compared to traditional farms.
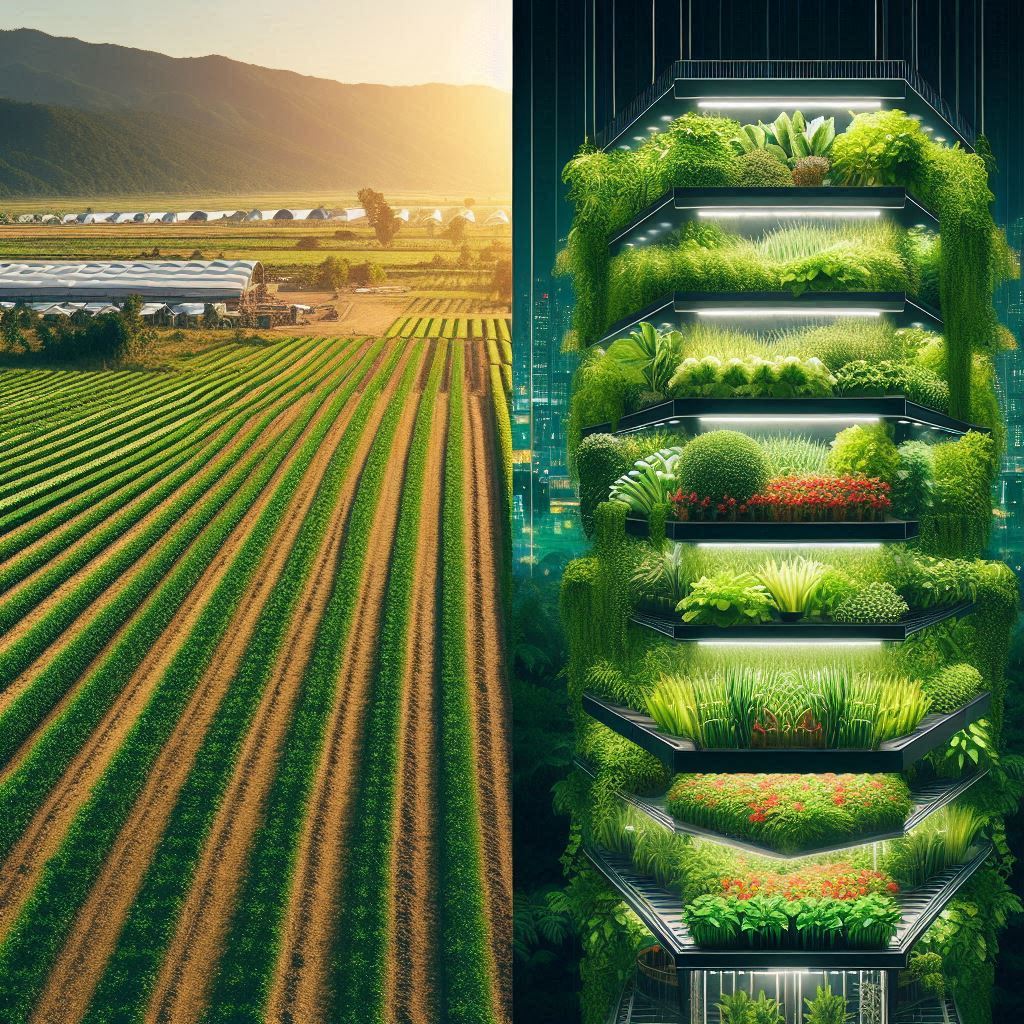

2. Water Efficiency: A Drop Saved is a Crop Nourished
The threat of water scarcity is growing across the globe. Traditional agriculture is a major water consumer, with irrigation practices often leading to significant water waste. Vertical farming offers a solution by utilizing hydroponic or aeroponic systems. These innovative techniques deliver nutrients directly to plant roots, minimizing water usage by up to 95% compared to traditional methods. This dramatic reduction in water consumption makes vertical farming a beacon of sustainability in a world facing water scarcity.
3. Controlled Environment: Weatherproofing Your Harvest
The whims of nature can wreak havoc on traditional agriculture. Unpredictable weather patterns, from droughts to floods, can devastate crops and lead to significant financial losses for farmers. Vertical farming eliminates this element of risk by creating a controlled environment. With precisely controlled temperature, humidity, and lighting, vertical farms can optimize growing conditions for specific crops, irrespective of external weather fluctuations. This translates to higher yields, reduced risk of crop failure, and the potential for year-round production.
4. Reduced Reliance on Pesticides: Vertical Farming Environmental Benefits
Traditional agriculture’s dependence on pesticides poses a significant threat. These chemicals, while effective in controlling pests, can have a detrimental impact on human health, potentially leading to a range of concerning issues. Some specific health concerns linked to pesticide exposure include:
- Neurological diseases: Studies suggest chronic exposure to certain pesticides may increase the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. (Association between exposure to pesticide and neurodegenerative diseases)
- Certain cancers: Research indicates potential links between specific pesticides and an increased risk of some cancers, such as leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Developmental problems: Exposure to pesticides during pregnancy or early childhood may be linked to developmental issues in children.

Furthermore, pesticide runoff contaminates water sources, harming vital pollinators like bees and butterflies, and disrupting delicate ecosystems. This disrupts the natural balance, potentially leading to reduced crop yields in the long run due to a lack of pollination.
Vertical farms offer a compelling solution. Their controlled environments with restricted access significantly minimize pest exposure. Additionally, techniques like introducing beneficial insects (ladybugs for aphids) and maintaining precise temperatures create a natural defense system, suppressing pest populations without resorting to harmful chemicals. This translates to safer food for consumers (studies have shown a reduction in pesticide residue levels) and a more sustainable approach to agriculture that promotes biodiversity and healthy ecosystems.
5. Year-Round Bounty: Vertical Farming Sustainability
Seasonal limitations are a major challenge for traditional farms. Droughts, floods, and unpredictable weather patterns can disrupt yields, create periods of scarcity, and drive up food prices. Vertical farms, on the other hand, decouple production from the whims of nature. Their controlled environments allow for consistent year-round production, regardless of the season outside. This ensures a steady supply of fresh, local produce for consumers, even during harsh weather conditions. Imagine enjoying locally-grown strawberries in December or crisp lettuce during a summer heatwave – vertical farming makes this a reality. This local production also reduces the need to import fruits and vegetables from other countries, minimizing transportation costs and the associated carbon footprint.
6. Minimizing Food Waste: From Farm to Table, with Less Loss
Food waste is a prevalent problem in traditional agriculture. Estimates suggest that up to one-third of all food produced is lost due to pests, diseases, and adverse weather conditions. Vertical farms address this issue head-on. Their controlled environments minimize losses by precisely regulating temperature, humidity, and lighting. This prevents spoilage caused by pests and diseases that thrive in unpredictable conditions. Additionally, the absence of unpredictable weather events reduces the risk of crop failure. By precisely monitoring nutrient delivery through hydroponics or aeroponics systems, vertical farms can also optimize plant growth and minimize waste due to deficiencies. This translates to less food waste, increased resource efficiency, and a more sustainable food system. By minimizing waste, vertical farms ensure a more secure and responsible approach to food production, maximizing the yield from the resources used.
 zx vbul
zx vbul
7. Urban Agriculture Potential: A Vertical Revolution in the City
Densely populated urban environments often face challenges in accessing fresh, local produce. Traditional agriculture relies on vast tracts of land, a luxury scarce in cities. This is where vertical farming emerges as a game-changer.
- Unleashing Potential in Limited Space:
Vertical farms are essentially indoor farms that utilize a vertical stacking system. Warehouses, rooftops, and even repurposed shipping containers can be transformed into vibrant hubs of food production. Imagine a network of vertical farms scattered throughout a city, transforming unused spaces into fertile landscapes. This eliminates the limitations of land availability, making vertical farming ideal for urban environments.
- Freshness Delivered: Farm to City Table
By growing food closer to consumers, vertical farms dramatically reduce transportation distances. This translates to fresher produce on your plate, bursting with flavor and nutrients. Imagine enjoying a salad with leafy greens harvested just hours before, a true farm-to-table experience in the heart of the city! Reduced transportation also minimizes the environmental impact associated with “food miles,” contributing to a more sustainable food system.
8. Potential for Local Food Systems: Building Resilience with Vertical Farms
Local food systems, where food production and consumption occur within a defined geographic area, offer numerous benefits:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Due to less transportation it contributes lesser carbon footprint.
- Enhanced Food Security: Local production makes communities less reliant on external food sources, promoting resilience in the face of disruptions to long-distance supply chains.
- Economic Boost: Local food systems support local businesses and jobs, strengthening the community’s economic fabric.
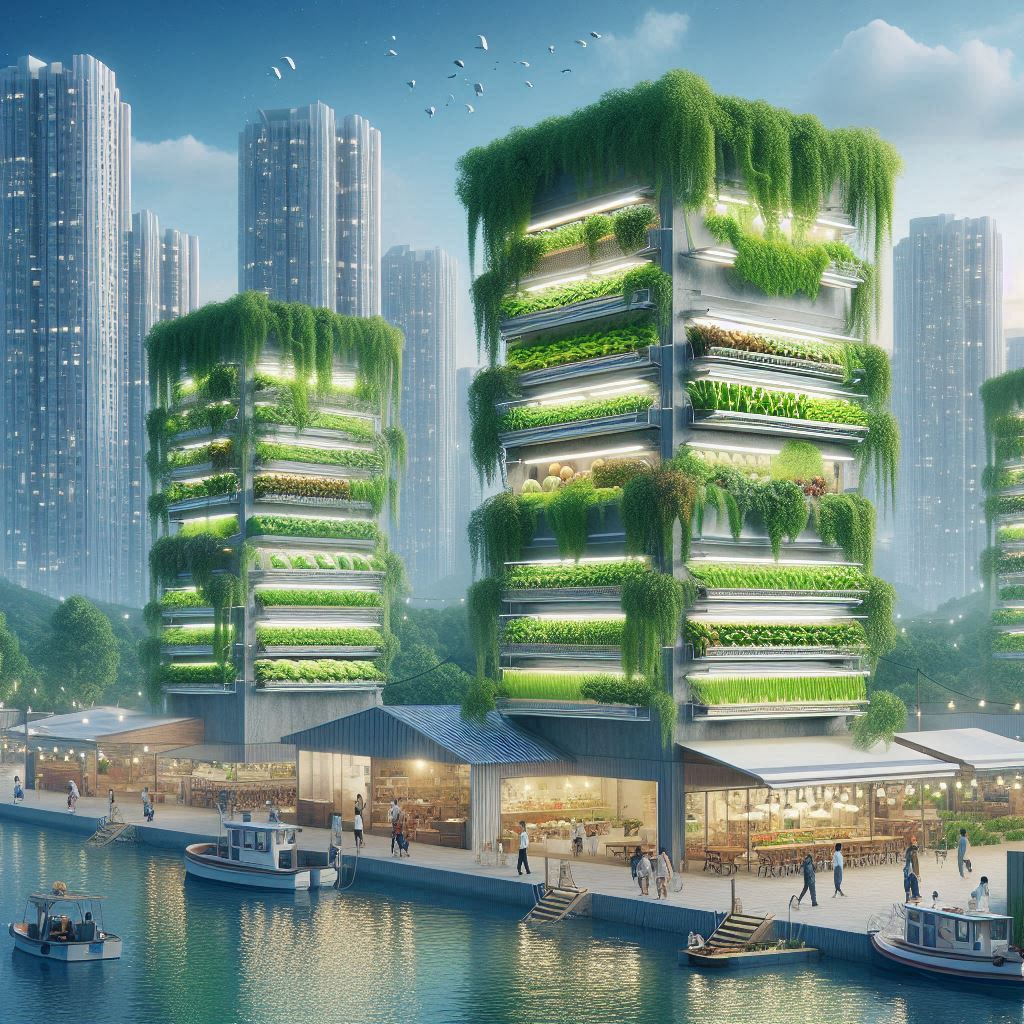

Vertical Farms: Cultivating a Stronger Local Food Network
Vertical farms can be a powerful driver of local food systems in urban areas:
- Year-Round Bounty: Unconstrained by seasons, vertical farms can provide a wider variety of fresh, high-quality produce year-round.
- Sustainability Champion: Reduced dependence on long-distance food transportation promotes sustainability and freshness.
- Community Hub: Vertical farms can become hubs for community engagement, fostering education and awareness about local food production. Imagine visiting a vertical farm and learning about the innovative techniques used to grow your food!
9. Improved Food Quality and Safety: Health benefits of vertical farming
Vertical farming’s controlled environment offers exciting possibilities for improved food quality and safety. Here’s why:
- Precise Control: Temperature, humidity, and lighting can be meticulously regulated, potentially optimizing plant growth and nutrient content. This could lead to the production of higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Reduced Contamination Risk: The closed-loop systems in vertical farms minimize exposure to harmful pathogens and pollutants that can contaminate crops in traditional agriculture. This translates to potentially safer food for consumers.
Important Note: While these possibilities are promising, more research is needed to definitively establish the impact of vertical farming on the nutritional profile of produce.
10. Potential for Job Creation: A New Landscape for Agricultural Employment
The rise of vertical farming has sparked concerns about job displacement in traditional agriculture. However, it’s important to consider the potential for new job opportunities:
Tech-Savvy Workforce: Vertical farms rely heavily on technology for automation, climate control, and data analysis. This creates demand for skilled professionals in areas like:
- Agricultural engineering to design and maintain complex systems.
- Data science to analyze plant growth and optimize production.
- Software development to create automation and monitoring tools.

New Roles in Urban Agriculture: As vertical farms become more integrated into urban environments, new positions will emerge in areas like:
- Urban farm management to oversee day-to-day operations.
- Community outreach to educate consumers and foster connections with local food production.
The transition to vertical farming may require adjustments in the agricultural workforce, but it also presents exciting opportunities for new skills and career paths in a rapidly evolving industry.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future on the Rise
Vertical farming presents a compelling vision for the future of food production. By offering a multitude of benefits, it has the potential to revolutionize agriculture:
- Reduced reliance on pesticides translates to safer food and a healthier environment.
- Year-round production ensures a steady supply of fresh produce, regardless of season.
- Minimized food waste promotes resource efficiency and sustainability.
- Urban agriculture’s potential brings fresh food production closer to consumers in cities.
- Improved food quality and safety (potential for enhanced nutrition) offer exciting possibilities for consumer health.
- Job creation fosters new opportunities in technology and urban agriculture.
Vertical farming is not just a novel concept; it’s a practical solution with the potential to address some of the most pressing challenges facing our food system. As research and development continue to refine this technology, we can expect even greater advancements in efficiency, affordability, and environmental impact.
The future of food is taking root, and vertical farming is at the forefront. We encourage you to learn more about this innovative approach and explore its potential to transform the way we grow and consume food. Together, we can cultivate a more sustainable and secure food system for generations to come.
Challenges and Ongoing Advancements
Vertical farming is a rapidly evolving technology, and it’s not without its challenges. Initial investment costs can be high, and energy consumption is an area of ongoing research. However, advancements are being made to address these limitations:
- Cost Reduction: As the technology matures and economies of scale come into play, vertical farming is expected to become more affordable.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Research is focusing on integrating renewable energy sources like solar power to reduce the environmental footprint associated with energy consumption.
By acknowledging and addressing these challenges head-on, we can pave the way for a future where vertical farming plays a significant role in creating a more sustainable and resilient food system for all. Explore other interesting blogs below: