Introduction: The Rise of Gravity Batteries in Energy Storage
As the world shifts towards sustainable energy, gravity batteries are emerging as a revolutionary solution for energy storage. But what is an anti-gravity battery and how does it work? Unlike traditional batteries that rely on chemical reactions, gravity battery systems store energy by lifting and lowering weights, converting gravitational potential energy into electricity. This innovation is transforming renewable energy storage, offering a long-term and eco-friendly alternative.
From large-scale grid solutions to gravity battery for home applications, this technology provides efficient energy retention without relying on lithium or other finite resources. Additionally, advancements in anti-gravity battery charging are paving the way for improved energy efficiency, ensuring a continuous power supply for households and industries alike. With the increasing demand for sustainable energy, weight battery systems are set to play a crucial role in the future of power storage.
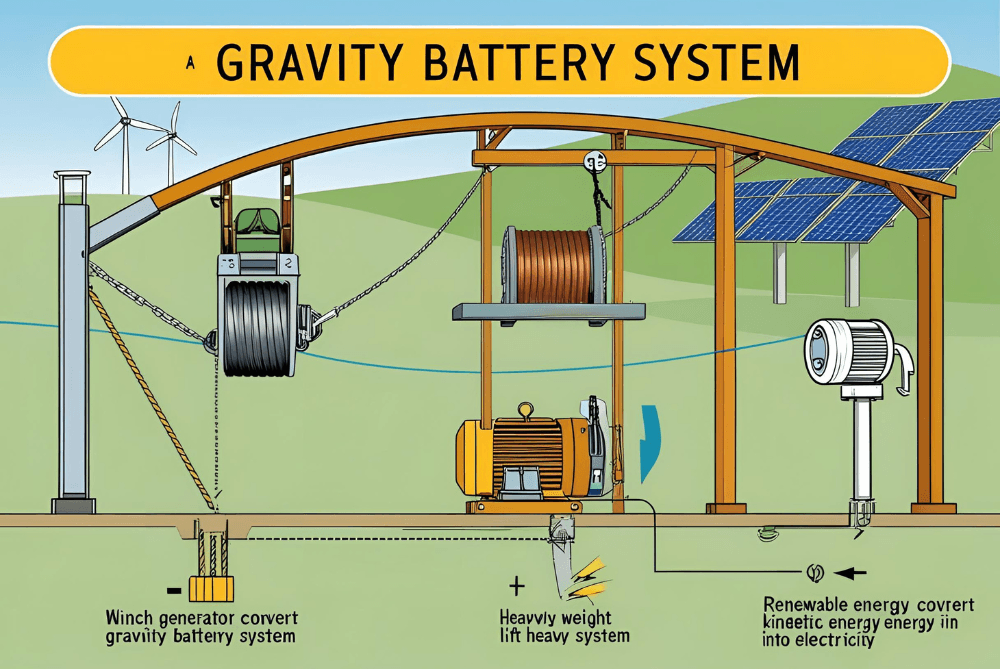
How Gravity Batteries Work
Gravity batteries are a promising energy storage technology that relies on mechanical potential energy rather than chemical reactions. These systems store energy by lifting heavy masses and release it by lowering them to generate electricity, offering an alternative to lithium-ion batteries for large-scale and home energy storage.
Basic Working Principle
Gravity batteries operate on a simple concept: when surplus energy is available, it powers a mechanism (such as a winch or crane) that lifts a heavy weight to a higher position. The stored potential energy is then converted back into electricity by gradually lowering the weight, which drives a generator. This process allows for energy storage and controlled release when needed, making gravity batteries highly useful for grid stability and renewable energy integration.
Key Components of a Gravity Battery
A gravity battery consists of:
- Winch System – Lifts and lowers the weight using excess electricity.
- Heavy Mass (Weight Battery) – Can be made of concrete blocks, steel, or other dense materials.
- Generator – Converts kinetic energy from the descending weight into electricity.
- Support Structure – Includes cranes, vertical shafts, or rail systems to hold and move the weight efficiently.
Some gravity battery designs, such as those by Energy Vault, use a crane-stacked system with concrete blocks, while others, like Gravitricity, utilize deep mine shafts to raise and lower weights efficiently. These designs ensure efficient long-term energy storage with minimal maintenance needs.
Comparison with Chemical Batteries
Gravity batteries offer several advantages over traditional lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries:
- Longevity: Gravity-based systems can operate for decades (potentially 50+ years) with minimal degradation, whereas lithium-ion batteries typically degrade after 10-20 years.
- Efficiency: Some gravity systems, like those by Energy Vault, achieve around 85% efficiency—comparable to lithium-ion batteries (90%) and superior to pumped hydro storage (70-80%).
- Eco-Friendliness: Unlike chemical batteries, gravity batteries do not rely on rare or toxic materials, making them more sustainable.
- Scalability: While chemical batteries can be deployed anywhere, gravity batteries require significant infrastructure, such as cranes, towers, or deep mine shafts, making them more suitable for large-scale storage rather than portable applications.
Gravity Battery for Home Use
Researchers at Purdue University have explored the feasibility of using gravity batteries for residential energy storage. A proposed system involves using a home’s attic and basement to lift and lower a weight, storing excess solar energy during the day and releasing it at night. While still in early development, this concept could offer homeowners a durable and eco-friendly energy storage alternative in the future.
Gravity batteries present a viable and sustainable energy storage solution for grid-scale applications and potentially for home use as technology advances. They offer a long-lasting, efficient alternative to chemical batteries, particularly for renewable energy storage and off-grid power applications.
Advancements in Anti-Gravity Battery Charging
What is an Anti-Gravity Battery? Theoretical Concepts and Current Research
The concept of an anti-gravity battery is largely theoretical, rooted in emerging research into gravitational interactions with superconductors and magnetic levitation. While true “anti-gravity” is not yet feasible with current physics, researchers are exploring ways to manipulate gravitational effects using superconductors and diamagnetic materials. Some studies suggest that superconductors could alter local gravitational fields at a microscopic level, which has led to speculation about their potential in energy storage and transfer systems.
Exploring Innovations: Magnetic Levitation Energy Storage and Superconducting Materials
One of the most promising advancements related to anti-gravity battery charging involves magnetic levitation (maglev) energy storage. Researchers are developing materials with enhanced levitation properties, reducing friction and energy loss in rotating energy storage systems like flywheels. These innovations could significantly improve energy efficiency and provide ultra-stable power sources for futuristic applications, including spacecraft and autonomous systems.
Furthermore, superconducting materials play a key role in this field. Scientists have found that when cooled to extremely low temperatures, certain materials exhibit properties that could lead to novel energy storage methods, including magnetic energy confinement and near-zero resistance energy flow. The potential for superconducting energy storage systems (SESS) is being explored as an alternative to conventional batteries.
Limitations and Challenges: Can Anti-Gravity Technology Be Practically Implemented?
Despite exciting progress, there are several challenges to implementing anti-gravity battery charging:
- Material Limitations – Many of the superconductors required for these systems operate only at ultra-low temperatures, making large-scale implementation costly and impractical.
- Energy Requirements – Magnetic levitation systems require continuous energy input to maintain their stability, which could offset their efficiency gains.
- Lack of Practical Testing – The idea of using superconductors to modify gravitational effects is still largely theoretical and lacks real-world proof.
- Economic Viability – The cost of developing and deploying superconducting and maglev-based energy storage systems is significantly higher than traditional battery technologies.
The Future of Anti-Gravity Battery Charging
While true anti-gravity batteries remain within the realm of speculative physics, advancements in superconducting materials and magnetic levitation could revolutionize energy storage and transportation in the future. Research efforts are ongoing, and breakthroughs in material science and quantum physics could lead to practical applications of these futuristic concepts.
Gravity Batteries for Home Use
Can You Install a Gravity Battery for Home?
Gravity batteries for home use are emerging as a potential alternative to chemical battery storage. These systems work by lifting heavy weights and lowering them to generate electricity when needed. While large-scale gravity storage projects are being developed worldwide, home-based solutions are still in the early stages. Companies are exploring modular, scalable gravity battery designs that can integrate with residential renewable energy systems, particularly solar power.
Commercially Available Options and DIY Solutions
Currently, there are limited commercial gravity battery solutions specifically designed for home use. However, innovators are developing small-scale versions that could serve as efficient home energy storage units. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, gravity batteries don’t degrade over time, making them a long-lasting solution.
For DIY enthusiasts, homemade energy storage solutions are gaining traction. Some hobbyists are repurposing industrial lifting mechanisms to create experimental gravity storage devices. DIY solutions for home energy storage are popular among those who want off-grid or backup power, similar to how DIY lithium-ion battery projects have evolved in recent years.
Cost Analysis: Gravity Battery vs. Traditional Home Battery Storage
A gravity battery’s initial cost depends on the materials, installation, and the weight used for energy storage. While long-term operational costs are low due to minimal maintenance, the upfront investment could be high.
In contrast, traditional home battery storage systems, like the Tesla Powerwall ($12,000 with installation) and LG Chem RESU16H ($15,000), provide predictable energy storage with warranties of around 10 years.
Gravity batteries, if scaled down for home use, may offer cost advantages in the long run due to their longer lifespan and lack of reliance on rare materials. However, installation complexity and space requirements could be limiting factors.
Comparing Gravity Batteries with Other Energy Storage Solutions
Efficiency, Scalability, and Environmental Impact
Gravity batteries have high efficiency (above 80%) and can last for decades without material degradation. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, they do not rely on scarce metals, making them environmentally friendly. However, they require space and height for weight displacement, which can be a challenge for residential applications.
How Gravity-Based Energy Storage Competes with Lithium-Ion Batteries and Pumped Hydro Storage
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are widely used for home and grid storage due to their compact size, high energy density, and established supply chain. However, they degrade over time and pose recycling challenges.
- Pumped Hydro Storage: The most established form of gravity storage, but it requires large water reservoirs and is not feasible for home use.
- Gravity Batteries: Offer a sustainable alternative, but currently, their scalability for home applications is limited. Research is ongoing to develop compact designs.
Future Role of Weight Battery Systems in a Net-Zero Energy Grid
As energy grids transition to renewables, gravity batteries could play a role in long-term energy storage solutions. While current focus is on large-scale implementations, future advancements could lead to residential applications, complementing or even replacing chemical batteries in off-grid and backup power scenarios.
Challenges & Future Prospects
Technical Challenges: Energy Density, Infrastructure, and Scalability
Gravity batteries face key challenges in energy density and infrastructure development. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which store energy chemically in a compact space, gravity batteries require large-scale physical movement of masses, making them inherently space-intensive. The infrastructure needed—such as deep shafts or high towers—can be costly and complex to integrate with existing energy grids. However, new advancements are addressing these issues, with companies like Gravitricity repurposing abandoned mine shafts to reduce infrastructure costs.
Scalability remains another challenge. While pumped hydro storage systems, a similar gravity-based technology, have been widely deployed, gravity batteries are still in their early commercial stages. Companies such as Energy Vault are developing modular tower-based systems to improve scalability and efficiency.
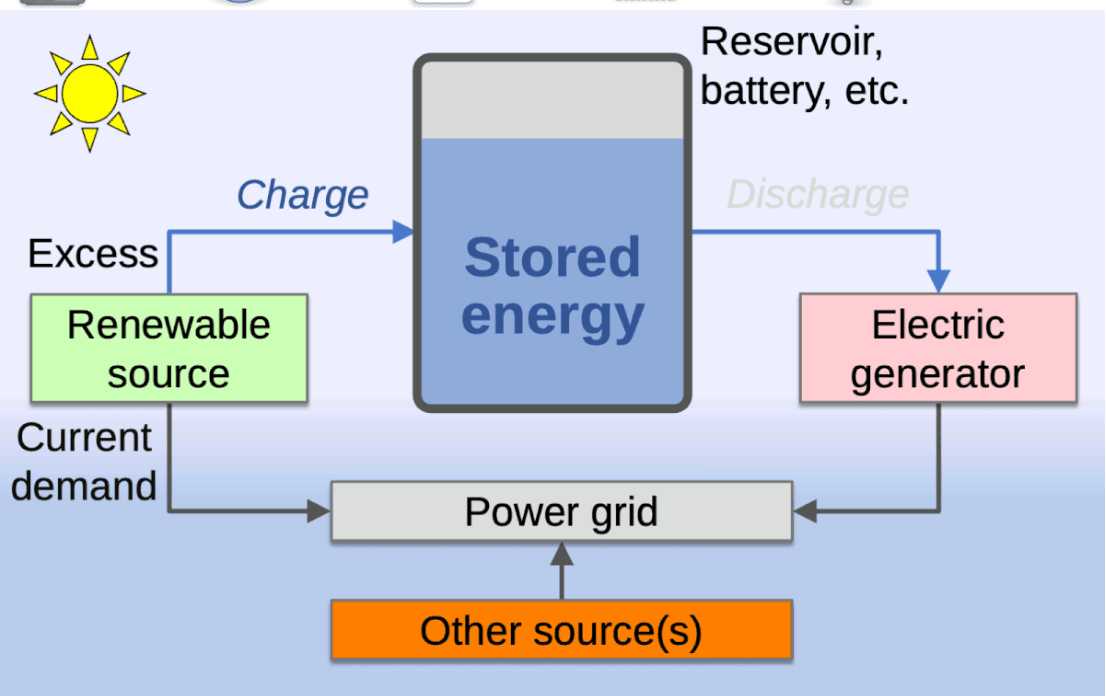
Breakthroughs in Material Science and AI-Driven Energy Optimization
Advancements in material science are crucial for improving gravity battery technology. Lightweight but high-strength materials can increase the efficiency of lifting mechanisms, while AI-powered energy optimization can enhance performance. For example, smart grid integration and automated energy management systems are being explored to dynamically adjust power output and optimize energy storage based on demand.
AI and machine learning are also being used to predict energy needs and automate load balancing, helping gravity batteries become more responsive to grid fluctuations.
Predictions for Gravity Batteries in the Global Energy Market
The rapid increase in gravity battery patent filings—rising from 40 patents in 2019 to over 320 in 2024—indicates growing interest and investment in this technology. With China leading in patent development, and companies like Energy Vault and Gravitricity securing commercial deals, gravity energy storage is poised for a significant role in the transition to sustainable energy. While it may not replace lithium-ion batteries entirely, gravity batteries offer a low-maintenance, long-duration storage solution that could complement existing technologies in the push for a net-zero energy future.
Conclusion: Is Gravity the Future of Energy Storage?
Key Benefits: Cost-Effectiveness, Longevity, and Sustainability
Gravity batteries offer several advantages over chemical-based storage:
- Low Maintenance: Unlike lithium-ion batteries, gravity batteries do not degrade over time and can last for decades with minimal upkeep.
- Sustainability: They do not rely on rare metals like lithium or cobalt, making them an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Once installed, gravity batteries have lower operating costs compared to chemical batteries, with some designs promising energy storage at half the cost of lithium-ion.
Potential Applications: Grid-Level Storage, Remote Power, and Off-Grid Energy Solutions
Gravity batteries are ideal for large-scale, long-duration energy storage. They can be used for:
- Grid stabilization, providing backup power during peak demand.
- Remote and off-grid locations, such as Arctic research stations or developing regions where traditional energy storage is impractical.
- Disaster resilience, offering a reliable energy source in emergencies.
Final Thoughts: Can Gravity-Powered Batteries Revolutionize Renewable Energy?
While still an emerging technology, gravity batteries show promise as a long-term energy storage solution. As material and AI advancements improve efficiency, and infrastructure costs decrease, they could play a vital role in a net-zero future. While they may not entirely replace lithium-ion batteries, gravity storage is set to be a key part of the energy transition.
Explore More on Cutting-Edge Energy Innovations:
If you found gravity batteries fascinating, check out these insightful articles:
🔹 Octillion Power Systems & Tata Battery: Pioneers in EV Energy
🔹 Unveiling Dark Oxygen: Mining Seabed for Battery Materials
🔹 The Invention of Battery Technology: A Journey Through Time
🔹 Iron-Air Batteries: A Game Changer for Energy Storage
🔹 The Potential of Americium Batteries
Stay ahead in the world of energy advancements! 🚀⚡