The advancement of nanorobots in medicine has opened new frontiers in cancer treatment, offering targeted, efficient, and minimally invasive therapies. Recent breakthroughs suggest that nanobots could enhance drug delivery, reduce side effects, and even aid in cancer diagnosis and tumor elimination.
Introduction: The Nanobots Cancer Cure
Nanotechnology is transforming medicine, and one of its most promising applications is in cancer treatment. Nanobots—microscopic machines engineered to operate at the nanoscale—have the potential to revolutionize oncology by delivering drugs precisely to cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues, and improving treatment efficacy.
Recent research has demonstrated that nanorobots can penetrate tumors and enhance the effects of radiopharmaceuticals, significantly reducing tumor size in animal models. Clinical trials and experimental treatments are ongoing, bringing us closer to a future where nanobots in medicine may become a standard cancer therapy.
This article explores:
- What are nanobots, and how do they work?
- Types of nanobots used in medicine
- Mechanisms behind their cancer-fighting abilities
What Are Nanobots and How Do They Work?
Definition and Structure of Nanorobots
Nanobots, also called nanorobots or nanomachines, are tiny devices ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers in size—smaller than human cells but large enough to interact with biological systems. Their composition varies, but they are typically made from biocompatible materials such as DNA, proteins, lipids, or synthetic polymers.
These microscopic machines often include:
- Sensors to detect cancer markers
- Propulsion mechanisms (chemical, magnetic, or enzyme-driven) to navigate within the bloodstream
- Payloads (such as drugs or therapeutic agents) to target tumors
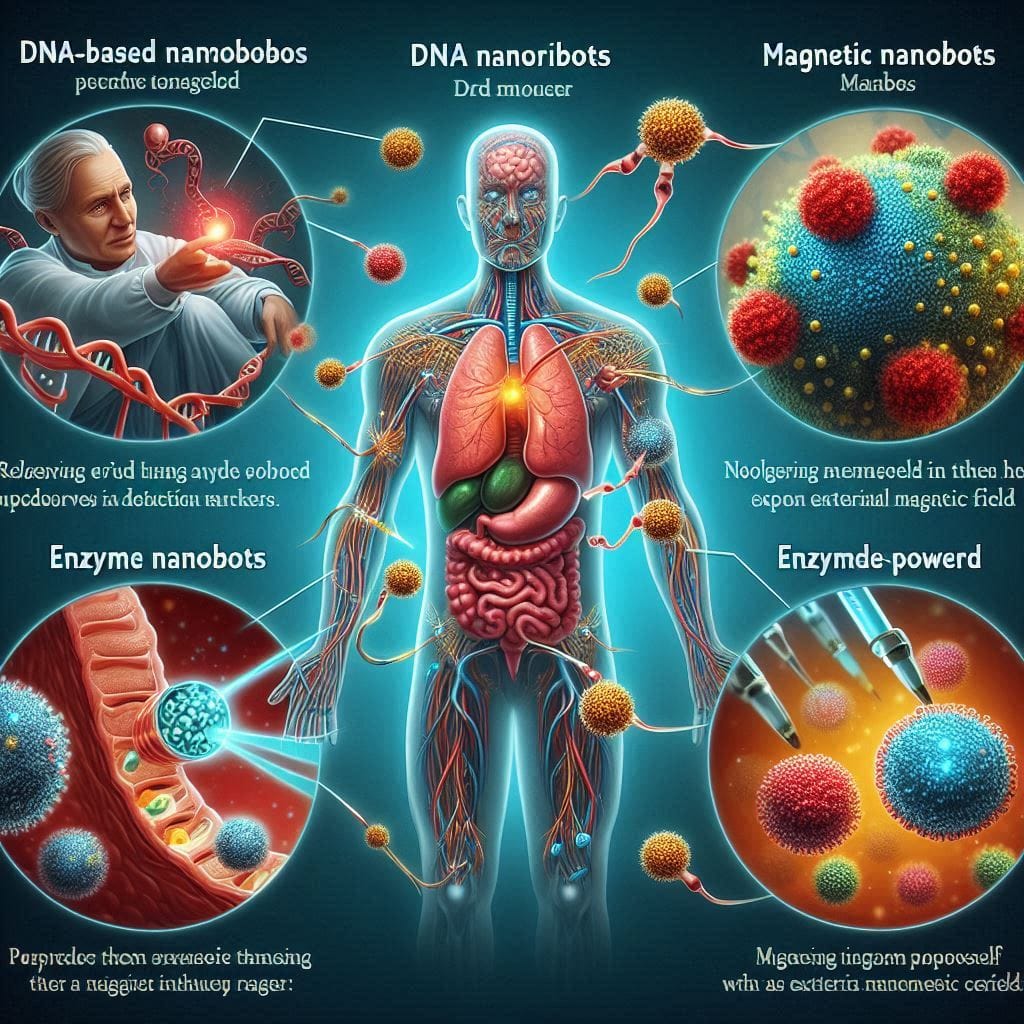
Types of Nanobots in Medicine
- DNA-Based Nanorobots – Designed to release drugs only when they detect specific cancer markers.
- Magnetic Nanobots – Controlled externally using magnetic fields for targeted movement.
- Enzyme-Powered Nanobots – Use biological reactions for self-propulsion.
- Biohybrid Nanobots – Combine synthetic components with living cells for enhanced adaptability.
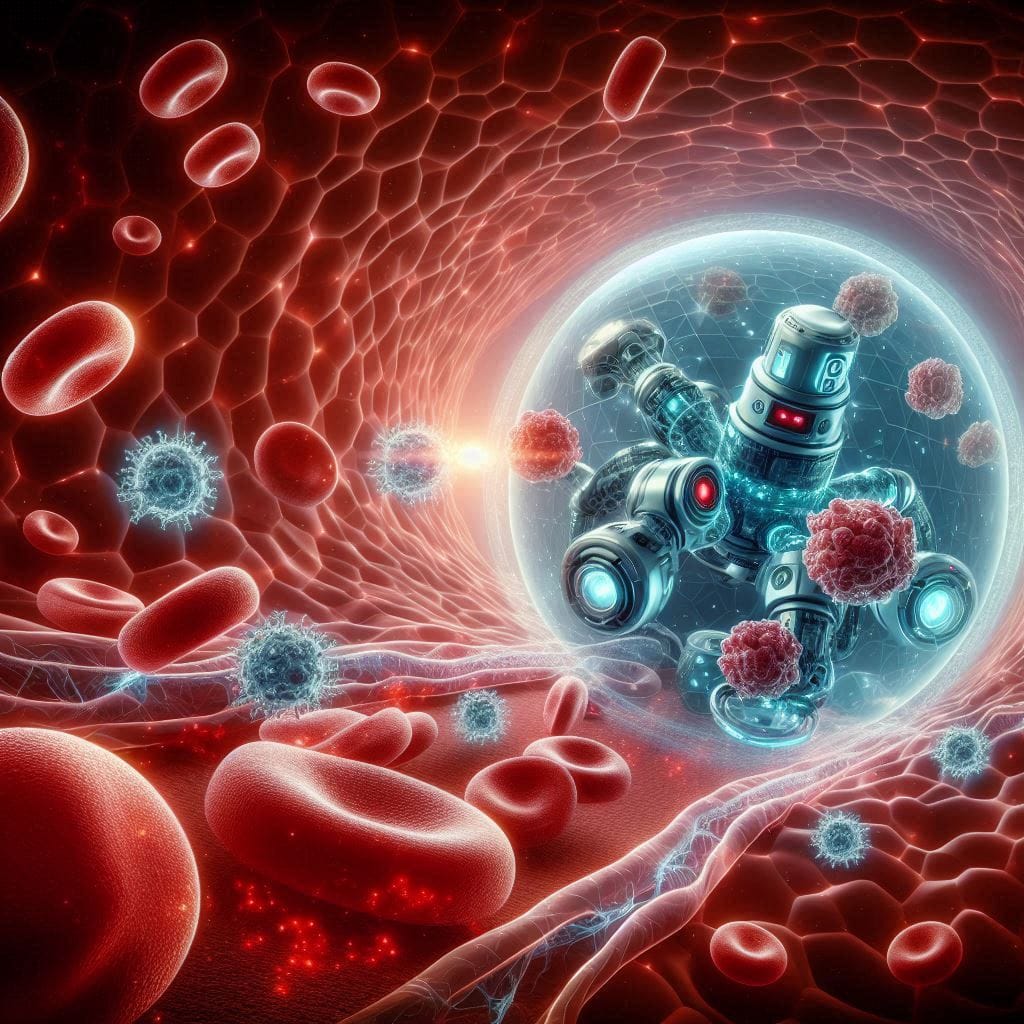
Mechanisms of Action
Nanobots navigate through the bloodstream, detect tumor sites, and deliver drugs precisely to cancer cells. They function by:
- Recognizing cancer-specific proteins or pH levels
- Penetrating tumors through self-propelling chemical reactions
- Delivering radioisotopes or chemotherapy drugs directly to tumors
- Breaking down the extracellular matrix of cancer cells, allowing deeper drug penetration
A recent study demonstrated a 90% reduction in tumor size using nanobots loaded with radiopharmaceuticals. The nanobots accumulated within tumors due to their ability to manipulate the local pH and extracellular environment.
Future Prospects
Ongoing clinical trials aim to refine nanobot-based therapies for greater efficiency, safety, and scalability. The emergence of companies like Nanobots Therapeutics, which is working on commercializing nanobot treatments, indicates that the technology could soon become part of mainstream oncology.
As nanorobots in medicine continue to evolve, they hold immense promise for revolutionizing cancer detection, drug delivery, and tumor elimination, offering new hope for cancer patients worldwide.
How Nanobots Are Transforming Cancer Treatment
Nanotechnology is at the forefront of revolutionizing cancer treatment. Nanorobots in medicine are engineered to perform highly specialized tasks at the molecular level, offering precision in treating cancer that traditional methods lack. From targeted drug delivery to real-time tumor detection, nanobots cancer treatment is shaping the future of oncology.
Targeted Drug Delivery: The Precision of Nanobots
One of the most promising aspects of nanobots in cancer treatment is their ability to deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to cancerous cells while sparing healthy tissues. Traditional chemotherapy exposes the entire body to toxic substances, leading to severe side effects. However, nanobots cancer cure techniques use nanoparticle carriers—such as liposomes, polymeric micelles, and metal-organic frameworks—that encapsulate chemotherapy drugs and release them only in the tumor microenvironment.
Recent studies have demonstrated that gold-based nanorobots and DNA origami nanobots can identify cancer markers and release therapeutic agents with high accuracy. A research team at Tokyo Women’s Medical University has successfully used ultrasound-triggered nanocarriers to deliver chemotherapy directly into tumors, significantly reducing drug dosages while maintaining effectiveness.
Cancer Cell Destruction: Heat, Self-Destruction, and Immune Activation
Beyond drug delivery, nanobots cancer treatment includes innovative cancer cell destruction techniques. Three key methods include:
- Heat-Based Therapy: Magnetic and metallic nanobots can generate localized heat when exposed to an external magnetic field, killing cancer cells while sparing surrounding tissues.
- Programmed Self-Destruction: Certain DNA-based nanobots can trigger apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells upon recognizing specific proteins.
- Immune System Activation: Nanobots coated with immune-activating molecules can alert the immune system to recognize and attack tumors. Researchers are exploring immune-nanorobots that deliver immune checkpoint inhibitors precisely where they are needed, reducing the risk of autoimmune reactions.
Real-Time Cancer Detection and Monitoring
Early detection is crucial for improving cancer survival rates, and nanorobots in medicine are now being developed to identify tumors before they are detectable via conventional imaging. Some quantum dot and biosensor nanobots can detect cancerous biomarkers in the bloodstream within minutes.
At Tokyo Medical University, researchers are conducting human trials on sonodynamic nanobot therapy, which uses ultrasound waves to activate nanobots injected into the bloodstream. The technique has successfully reduced tumor size in terminal-stage pancreatic and bone cancer patients.
Advantages Over Traditional Cancer Treatments
The benefits of nanobots cancer cure strategies compared to conventional chemotherapy and radiation therapy are significant:
✔ Higher Precision: Targets only cancerous cells, reducing collateral damage.
✔ Fewer Side Effects: Minimizes damage to healthy tissues, decreasing nausea, hair loss, and fatigue.
✔ Non-Invasive: Many nanobot therapies work without surgical intervention.
✔ Real-Time Monitoring: AI-enhanced nanobots can continuously assess treatment efficacy.
While nanorobots cancer treatment is still in experimental stages, human trials have shown promising results. With advancements in AI integration, biocompatibility, and real-time tumor tracking, nanobots cancer cure technologies may soon become a standard in oncology. However, regulatory approvals, cost, and large-scale clinical trials remain key challenges before widespread implementation.
Clinical Trials and Real-World Applications
Current Research and Breakthroughs in Nanobot Cancer Treatment
Recent advancements in nanobots cancer clinical trials have demonstrated promising results. A notable study from Tokyo Women’s Medical University combined nanobots with high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), showing dramatic tumor reduction in canine trials. This technique, called sonodynamic therapy, successfully shrank tumors in dogs and is now in early-stage human trials, especially for unresectable pancreatic cancer.
Additionally, researchers have been developing DNA-based nanobots that specifically target cancer cells. These nanobots use molecular recognition to bind to tumor markers, releasing drugs only when they reach cancerous tissues. This targeted approach minimizes side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Human Clinical Trials: Are We There Yet?
While nanorobots in medicine have shown success in preclinical models, large-scale human trials are still in early stages. Several biotech firms are conducting first-in-human studies for cancer-targeting nanobots. One major challenge is ensuring the biocompatibility and long-term safety of these tiny machines. Regulatory agencies like the FDA require rigorous testing before approval, which has slowed down widespread adoption.
Some of the most promising clinical trials involve magnetic nanobots that can be guided to tumors using external magnetic fields. These trials have demonstrated success in selectively destroying cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue, a key goal in precision oncology.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Experimental treatments using nanobots cancer cure technologies have yielded groundbreaking results. In a study using DNA nanobots, researchers successfully cut off blood supply to tumors in mice, leading to significant tumor shrinkage. Another case involved the use of enzyme-powered nanobots, which were able to penetrate deep into tumor tissues and deliver drugs more effectively than standard nanoparticles.
Challenges and Ethical Concerns in Nanobot Cancer Treatment
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Despite their potential, nanorobots in medicine come with challenges. One major concern is toxicity—some nanomaterials may trigger unwanted immune responses or accumulate in organs, causing unforeseen complications. Ensuring that these microscopic machines safely degrade after performing their function is an ongoing area of research.
Ethical Concerns and Regulatory Hurdles
The FDA and other regulatory bodies face difficulties in setting safety standards for nanobot cancer clinical trials. Questions around long-term safety, privacy concerns, and unintended consequences remain. Additionally, ethical concerns arise about the potential misuse of nanobots, such as unauthorized monitoring or non-consensual medical interventions.
Cost and Accessibility Issues
One major hurdle is affordability. Advanced nanorobots in medicine require high-precision manufacturing, making them expensive. If nanobots cancer cure treatments become commercially available, will they be accessible to all patients, or will they remain an exclusive option for the wealthy? Governments and healthcare systems will need to address these disparities to ensure equitable access to this revolutionary technology.
As nanorobots cancer treatment advances, overcoming these challenges will be key to unlocking their full potential in modern medicine.
Future of Nanobots in Medicine: Beyond Cancer Treatment
Nanobots are set to revolutionize medicine beyond just cancer treatment, with their applications expanding into neurology, cardiology, regenerative medicine, and even AI-driven precision therapies. Their integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is expected to significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment.
Potential Applications in Other Diseases
While nanobots cancer cure remains a major focus, researchers are also exploring their use in:
- Neurological Disorders: Nanobots could help treat conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and stroke by repairing damaged neurons and delivering neuroprotective drugs directly to affected brain regions.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: They could remove arterial plaques, repair blood vessels, and monitor heart conditions in real-time, reducing the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
- Regenerative Medicine: Nanobots could facilitate tissue repair and organ regeneration, potentially offering solutions for organ failure without relying on transplants.
Integration with AI and Robotics
Nanobots are being designed to function autonomously with AI, making them more efficient in diagnosing and treating diseases. AI can help nanobots:
- Identify cancer cells and other disease markers with pinpoint accuracy.
- Optimize drug delivery by adapting dosage in real-time based on the patient’s response.
- Predict disease progression using machine learning models to enhance early detection.
According to a 2023 SNS Insider report, the nanorobotics market was valued at $7.46 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $17.56 billion by 2030, highlighting the rapid growth and potential adoption of nanobots in mainstream medicine (Clinical Services Journal, 2024).
Timeline for Mainstream Adoption
While experimental nanobot treatments are already in development, experts predict that widespread clinical use could take another 10–15 years due to:
- Regulatory approvals and safety trials
- Scaling up production for affordability
- Integration with existing healthcare systems
However, successful human trials in the next five years could speed up adoption, making nanobots a staple in medicine sooner than expected.
Nanobots are ushering in a new era of medicine, offering targeted therapies, early disease detection, and personalized treatments that surpass traditional methods. While challenges remain, AI-driven nanobots have the potential to transform healthcare, not just in cancer treatment but across multiple fields. The coming decade will be critical in determining whether these microscopic medical marvels will finally move from laboratories to hospitals worldwide.
Conclusion
Nanobots are ushering in a new era of medicine, offering targeted therapies, early disease detection, and personalized treatments that surpass traditional methods. While challenges remain, AI-driven nanobots have the potential to transform healthcare, not just in cancer treatment but across multiple fields. The coming decade will be critical in determining whether these microscopic medical marvels will finally move from laboratories to hospitals worldwide.
Explore our other interesting articles: