Introduction: Why Understanding the ‘Father of Chemistry’ Matters
Who Really is the Father of Chemistry?
Imagine a world without medicines, clean water, or advanced materials—without chemistry, modern life as we know it wouldn’t exist. But who laid the foundation for this powerful science? If you Google “Who is the Father of Chemistry?”, you’ll often see the name Antoine Lavoisier pop up. But what if I told you there isn’t just one?
The Father of Chemistry title isn’t exclusive—it belongs to multiple pioneers across different eras. Alchemy’s experimental roots, Boyle’s gas laws, and Lavoisier’s revolutionary discoveries all shaped chemistry into the precise science we rely on today.
Bridging the Content Gap: More Than Just One Name
Most articles stop at Lavoisier, but chemistry’s evolution was a team effort:
🔥 Jābir ibn Hayyān (Geber) (8th–9th century): The father of early chemistry, pioneering distillation, crystallization, and acids.
💨 Robert Boyle (17th century): Defined elements and gases, debunking alchemical myths.
🧪 Antoine Lavoisier (18th century): Identified oxygen’s role in combustion, leading to modern chemical laws.
⚛ John Dalton (19th century): Introduced the atomic theory, defining elements at the molecular level.
Alchemy vs. Modern Chemistry: A Science Transformed
Alchemy was a mix of mysticism and experimentation, aiming to turn metals into gold and create elixirs of immortality. However, it lacked the scientific method. The transformation into modern chemistry came when scientists like Boyle and Lavoisier shifted the focus to quantitative experiments and precise laws, paving the way for industries from medicine to energy.
Why This Matters Today
By understanding who the real Fathers of Chemistry are, we gain deeper insight into how science evolved from speculation to precision. Every time we use pharmaceuticals, clean fuels, or new materials, we’re benefiting from centuries of scientific breakthroughs.
Ready to dive deeper into the revolution of chemistry? Let’s explore the minds behind the discoveries that shaped our world. 🔬🚀
The Many Fathers of Chemistry: Why There’s No Single Answer
Chemistry is not the achievement of a single mind but a culmination of discoveries made over centuries. While the Father of Chemistry title is often linked to Antoine Lavoisier, multiple pioneers have significantly shaped the field. Each contributed in a unique way—whether in chemical laws, experimental methods, atomic theory, or the classification of elements. This section explores their groundbreaking work.
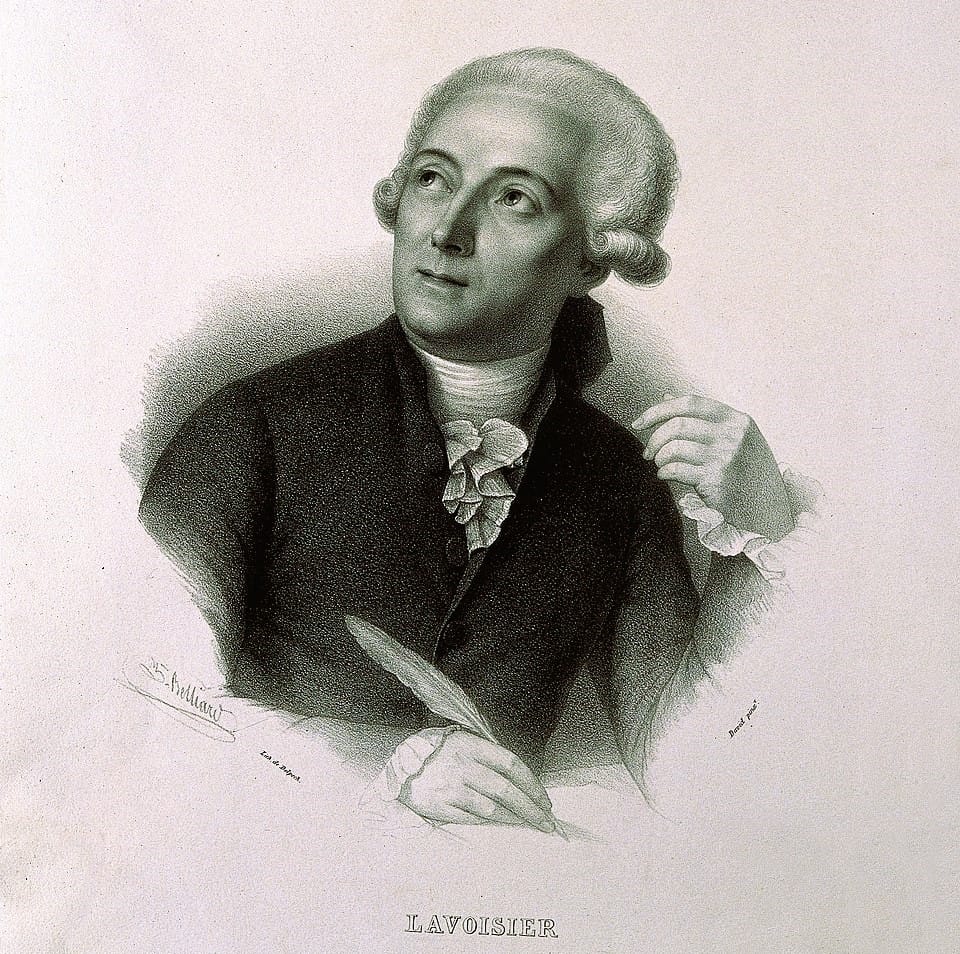
Antoine Lavoisier – The Father of Modern Chemistry
🧪 Revolutionizing Chemical Reactions & the Oxygen Theory
Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794) is regarded as the Father of Modern Chemistry due to his pioneering work in chemical reactions, combustion, and the scientific method. Before Lavoisier, the phlogiston theory dominated, falsely suggesting that a mysterious substance was released during burning. He debunked this theory by proving that oxygen is essential for combustion.

Key Contributions:
✅ The Oxygen Theory of Combustion – Identified oxygen’s role in burning, respiration, and rusting, disproving outdated theories.
✅ The Law of Conservation of Mass – Proved that matter is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions, laying the foundation for modern chemistry.
✅ Reformed Chemical Nomenclature – Introduced systematic naming of elements and compounds, many of which are still in use today.
✅ Authored the First Chemistry Textbook – Traité Élémentaire de Chimie (1789), establishing chemistry as a quantitative science.
Lavoisier’s contributions helped shift chemistry from qualitative observation (alchemy) to precise measurements and reproducible experiments, defining chemistry as a true science.
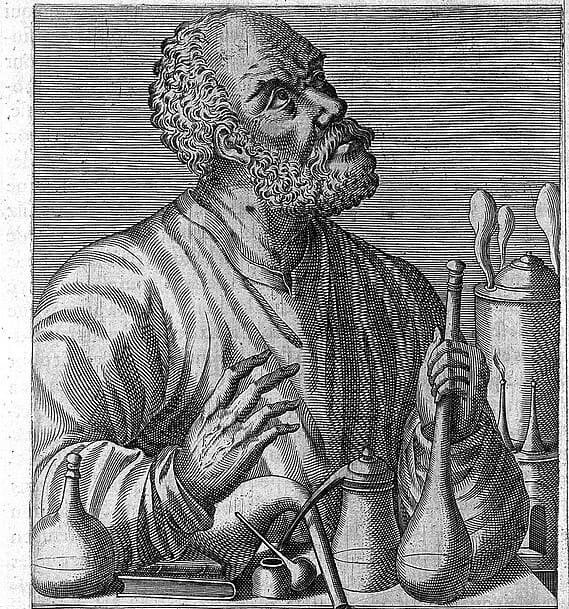
Jabir Ibn Hayyan – The Father of Early Chemistry/Alchemy
🔥 Pioneer of Alchemy & Early Laboratory Techniques
Jabir Ibn Hayyan (c. 721–815) , also known as Geber, was one of the earliest scientists to apply systematic experimentation in chemical processes. His work laid the foundation for modern chemical techniques, particularly in distillation, crystallization, and acid preparation.
Key Contributions:
✅ Developed Distillation Techniques – Invented the alembic still, refining the distillation of alcohol and essential oils.
✅ Discovered Strong Acids – First to prepare sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and hydrochloric acid, crucial in modern industry.
✅ Introduced Experimental Chemistry – Developed over 2,000 laboratory processes, including sublimation, filtration, and evaporation.
✅ Father of Early Alchemy – His work influenced Western alchemists, paving the way for later scientists like Boyle and Lavoisier.

Jabir’s contributions were so vast that alchemy transitioned from a mystical pursuit to an early experimental science, laying the groundwork for modern chemistry.
Robert Boyle – The Father of Experimental Chemistry
📏 Applying the Scientific Method to Chemistry
Robert Boyle (1627–1691) challenged alchemy by advocating for an evidence-based, experimental approach. His work in gases, elements, and the scientific method led to Boyle’s Law, a fundamental principle in physics and chemistry.
Key Contributions:
✅ Boyle’s Law – Demonstrated that gas pressure and volume are inversely proportional, forming the foundation of gas laws.
✅ Defined Elements Scientifically – Proposed that elements are basic substances that cannot be broken down further, which directly influenced modern atomic theory.
✅ Separated Chemistry from Alchemy – His book, The Sceptical Chymist (1661), argued against the mystical ideas of alchemy, promoting chemistry as a quantifiable science.
✅ Established the Scientific Method in Chemistry – Focused on reproducibility, observation, and controlled experiments.
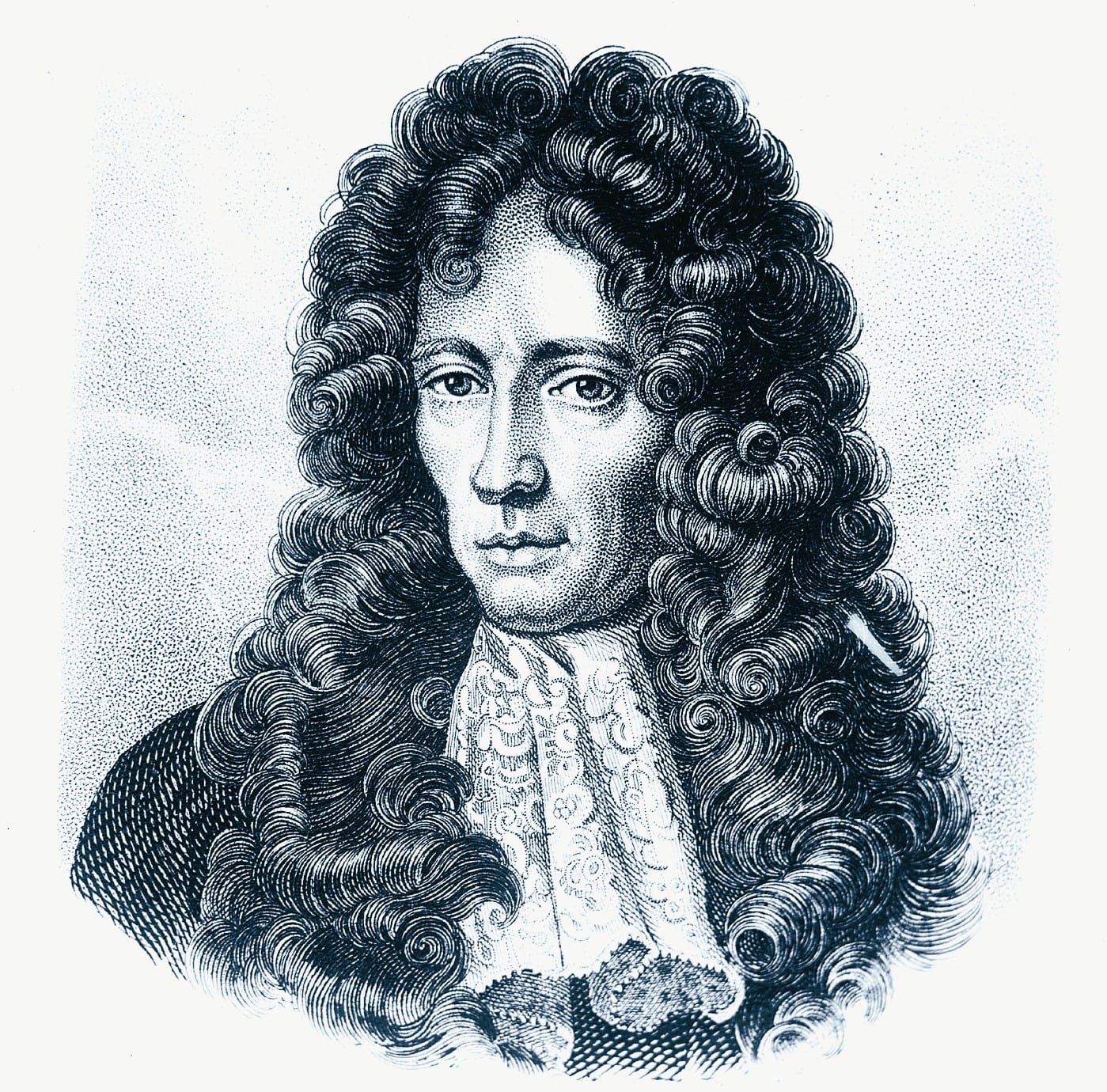

Boyle’s approach transformed chemistry from philosophical speculation into a scientific discipline, making him one of the most influential pioneers.
Dmitri Mendeleev – The Father of the Periodic Table
🧩 Organizing the Chemical Elements
Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1907) made one of the most critical breakthroughs in chemistry: the Periodic Table. His classification of elements based on atomic weight and properties allowed for predicting unknown elements, revolutionizing chemical research.
Key Contributions:
✅ Developed the First Accurate Periodic Table – Arranged elements by atomic mass and chemical properties, revealing periodic trends.
✅ Predicted Undiscovered Elements – Left gaps in his table for unknown elements like gallium, scandium, and germanium, which were later discovered.
✅ Established Periodic Law – Stated that element properties repeat periodically when arranged by atomic weight, forming the basis of modern chemistry.
✅ Advanced Chemical Education – His work helped standardize chemical study worldwide.
Mendeleev’s periodic table remains one of the greatest scientific achievements, enabling chemists to understand atomic behavior, reactivity, and element classification.

Why There’s No Single Father of Chemistry
Each of these pioneers transformed chemistry in different ways:
✅ Jabir Ibn Hayyan introduced systematic experimentation and acids.
✅ Robert Boyle separated chemistry from alchemy and introduced experimental methods.
✅ Antoine Lavoisier established chemical laws and combustion theory.
✅ Dmitri Mendeleev developed the periodic table, guiding future discoveries.
Chemistry is a constantly evolving science, and its progress owes credit to multiple pioneers across different centuries. Understanding the contributions of these Fathers of Chemistry helps us appreciate how modern chemistry emerged from centuries of experimentation and discovery.
India’s Contribution: Who is the Father of Chemistry in India?
India has a long and rich history of chemical sciences, dating back to ancient alchemy and evolving into modern chemical research. Several pioneers have played a crucial role in shaping Indian chemistry.
Prafulla Chandra Ray: The Father of Modern Chemistry in India
Prafulla Chandra Ray (1861–1944) is widely regarded as the Father of Chemistry in India due to his groundbreaking contributions to chemical research and industrial development. He is best known for synthesizing mercurous nitrite (Hg₂(NO₂)₂), an important discovery in inorganic chemistry. Beyond his research, he founded Bengal Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals, India’s first pharmaceutical company, promoting indigenous chemical industries.
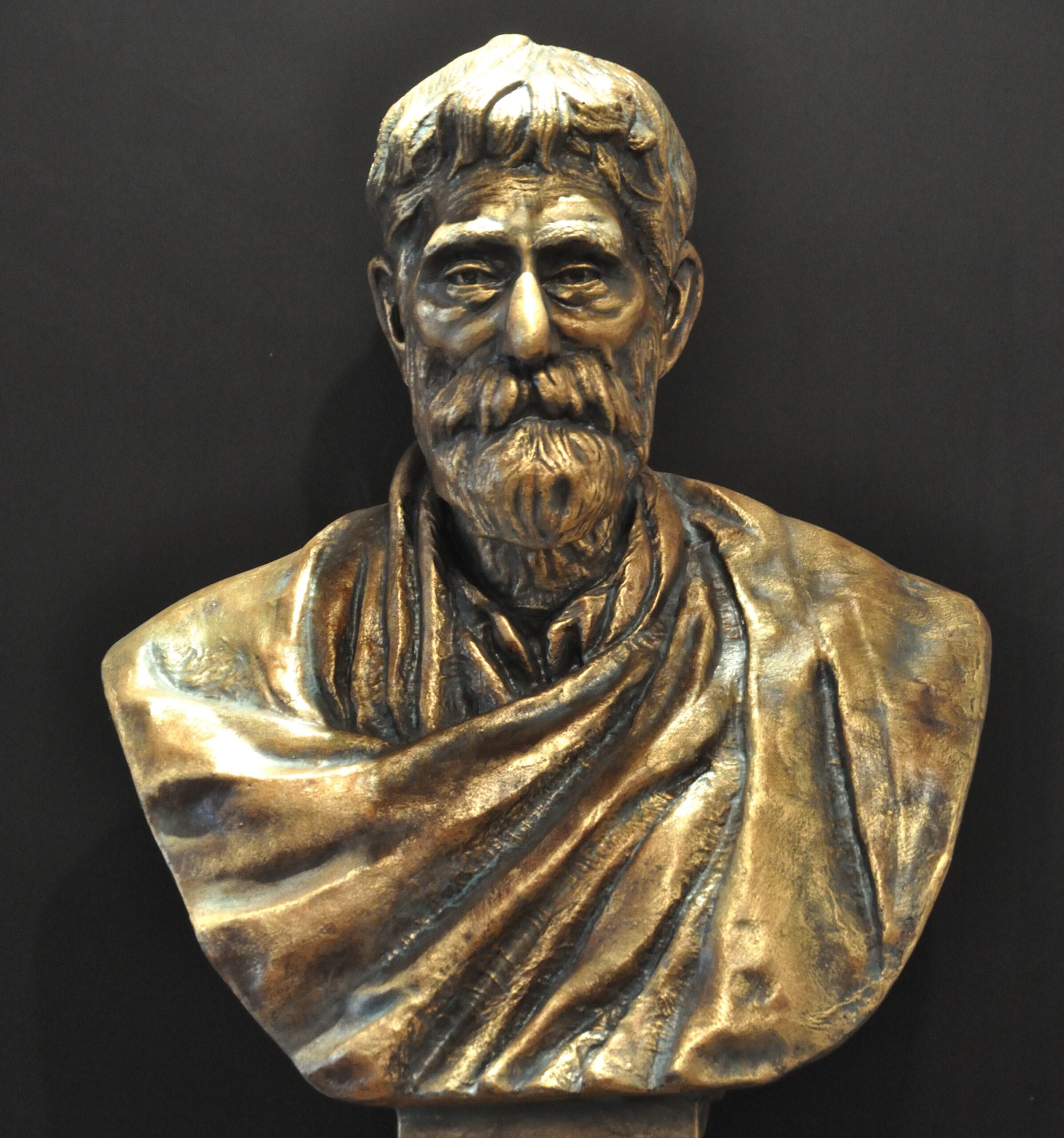

Ray was also a dedicated educator and historian, authoring A History of Hindu Chemistry, which documented India’s ancient contributions to chemistry. His accolades include honorary doctorates and prestigious fellowships, such as the Faraday Gold Medal and knighthood by the British government.
Nagarjuna: The Ancient Indian Alchemist
In ancient India, Nagarjuna (c. 8th–9th century CE) was a pioneer in alchemy and early chemistry. He made significant advancements in metallurgy, particularly in refining metals and preparing chemicals for medicinal use. His texts, such as Rasaratnakara, discuss sulfur-based compounds, distillation, and transmutation of metals, showcasing an early understanding of chemical processes.
C.N.R. Rao: A Modern Indian Chemistry Pioneer
C.N.R. Rao is a globally renowned chemist in the field of solid-state and materials chemistry. He has contributed extensively to nanotechnology and advanced materials, influencing research in semiconductors, superconductors, and molecular electronics. His work has earned him the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian award, for scientific contributions.
Analyzing India’s Deep-Rooted Legacy in Chemistry
Many discussions about chemistry’s history often focus on European scientists, overlooking India’s vast contributions. While Acharya Prafulla Chandra Ray is recognized, deeper analysis of Nagarjuna’s alchemical studies and modern breakthroughs by scientists like C.N.R. Rao is essential to understand India’s impact on global chemistry.
Overlooked Chemists Who Changed the World
While famous figures like Lavoisier and Mendeleev shaped modern chemistry, many lesser-known chemists made groundbreaking contributions that went underappreciated. Here are some chemists whose work changed the world:
Alice Ball: The Forgotten Pioneer Who Revolutionized Leprosy Treatment
Alice Ball, an African American chemist, developed the first effective treatment for leprosy, known as the Ball Method. In the early 20th century, leprosy was a devastating disease with no reliable cure. Ball successfully extracted the active compounds from chaulmoogra oil and made them injectable, providing a viable treatment. Unfortunately, her work was stolen—her mentor took credit for it after her untimely death at 24. Today, her contributions are rightfully acknowledged in medical and scientific communities.
Marie Maynard Daly: Pioneering Cardiovascular Chemist
Marie Maynard Daly was the first Black woman in the U.S. to earn a PhD in chemistry (1947). Her research was fundamental in understanding how hypertension and high cholesterol contribute to heart disease. She provided crucial insights into how diet affects arterial health, laying the groundwork for modern heart disease prevention strategies. Her work also helped develop medications like ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers to manage high blood pressure. Despite racial and gender barriers, Daly’s contributions influenced dietary guidelines and preventive cardiology today.
St. Elmo Brady: Breaking Barriers in Acid Research
St. Elmo Brady became the first African American chemist to earn a PhD (1916) and was instrumental in acid-base chemistry and molecular interactions. His research at institutions like the University of Illinois advanced knowledge of complex acids and their industrial applications, leading to developments in materials science and pharmaceuticals. He also championed STEM education, establishing strong chemistry programs at historically Black colleges.
Winifred Burks-Houck: Champion of Environmental Chemistry
Winifred Burks-Houck made significant contributions to hazardous waste management and chemical safety. As a leading environmental chemist, she worked on reducing industrial pollution and ensuring safer disposal methods for toxic substances. She was also a strong advocate for diversity in STEM, leading efforts to support underrepresented scientists.
Why These Chemists Matter
Despite their immense contributions, these chemists were often overlooked due to systemic biases, racial discrimination, or historical erasure. By recognizing their work, we gain a more complete understanding of chemistry’s evolution and ensure that their legacies continue to inspire future generations.
The Role of Alchemy: The Missing Link to Modern Chemistry
Alchemy is often dismissed as a pseudoscience filled with mystical symbols and secret formulas, but its contributions to the history of chemical discoveries are undeniable. Many fundamental chemical processes, laboratory tools, and experimental methods originated in the work of ancient and medieval alchemists. Without their discoveries, modern chemistry would not exist.
Alchemy’s Role in Laboratory Tools: The Foundation of Modern Chemistry
One of the greatest contributions of alchemists was the development of laboratory tools and techniques that became the foundation for modern experimental chemistry. Early alchemists in China, India, the Islamic world, and medieval Europe refined laboratory equipment that is still in use today.
- Distillation: Paving the Way for Purification & Separation
Alchemists developed and perfected distillation, a process used to separate mixtures based on different boiling points. This was initially used for extracting essential oils, alcohol, and acids.
- The Alembic: An invention of early Islamic alchemists, such as Jabir Ibn Hayyan (Geber), this device allowed for more efficient distillation, leading to the production of pure alcohol, nitric acid, and sulfuric acid.
- Impact on Modern Chemistry: Distillation remains crucial in industries such as petroleum refining, pharmaceuticals, and food production.
- Crucibles: High-Temperature Chemical Reactions
Alchemists used crucibles, heat-resistant vessels, to conduct high-temperature reactions. These were essential for metallurgy, allowing for:
- Purification of metals like gold, silver, and copper.
- Testing reactions of minerals and ores, which contributed to early chemistry and metallurgy.
- Foundation for Industrial Chemistry: Today, crucibles are widely used in industries such as metallurgy, ceramics, and material science.
- Filtration & Sublimation: Refining Chemical Processes
- Filtration: Alchemists developed filtration techniques to separate solids from liquids, an essential process in modern chemistry.
- Sublimation: The process of converting solids directly into gas was first studied by alchemists and is now crucial in pharmaceuticals and material science.
These foundational tools allowed chemistry to evolve from mystical experimentation into a structured scientific discipline.
Contributions of Alchemists to Acids, Bases, and Metallurgy
Alchemists discovered some of the most important chemical substances used today, particularly strong acids and early bases.
- Discovery of Strong Acids & Bases
Alchemists were the first to isolate and use:
- Nitric Acid (HNO₃) – Used in refining metals and dissolving substances.
- Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) – Now one of the most widely used industrial chemicals, essential in fertilizers and batteries.
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) – Used in alchemy to dissolve metals and purify substances.
Their experiments laid the foundation for acid-base chemistry, which later scientists, like Robert Boyle and Antoine Lavoisier, expanded into modern chemical principles.
- Early Metallurgy & Elemental Discoveries
Alchemists were pioneers in extracting, refining, and combining metals:
- Chinese alchemists focused on gold purification techniques and early forms of gunpowder.
- Indian alchemists (like Nagarjuna) experimented with sulfur and mercury compounds.
- Islamic and European alchemists developed methods for refining silver, gold, and iron.
These metallurgical advancements directly contributed to the Industrial Revolution and modern material science.
Why Alchemists Are Often Forgotten Despite Their Foundational Work
Despite their essential role in the history of chemical discoveries, alchemists are often overlooked due to:
- The Mysticism & Symbolism of Alchemy
Alchemists often recorded their findings in coded language and esoteric symbols, which made their knowledge inaccessible to many. The legendary Philosopher’s Stone, believed to grant immortality and turn base metals into gold, was a metaphor for transformation but led many to dismiss alchemy as a superstition.
- Lack of Scientific Rigor
Unlike modern chemists, alchemists did not follow a strict scientific method. Many of their experiments were trial and error, often blending chemical processes with spiritual beliefs. This made alchemy seem unreliable compared to later empirical studies.
- The Rise of Empirical Science
By the 17th and 18th centuries, chemists like Robert Boyle, Antoine Lavoisier, and John Dalton shifted chemistry toward measurable, repeatable experiments. Alchemy was gradually dismissed as outdated, despite its many contributions.
Alchemy’s Lasting Legacy in Chemistry
Although alchemy eventually faded, its impact on modern chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and metallurgy is undeniable. Many of its discoveries, tools, and techniques laid the groundwork for scientific progress. Today, elements like mercury, sulfur, and phosphorus—first studied by alchemists—are critical in industrial processes, medicine, and technology.
By recognizing the contributions of alchemists to the history of chemical discoveries, we gain a deeper appreciation of how chemistry evolved from mystical experiments into the precise science it is today.
How the Definition of ‘Father of Chemistry’ Will Evolve in the Future
AI-Driven Chemical Research & Automation in Material Science
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing chemistry by accelerating chemical discovery, automating synthesis, and optimizing materials development. Researchers are using AI to design new metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and covalent-organic frameworks (COFs) for applications in clean energy and sustainable materials. For instance, Professor Omar Yaghi’s Bakar Institute of Digital Materials for the Planet is leveraging AI to predict material properties with unprecedented accuracy.
Autonomous robotic labs, often called “AI Chemists,” are now conducting chemical experiments without human intervention. These systems use machine learning models to design and refine chemical reactions, drastically cutting the time needed to develop new compounds.
CRISPR & DNA Chemistry as New Frontiers
Gene-editing technologies like CRISPR are reshaping biochemistry, leading to breakthroughs in synthetic biology, pharmaceuticals, and even nanochemistry. Scientists are exploring the possibility of chemically programming DNA and proteins to develop new materials and medicines.
Future Pioneers: Who Will Be the “Father of AI Chemistry”?
With AI increasingly conducting chemical research, the title “Father of Chemistry” might belong to a machine-learning algorithm rather than a human scientist. Pioneers in AI-driven drug discovery, such as Alex Zhavoronkov at Insilico Medicine, are already using AI to design new drugs and materials faster than ever before.
Conclusion: Why Chemistry Has No Single ‘Father’
Chemistry has evolved through centuries of contributions from multiple scientists across different eras and regions. Antoine Lavoisier may be recognized as the Father of Modern Chemistry, but without the experimental methods of Robert Boyle, the elemental classification of Dmitri Mendeleev, or the foundational alchemical work of Jabir Ibn Hayyan, chemistry as we know it would not exist.
In India, pioneers like Prafulla Chandra Ray and Nagarjuna played key roles in alchemy, metallurgy, and modern chemical research, yet their work is often underappreciated globally. Even today, chemists like C.N.R. Rao continue pushing the boundaries of solid-state chemistry.
With AI-driven chemical discovery, automation, and genetic chemistry, the definition of a “Father of Chemistry” may continue evolving. The next revolutionary figure in chemistry might not be a human but an AI-powered system capable of generating chemical innovations independently.
Final Thought: Who do you think deserves the title of the Father of Chemistry? Should we recognize one figure, or should we acknowledge that chemistry has always been a collaborative and evolving field?
Discover More Stories That Shaped Science:
If uncovering the legacy of the father of chemistry sparked your curiosity, you’ll love diving into these groundbreaking moments in scientific history:
🧠 The Father of Physics: Pioneers Who Shaped the Scientific World – From Aristotle to Einstein, explore how the greatest minds redefined our understanding of the universe.
⚡ The War of Currents: Edison vs. Tesla – Step into one of the most electrifying rivalries in science, where innovation, ambition, and ego collided.
🚀 Failed Inventions That Changed the World – Discover how some of history’s biggest flops led to unexpected success and scientific progress.
👩🔬 Top 10 Female Inventors Who Changed the World – Meet the brilliant women behind some of the most influential inventions in science and tech.






