Introduction: Iron-Air Batteries
As the global demand for renewable energy storage solutions grows, iron-air batteries are emerging as a game-changing technology for long-duration energy storage. These batteries have the potential to revolutionize the power industry by addressing intermittency challenges associated with solar and wind energy. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, which have limitations in cost and resource availability, iron-air batteries leverage cheap and abundant iron to provide a low-cost, scalable, and highly efficient alternative for grid storage.
Why Are Iron-Air Batteries Important for the Future of Renewable Energy?
One of the biggest challenges in renewable energy adoption is storage. Solar and wind power generation is intermittent—meaning electricity production fluctuates with weather conditions. Iron-air batteries can store large amounts of energy for multiple days, making them ideal for stabilizing the power grid during outages, extreme weather events, and peak demand periods.
Iron-Air vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries: Key Differences
- Lower Cost: Iron-air batteries cost one-tenth of lithium-ion batteries, making them a cost-effective alternative.
- Longer Storage Duration: They provide up to 100 hours of energy storage, compared to 4–6 hours for most lithium-ion batteries.
- Eco-Friendly Composition: Unlike lithium-ion, which relies on rare-earth metals and resource-intensive mining, iron-air batteries use abundant and domestically available iron, reducing environmental impact.
What Are Iron-Air Batteries?
Iron-air batteries use a unique “reversible rusting” process to store and release energy. When discharging, the iron reacts with oxygen from the air, forming iron oxide (rust) and generating electricity. When charging, an electrical current reverses this reaction, converting the rust back into iron and releasing oxygen.
A Brief History of Iron-Air Battery Research
Iron-air battery technology is not entirely new. It was first researched in the 1970s by Westinghouse Electric Corporation for potential use in electric vehicles. However, it was never commercialized due to limitations in efficiency and cost. The renewed interest in grid-scale energy storage has driven companies like Form Energy to develop and commercialize this promising technology.
Why Are Iron-Air Batteries Considered a Game-Changer?
- Ultra-Low Cost: Made from cheap and widely available materials.
- Long-Term Storage: Provides days of backup power, unlike short-term lithium-ion storage.
- Safe & Non-Flammable: No risk of overheating or fire hazards, unlike lithium-ion technology.
How Do Iron-Air Batteries Work?
Iron-air batteries operate through a reversible oxidation-reduction cycle involving iron and oxygen. During discharge, iron reacts with oxygen from the air to form iron oxide (rust), releasing electrons that generate electricity. When recharging, an external power source reverses this reaction, converting iron oxide back into metallic iron, effectively storing energy.
These batteries utilize a water-based electrolyte and operate at ambient temperatures, making them safer and more environmentally friendly than lithium-ion alternatives. Their efficiency varies based on reaction kinetics and electrolyte stability, but they offer superior energy storage for long durations at a lower cost.
Iron-Air Battery Advantages
Ultra-Low Cost Compared to Lithium-Ion
- Iron is abundant and inexpensive, unlike lithium and cobalt, making iron-air batteries significantly cheaper. This affordability makes them ideal for grid-scale energy storage.
Long-Duration Energy Storage
- Unlike lithium-ion, which typically stores energy for 4-6 hours, iron-air batteries can store power for 100+ hours, addressing the intermittency of solar and wind energy. This makes them a game-changer for renewable integration.
Environmentally Friendly Materials
- These batteries use iron, air, and water, avoiding toxic metals like cobalt or nickel, and are fully recyclable, reducing environmental impact.
High Energy Density
- Iron-air technology can store 1/10th the cost per kWh compared to lithium-ion while maintaining a competitive energy density, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
Scalability and Commercial Viability
- With companies like Form Energy pioneering this technology, iron-air batteries are becoming a commercially viable solution for industrial, residential, and grid-scale energy storage.
Challenges and Limitations of Iron-Air Batteries
Despite their promise, iron-air batteries face several challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption in grid-scale energy storage.
Slower Charging Times Compared to Lithium-Ion
One of the primary limitations of iron-air batteries is their slower charging times. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which can charge in a matter of hours, iron-air batteries rely on a chemical oxidation and reduction cycle, which takes significantly longer. This is because the iron needs to rust and then be reduced back to its original state, which is a relatively slow electrochemical process.
Lower Round-Trip Efficiency
Iron-air batteries typically have a round-trip efficiency of around 50-60%, whereas lithium-ion batteries can reach up to 90% efficiency. This energy loss primarily occurs due to unwanted side reactions, such as hydrogen evolution at the iron electrode and overvoltage issues at the air electrode. The inefficiencies in energy conversion make them less attractive for applications where high efficiency is a priority.
Scaling Up for Mass Production
Although iron is abundant and cost-effective, mass production of iron-air batteries still poses challenges. The manufacturing process requires advanced materials for electrodes and electrolytes, and further research is needed to enhance the stability of the air electrode, which is prone to degradation due to flooding and catalyst poisoning. Innovations, such as bipolar plate designs and improved electrode surface passivation, are being explored to address these issues.
Iron-Air Batteries vs. Lithium-Ion and Other Energy Storage Technologies
As the energy sector seeks efficient and cost-effective solutions, iron-air batteries are being compared with lithium-ion and other storage technologies.
Cost Comparison
One of the biggest advantages of iron-air batteries is their low cost. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which rely on expensive and rare metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, iron is one of the most abundant and affordable elements on Earth. This makes iron-air batteries a highly cost-effective alternative for long-duration energy storage.
Lifespan and Durability
While lithium-ion batteries degrade over time due to chemical instability and cycle fatigue, iron-air batteries can last over 30 years, with more than 10,000 charge-discharge cycles. This makes them ideal for grid-scale energy storage where long-term reliability is crucial. However, their lower round-trip efficiency compared to lithium-ion batteries remains a drawback.
Application Differences
- Lithium-ion batteries are best suited for applications requiring high energy density, quick charging, and portable power sources, such as electric vehicles and consumer electronics.
- Iron-air batteries excel in long-duration energy storage, making them ideal for grid backup, renewable energy storage, and industrial applications.
- Flow batteries and solid-state batteries are also competing technologies, with different strengths in energy density, lifespan, and scalability.
While iron-air batteries are a promising breakthrough in energy storage, they are not a direct replacement for lithium-ion batteries. Instead, they serve complementary roles in the energy ecosystem, particularly in grid-scale storage and renewable energy integration. As research continues, improving efficiency, scalability, and manufacturing processes will determine their future success in the energy industry.
Applications of Iron-Air Batteries
Renewable Energy Storage
Iron-air batteries are a breakthrough technology for long-duration grid storage, especially for balancing intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which typically provide short-duration storage (4-6 hours), iron-air batteries can store energy for up to 100 hours. This makes them ideal for stabilizing grids and ensuring a continuous power supply during low renewable generation periods.
The Power Up New England project in the U.S. is currently integrating an 85 MW/8.5 GWh iron-air battery system, developed by Form Energy, to complement offshore wind power. This system will help optimize electricity distribution, reduce transmission congestion, and enhance grid resilience.
Industrial and Commercial Use Cases
Large-scale industries and manufacturing plants require stable power to avoid costly downtime and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Iron-air batteries, being low-cost and highly scalable, can act as backup power sources or provide energy during peak demand hours, significantly cutting energy costs.
The 1 GWh iron-air demonstration system under construction in Minnesota by Form Energy will be tested for industrial-scale storage applications. It aims to replace coal-fired power plants by supplying low-cost renewable energy storage at a fraction of the cost of lithium-ion alternatives.
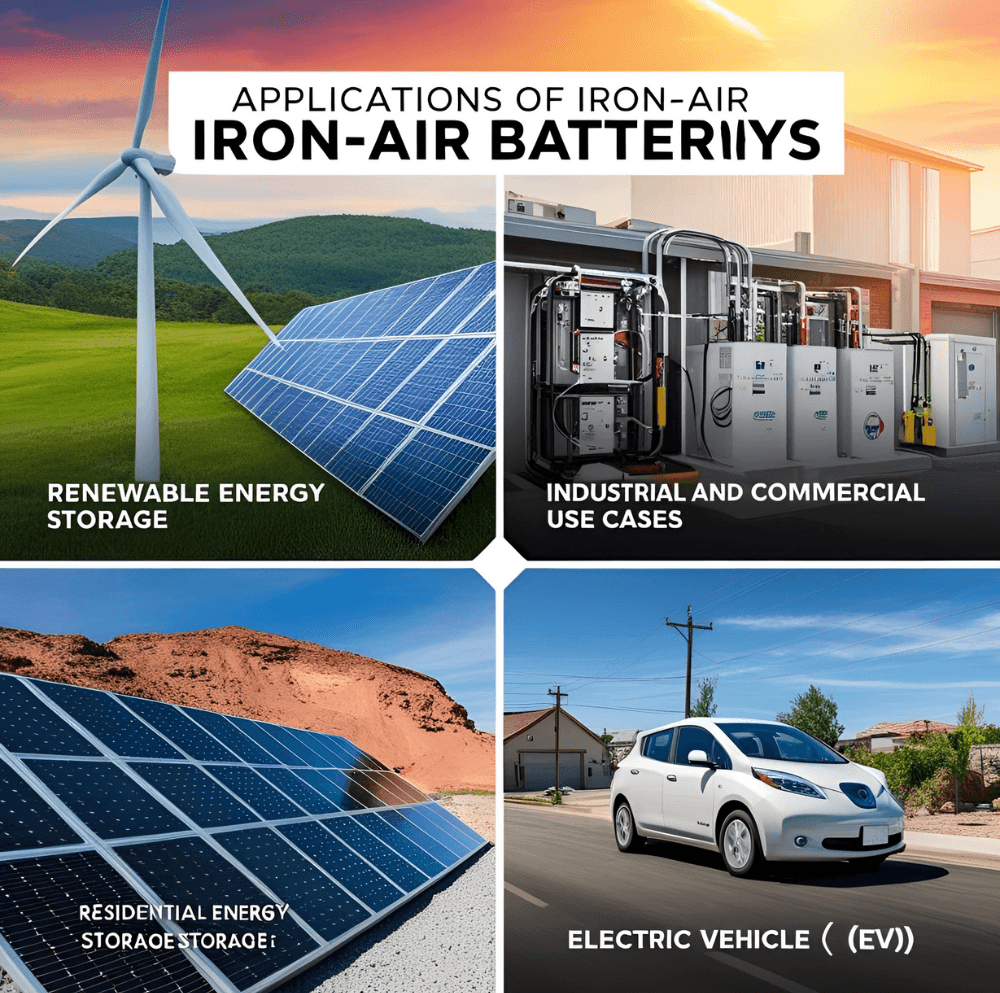
Residential Energy Storage Possibilities
While iron-air batteries are currently designed for grid-scale and industrial applications, there is potential for residential energy storage in the future. Homeowners using solar panels could benefit from long-duration storage, ensuring backup power during extended cloudy days or grid failures. However, the current size and slower charge/discharge cycles make them less suited for small-scale home use compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Potential
Although iron-air batteries offer low-cost, long-duration storage, they are not ideal for EVs due to their large size and slower charge-discharge cycles. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which provide rapid energy discharge for high-power applications, iron-air technology is optimized for steady, multi-day energy storage.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research is exploring ways to miniaturize and optimize iron-air chemistry for transportation applications. If successful, future advancements could enable iron-air batteries to power electric buses, trucks, and heavy-duty vehicles that require longer range and lower costs.
Iron-air batteries have the potential to revolutionize energy storage by making renewable energy more reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable. While they are currently best suited for grid storage and industrial applications, ongoing research could expand their use into residential and transportation sectors.
Companies Leading Iron-Air Battery Development
Major Players in the Industry
Several companies are at the forefront of iron-air battery development, aiming to revolutionize long-duration energy storage. The most notable player is Form Energy, a U.S.-based company that has attracted significant investment. Form Energy has raised over $800 million in funding, with backers including Bill Gates’ Breakthrough Energy Ventures and ArcelorMittal. The company is currently building its first large-scale battery manufacturing facility in Weirton, West Virginia, a $760 million project expected to create around 750 jobs. The first commercial batteries are projected to roll out in 2024.
While Form Energy dominates the space, other startups and research institutions are also exploring iron-air technology. Some key industry players include:
- ESS Inc. – A company specializing in long-duration iron-based batteries.
- Zinc8 Energy Solutions – While focused on zinc-air batteries, the company is developing technology with similar principles.
- Research collaborations – Universities and national laboratories in the U.S., China, and Europe are actively working on improving the efficiency of iron-air batteries.
Current Research and Innovations
Iron-air batteries offer an ultra-low-cost alternative to lithium-ion storage, using abundant iron and oxygen instead of expensive metals like lithium or cobalt. Form Energy’s system is designed to provide 100+ hours of energy storage, making it ideal for balancing intermittent renewable sources such as wind and solar. These batteries work by oxidizing and reducing iron, a process that is slower than lithium-ion charging but significantly more cost-effective for grid-scale applications.
Innovations in the sector include:
- Scaling up commercial production – The biggest challenge remains bringing iron-air batteries from prototypes to mass production. Form Energy’s West Virginia plant is a major step in this direction.
- Hybrid storage solutions – Some energy companies are pairing iron-air batteries with lithium-ion systems to maximize efficiency, using lithium for short bursts of power and iron-air for multi-day storage.
- Government funding and grants – The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has allocated $325 million to support long-duration energy storage commercialization, with Form Energy being one of the shortlisted recipients.
Projected Timeline for Commercialization
The first iron-air battery systems are expected to be deployed in 2024, with a full-scale commercial rollout anticipated by 2026. Form Energy has secured deals with multiple U.S. utilities, including PG&E and Puget Sound Energy, to integrate its batteries into the grid.
As demand for cost-effective, long-duration energy storage grows, more companies are likely to enter the iron-air battery space. While lithium-ion remains dominant, iron-air batteries are positioned as a game-changer for renewable energy storage, particularly in grid applications.
Future Prospects: Can Iron-Air Batteries Revolutionize Energy Storage?
Ongoing Research and Breakthroughs
Iron-air battery technology is advancing rapidly, driven by research and industry investment. These batteries leverage reversible rusting, a process that allows iron to react with oxygen to store and release energy. One major breakthrough is Form Energy’s iron-air battery system, which offers energy storage at just 10% of the cost of lithium-ion batteries, making it a game-changer for grid-scale storage solutions. Researchers at institutions like the USC Wrigley Institute are working on improving the efficiency and energy density of iron-air batteries, ensuring they can compete with lithium-ion alternatives in the long run.
Government and Industry Support
The U.S. government and energy sector are recognizing the potential of long-duration energy storage (LDES). The Department of Energy recently announced a $100 million investment to support the development of LDES solutions like iron-air batteries, which can store energy for over 100 hours—far exceeding the 4-5 hours provided by lithium-ion technology. Companies like Form Energy are also receiving state-level support, with a new iron-air battery plant being developed in Maine, utilizing the site of an old paper mill for production.
Potential Role in Achieving Global Energy Sustainability Goals
Iron-air batteries could play a crucial role in reducing dependence on fossil fuels and stabilizing renewable energy grids. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which require rare and environmentally damaging materials like cobalt and nickel, iron-air batteries rely on abundant and recyclable iron, making them more sustainable. Their ability to store renewable energy for multiple days ensures a stable power supply during fluctuations in solar and wind generation. This could significantly accelerate the transition to a clean energy future by making renewables more reliable.
Conclusion
Iron-air batteries are positioned to be a disruptive force in energy storage, offering low-cost, long-duration, and sustainable solutions for renewable energy. However, challenges such as efficiency improvements, scalability, and commercialization timelines still need to be addressed before widespread adoption. With continued research, industry investment, and government backing, these batteries could revolutionize how we store and use energy, potentially replacing lithium-ion in grid-scale applications.
Related Reads You Might Find Interesting:
If you’re intrigued by the potential of Iron-Air Batteries in energy storage, you might also find these innovations fascinating:
🔋 Hydrogen vs. Electric – Compare the strengths and challenges of hydrogen fuel cells and battery-electric systems in the race for sustainable energy solutions.
🚁 Hydrogen-Powered Drones – Discover how hydrogen fuel cells are enabling drones to fly longer while maintaining zero emissions, revolutionizing aerial technology.
⚡ Invention of Battery Technology – Explore the history and breakthroughs in battery advancements, from early chemical cells to cutting-edge storage solutions.
🌱 Electricity Generating Slime – Learn how bioengineered slime is producing electricity and its potential to drive sustainable energy innovations.
🚀 Advanced Energy Storage – Delve into the latest breakthroughs in energy storage systems that are shaping the future of transportation and renewable energy.
🌍 Harnessing Soil Electricity – Uncover how scientists are tapping into soil microbes to generate clean energy, offering a unique approach to sustainable power generation.
Stay ahead of the curve by exploring these groundbreaking energy technologies! 🚀






