Introduction — What Are Exosomes & Why They’re Buzzing
Exosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles, typically ranging from 30–150 nanometers (sometimes up to 200 nm), that are secreted by nearly all types of cells, including stem cells. Once thought to be just cellular “debris,” exosomes are now recognized as critical messengers in intercellular communication, transporting proteins, lipids, and genetic material such as mRNA and microRNA between cells.
What makes exosomes so exciting in medicine is their unique ability to influence the behavior of recipient cells. Instead of simply transferring molecules, they act like biological delivery systems, regulating processes like inflammation, collagen production, and tissue repair. This is why exosome-based therapies are rapidly emerging as one of the most promising frontiers in regenerative medicine.

Compared to traditional stem cell transplants, exosomes stem cell therapy offers several distinct advantages. Because exosomes are cell-free, they carry a much lower risk of immune rejection or tumor formation while still delivering the same regenerative signals. Studies show that they contain growth factors and signaling molecules that promote tissue healing, reduce inflammation, and stimulate collagen remodeling.
Cosmetic and dermatology fields are particularly interested in exosomes treatment for face rejuvenation. Early clinical applications suggest that exosomes may improve skin texture, reduce fine lines, and accelerate recovery after procedures like microneedling or laser therapy. By harnessing the body’s natural cell-to-cell communication tools, exosome-based therapies represent a next-generation approach to regeneration—smaller, safer, and potentially more powerful than stem cell therapy itself.
How Exosomes in Stem Cell Therapy Work Mechanistically
The therapeutic potential of exosomes begins with their origin. Most clinical research focuses on exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which can be isolated from bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord, or placenta. These stem-cell-derived exosomes carry the molecular “language” of regeneration, making them powerful tools for tissue repair and rejuvenation.
Before they can be used clinically, exosomes undergo isolation and purification. Standard methods include ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion filtration, and more advanced processes like tangential flow filtration, which helps preserve vesicle integrity. Purity is critical—impurities or degraded vesicles can compromise results or trigger immune responses. Current research focuses heavily on refining these purification methods to ensure consistency and safety.
Once purified, exosomes reveal their therapeutic cargo: a complex mixture of proteins, lipids, growth factors, antioxidants, and nucleic acids such as miRNA and mRNA. This cargo enables them to modulate cellular pathways involved in inflammation, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix remodeling (BioMed Central). For example, certain microRNAs in exosomes have been shown to reduce oxidative stress and promote collagen synthesis—key processes for skin rejuvenation and wound healing.
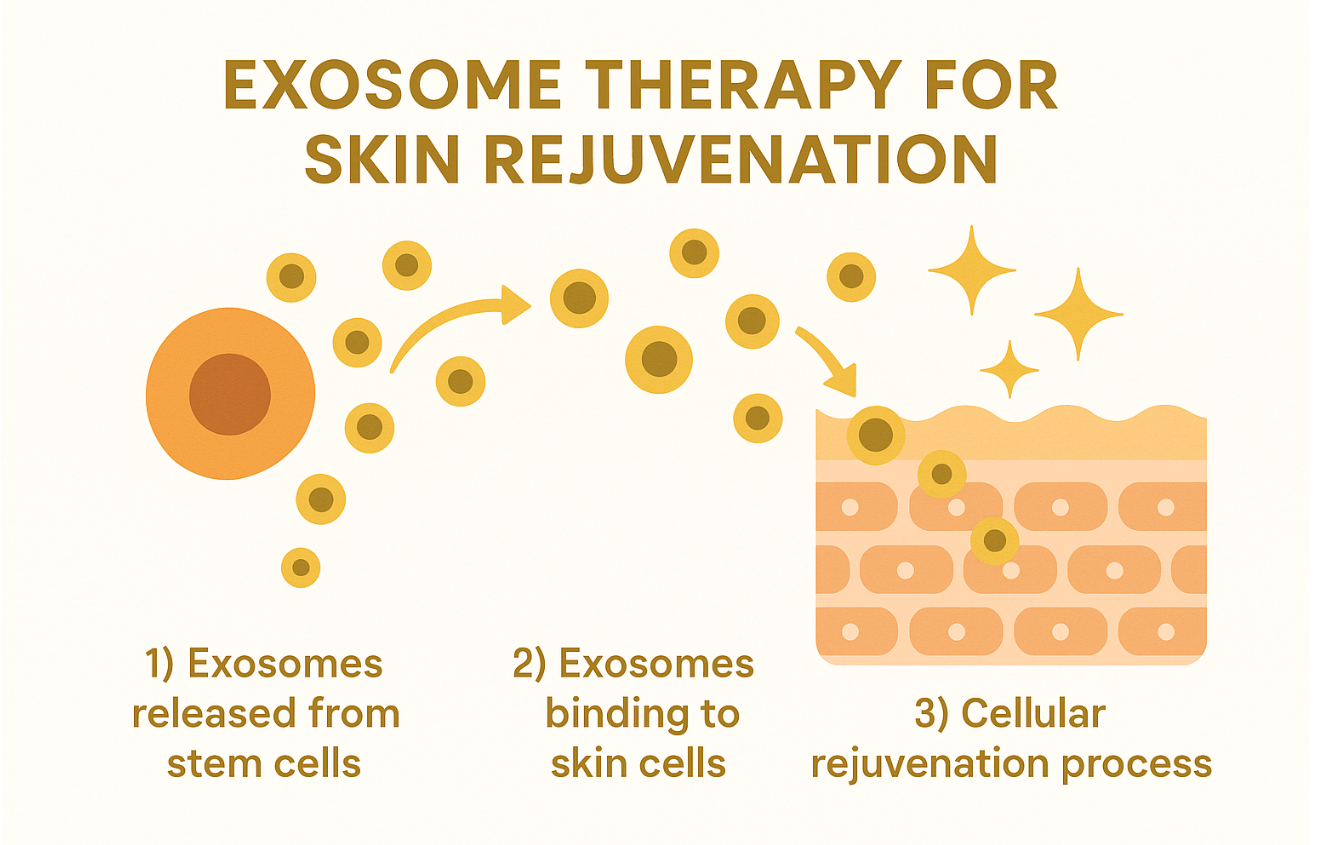
Delivery routes are tailored to the treatment goal. For regenerative dermatology, the most common methods are topical application combined with microneedling or direct intradermal injections, which allow exosomes to penetrate deeper skin layers. Clinical trials in other areas also explore intravenous and localized injections for systemic conditions. In aesthetic medicine, exosomes treatment for face via microneedling is gaining popularity, as it maximizes absorption and stimulates natural repair mechanisms simultaneously (e-exosomes.com).
By combining their regenerative cargo with precise delivery strategies, exosomes stem cell therapy offers a versatile, cell-free solution for both medical and cosmetic applications. Whether accelerating wound healing, reducing inflammation, or rejuvenating aging skin, exosome-based therapies are showing strong potential to transform the future of regenerative medicine.
Clinical Evidence: Exosomes Treatment for Face & Skin Rejuvenation
Clinical research into exosomes treatment for face and skin rejuvenation is growing rapidly, with several early trials showing promising outcomes in terms of safety, efficacy, and visible results. Unlike traditional skincare ingredients that act only on the surface, exosome-based formulations work at a cellular level to stimulate repair, improve barrier function, and encourage collagen production.
One well-cited split-face clinical trial tested an adipose-derived stem cell (ASC) exosome formulation against a placebo. Participants applied the treatment to only one side of the face, with the other side serving as control. Results revealed a measurable reduction in melanin content, leading to visible skin brightening compared to placebo. This demonstrated that exosomes can directly influence pigmentation pathways and even skin tone (MDPI).
Another study focused on women with sensitive skin. A group of 22 participants received treatments with human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC)-derived exosomes. Over several weeks, the trial reported clear improvements: enhanced skin barrier function, reduced roughness, decreased erythema (redness), and notably improved hydration levels. These findings point to exosomes’ ability to restore skin health by modulating inflammation and improving protective barriers.
A pilot clinical study published in Lippincott Journals investigated the combination of microneedling with stem cell-derived exosomes. Patients experienced significant improvements in skin texture, elasticity, and pore size reduction. Fine lines and wrinkles also showed visible softening. Because microneedling creates controlled micro-injuries, it enhances exosome penetration, delivering growth factors and RNA cargo deeper into the dermis where collagen remodeling occurs.
What Improvements Are Observed?
- Reduction in fine lines and wrinkles
- Visible improvement in skin elasticity and firmness
- Lightening of pigmentation spots and evening of tone
- Reduction in pore size and roughness
- Strengthening of the skin barrier and hydration levels
Timeline of Effects
Most patients begin to notice improvements within 2–4 weeks, with more dramatic changes in 3–6 months, as collagen synthesis and dermal remodeling are gradual processes. Unlike fillers or Botox, exosome results are subtle but long-lasting, reflecting real biological change.
Safety Profile
Across published trials, exosome-based therapies have been reported as generally safe with minimal side effects. Some patients experience mild redness, irritation, or swelling after microneedling-based delivery, but these resolve quickly. Importantly, no major immune reactions or systemic complications have been reported so far, reinforcing the appeal of exosomes stem cell therapy as a safer alternative to traditional cell-based interventions.
Together, these studies indicate that exosomes treatment for face offers a scientifically grounded, biologically active approach to skin rejuvenation—one that is both safe and effective when applied under clinical supervision.
Benefits vs Risks: What Stem Cell Exosomes Offer & Caveats
While exosome-based therapies are attracting global attention, it’s important to weigh their benefits and risks before widespread adoption.
Benefits of Exosome-Based Therapies
- Non-cellular therapy – Unlike stem cell transplants, which carry risks of uncontrolled growth or tumor formation, exosomes stem cell therapy is cell-free, reducing the chance of malignant transformation while retaining regenerative benefits.
- Good biocompatibility – Exosomes naturally exist in the human body and exhibit low antigenicity, meaning they are unlikely to trigger immune rejection or allergic reactions.
- Multipronged action – Their cargo contains antioxidants, anti-inflammatory molecules, and collagen-inducing growth factors, offering a holistic regenerative effect. Unlike single-target treatments, exosomes act across multiple pathways, improving pigmentation, elasticity, and hydration simultaneously.
Risks & Limitations of Exosome Therapies
- Lack of standardization – Not all exosome preparations are created equal. Variables such as stem cell source, isolation method, and dosage can significantly affect results. Current studies highlight that purity and consistency remain a challenge (PubMed).
- Regulatory concerns – Many stem cell clinics are already offering exosomes treatment for face without regulatory approvals. Reports in The Guardian highlight that such unregulated use raises safety and ethical concerns, particularly in markets where oversight is weaker.
- Variable results – While some patients report dramatic rejuvenation, others see only mild or temporary improvements. Studies published in MDPI note that long-term efficacy and durability of results are still under investigation.
Balanced Perspective
The evidence so far suggests that exosomes stem cell therapy represents a powerful new frontier in regenerative dermatology and medicine. However, without global regulatory guidelines and standardized production methods, outcomes may vary significantly between providers. For now, patients should seek treatments in reputable, research-backed clinics and remain cautious of exaggerated claims.
How Exosomes for Face Are Applied: Procedures & Best Practices
Exosomes treatment for face can be administered through several delivery methods, each designed to maximize absorption and effectiveness. The most common approach is topical application in serum form, where exosome-rich solutions are applied directly to the skin after cleansing. However, simple topical use often faces absorption limitations, so pre-treatments are used to enhance results.
A popular clinical approach involves microneedling combined with exosome serums. Microneedling creates controlled micro-channels in the skin, allowing exosomes to penetrate deeper into the dermis where collagen production and cellular repair occur. Some high-end medical spas also offer exosome facials, which combine exfoliation, light therapy, or microcurrent devices with exosome serums for comprehensive skin rejuvenation (e-exosomes.com). In regulated clinical settings, microinjections or intradermal delivery may also be performed to achieve targeted outcomes, though these are less common and require physician supervision.
Pre-treatment steps such as gentle exfoliation or microneedling are considered important enhancers since they improve the skin’s permeability and increase exosome uptake.
Session Frequency & Results
- Topical regimens: often recommended daily or twice daily for several weeks.
- Clinical procedures: typically involve 3–4 sessions spaced one month apart.
- Visible improvements: many studies report noticeable changes in hydration, elasticity, and pigmentation within ~4 weeks, with further benefits developing over several months.
By following evidence-based protocols, patients maximize the rejuvenation potential of exosome-based therapies while minimizing risks.
Exosomes Stem Cell Therapy Beyond Face: Other Therapeutic Areas
While exosomes stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in facial rejuvenation, research shows that its benefits extend to a wide range of therapeutic and regenerative applications.
Hair Regeneration & Alopecia
One of the most exciting emerging uses is in hair restoration. Early clinical trials suggest that exosome injections into the scalp can stimulate dormant follicles, improve blood supply, and encourage new hair growth in patients with androgenetic alopecia or thinning hair. Unlike traditional transplants, exosome therapy is minimally invasive and may complement PRP (platelet-rich plasma) treatments.
Wound Healing & Scar Remodeling
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells have demonstrated strong wound-healing properties. Studies show they accelerate closure of chronic wounds, reduce scarring, and promote angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation). This makes them particularly promising for burn victims, diabetic ulcers, and surgical scars. Their ability to modulate inflammation and stimulate collagen remodeling helps produce smoother, more functional skin during recovery.
Skin Disease Management
Exosomes are also under investigation for dermatological conditions such as psoriasis, vitiligo, and atopic dermatitis. In these cases, exosomes’ immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties help reduce flare-ups and restore healthy skin barrier function. For example, in psoriasis models, exosome therapy reduced inflammatory cytokine activity, while in vitiligo research, it has shown potential for stimulating melanocyte activity and repigmentation.
Broader Implications
Beyond dermatology, researchers are studying exosome-based therapies for neurological diseases, cardiovascular repair, and orthopedic regeneration — but in aesthetics and dermatology, they already represent one of the most clinically relevant frontiers of regenerative medicine.
In summary, exosomes treatment for face is only the beginning. With expanding clinical trials, exosome-based therapies could soon become mainstream options for hair loss, scar management, and chronic skin diseases, making them a cornerstone of future regenerative care.
Regulatory, Ethical, & Safety Landscape
The regulatory status of exosome-based therapies is currently complex and uneven worldwide. In the cosmetic sector, many exosome serums and topical formulations are sold as skincare products without stringent oversight. Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, these formulations often bypass rigorous clinical testing, especially in regions like the U.S., where they may be marketed under “cosmetic” labels rather than medical ones. However, countries such as the UK and those in the EU have implemented stricter guidelines, with some outright banning or restricting human-cell–derived exosome products due to safety and ethical concerns.
Quality assurance is another pressing issue. Exosomes are nanoscale vesicles isolated from stem cells, and ensuring their purity, potency, and stability is challenging. Studies point to risks of contamination, batch-to-batch variability, and degradation during storage or transport. Without standardized manufacturing and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) conditions, product consistency remains questionable.
Ethical sourcing of stem cells also plays a key role. Questions of donor consent, traceability, and whether fetal or embryonic sources are used are debated within the scientific and bioethics community. GMP-certified labs using adult stem cell–derived exosomes are generally preferred, as they align with higher ethical standards.
Ultimately, while exosomes stem cell therapy holds promise, regulatory clarity, improved manufacturing processes, and ethical transparency are critical for ensuring both safety and public trust.
FAQs
What is exosome-based therapy?
Exosome-based therapies use extracellular vesicles—tiny messengers naturally secreted by stem cells—to deliver proteins, RNA, and growth factors to recipient cells. These vesicles help regulate inflammation, promote tissue repair, and stimulate cell regeneration. In skincare, this translates into improved hydration, collagen stimulation, and potentially anti-aging effects.
How do exosomes stem cell therapy work?
Exosomes stem cell therapy works by mimicking the body’s natural cellular communication system. When applied topically or delivered via microneedling, exosomes penetrate the skin and signal resident cells to increase collagen and elastin production, reduce oxidative stress, and accelerate healing. In regenerative medicine, they also promote angiogenesis (new blood vessel growth) and reduce inflammation in injured tissues.
Are exosomes treatment for face safe and effective?
Current evidence suggests that exosomes treatment for face is generally safe when sourced ethically and manufactured under sterile, quality-controlled conditions. Small-scale studies and clinical experiences show improvements in skin texture, reduced pigmentation, and fewer wrinkles. However, because long-term safety data is still lacking, regulatory authorities remain cautious.
How long do results last after using exosomes on skin?
Visible improvements often begin within 4–6 weeks of consistent treatment. Results such as smoother skin, reduced wrinkles, and improved elasticity may last 3–6 months, depending on the individual’s skin type, age, and lifestyle. Maintenance treatments or daily topical applications are often recommended for sustained benefits.
Can exosomes reverse wrinkles and pigmentation?
Exosomes show potential in reducing fine lines, wrinkles, and pigmentation by promoting collagen synthesis and regulating melanin production. While they may not “reverse” aging entirely, clinical reports suggest significant visible rejuvenation compared to traditional serums. However, effectiveness varies, and more controlled trials are needed to confirm these claims.
Conclusion & What More Research Is Needed
Exosome-based therapies represent one of the most exciting frontiers in regenerative medicine and skincare. By leveraging the body’s natural communication system, exosomes offer a non-invasive, biologically active way to promote tissue repair, facial rejuvenation, and potentially broader therapeutic applications such as wound healing and hair regeneration. Early studies show that exosomes treatment for face can improve skin texture, hydration, and elasticity, making them a promising alternative to traditional anti-aging approaches.
However, many questions remain unanswered. Long-term safety, standardized dosing protocols, and large-scale randomized controlled trials are still lacking. Regulatory clarity and ethical sourcing of stem cells must also be addressed before exosome products can become mainstream medical treatments rather than niche or cosmetic options.
For students, clinicians, or beauty enthusiasts interested in this field, it’s worth following ongoing clinical trials, scientific reviews, and regulatory updates. As research progresses, exosome-based therapies could reshape the future of dermatology and regenerative medicine—but cautious optimism and rigorous science are key to unlocking their full potential.
✨ Interested in more breakthroughs reshaping modern medicine and biotech? Explore these fascinating reads next:
-
💉 Promising Results of the mRNA Cancer Vaccine in Trials – How personalized RNA therapies are changing the future of oncology.
-
🔷 Methylene Blue: Bridging Medicine and Future Technology – The century-old compound making a comeback in neuroscience and anti-aging research.
-
☢️ Terbium-161: Advancing Nuclear Cancer Therapy – A powerful isotope offering precision-targeted radiotherapy for hard-to-treat tumors.
-
🧬 AI-Designed Proteins: esmGFP and Evolutionary Simulation – How artificial intelligence is creating brand-new proteins never seen in nature.
👉 Check them out to discover how science, technology, and innovation are redefining the limits of human health.