Introduction: Why Industries Are Turning to Rooftop Solar
Industries are under increasing pressure to reduce operating costs and meet sustainability targets. One of the most effective ways to achieve both is by adopting a solar system for factories. With electricity bills consuming a significant portion of operational expenses, factory owners are now exploring rooftop solar for manufacturing units as a cost-effective and long-term solution.
The shift is also driven by Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals and carbon neutrality commitments. Transitioning to rooftop solar for manufacturing units helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhances the company’s green image in front of investors and customers.
What makes this shift even more appealing is the opportunity to utilize idle rooftop space, turning it into a power-generating asset. A well-planned solar system for factories not only slashes electricity bills but also future-proofs the business against rising energy costs.
📌 Stat: In 2024, India added over 2.5 GW of new industrial rooftop solar capacity, while the USA witnessed a 30% year-over-year increase in similar installations — highlighting the global momentum toward clean industrial energy.
What Is an Industrial Rooftop Solar System?
An industrial rooftop solar system is specifically designed to meet the high energy demands of factories, warehouses, and large-scale production units. Unlike residential systems, rooftop solar for manufacturing units involves higher capacity, more complex wiring, and specialized components to support industrial-grade equipment.
These systems are typically installed on the rooftops of production plants, fabrication units, or CNC machining workshops. A standard solar system for factories can range from 100 kW to several megawatts, depending on the site’s connected load and power usage patterns.
Key areas where rooftop solar for manufacturing units prove effective include running energy-intensive machines like chillers, air compressors, furnaces, extrusion lines, and injection molding systems. This not only ensures continuous power supply but also significantly lowers peak demand charges from the utility grid.
In short, a solar system for factories transforms underused industrial rooftops into active revenue-saving resources, delivering both financial and environmental returns.
Core Components of an Industrial Solar Setup
To fully understand how solar panels work in industry, it’s essential to break down the key components of a typical industrial rooftop solar system. Each part plays a crucial role in ensuring efficiency, durability, and real-time visibility of performance.
Solar Panels
Solar modules are the core component of the system. These are typically high-efficiency monocrystalline panels designed to capture maximum sunlight. To understand how solar panels work in industry, know that they convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity using the photovoltaic effect — forming the starting point of the entire energy flow.
Inverters
Since industrial machines run on alternating current (AC), inverters are used to convert the generated DC into usable AC. Depending on plant size and load distribution, factories may opt for central inverters (for large setups) or string inverters (for modular control). Their selection is crucial to how smoothly solar panels work in industry.
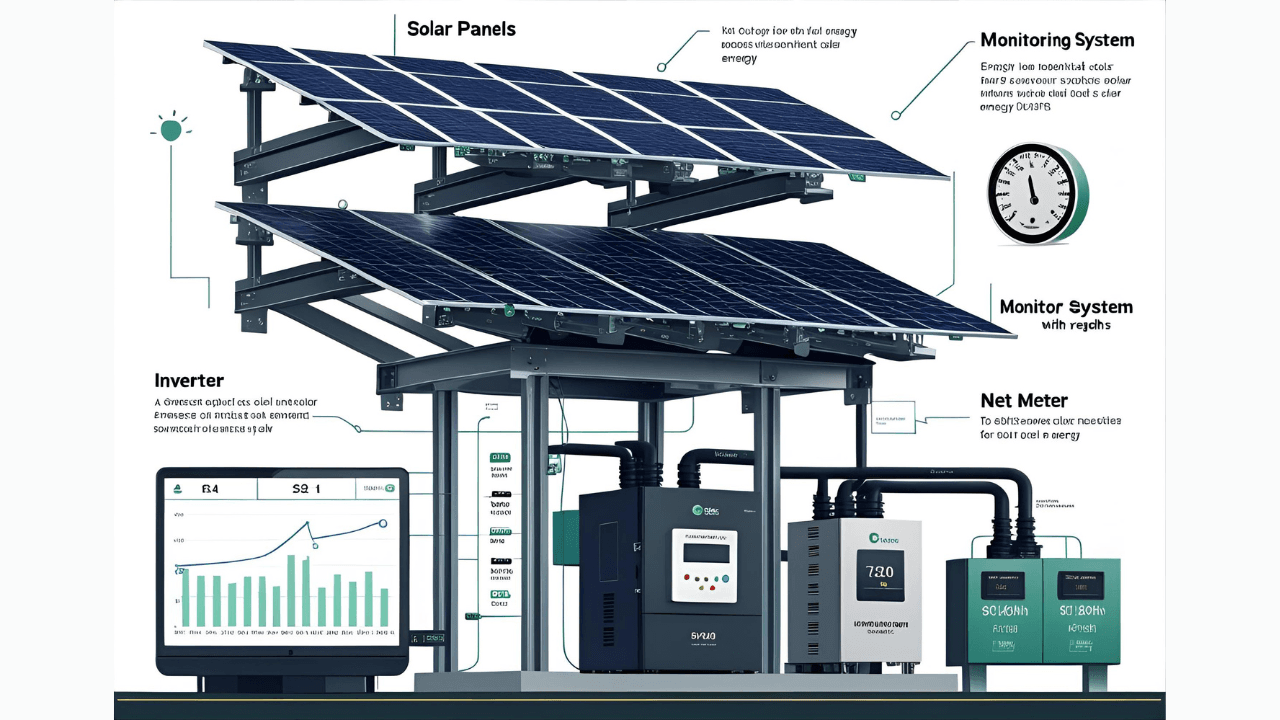
Mounting Structures
Industrial rooftops often experience harsh weather conditions and structural variations. Mounting systems are typically made of anti-corrosive, galvanized materials with wind-load resistance to protect solar panels and ensure durability.
Monitoring System
Modern systems include IoT-based dashboards or SCADA software that let factory owners track power generation, consumption, export-import ratios, and fault alerts in real time — critical for optimizing energy usage.
Net Meter
It monitors the extra electricity you send back to the grid. It’s a legal requirement in many regions and is vital for maximizing ROI through net metering benefits.
How the System Works: Step-by-Step Process
To grasp how solar panels work in industry, here’s a step-by-step walkthrough of how energy flows from sunlight to your factory equipment:
- Sunlight Absorption
Solar panels on the factory roof capture sunlight. Through the photovoltaic effect, solar cells convert light into direct current (DC) electricity. - DC Generation
This raw DC power is collected and channeled via cables into the inverter system. The energy output depends on the sunlight intensity and panel efficiency. - Inverter Conversion
Inverters convert the DC power into alternating current (AC), which is compatible with your industrial machines and electrical systems. - Energy Distribution
The AC electricity flows into your factory’s main distribution board, powering equipment like chillers, compressors, or CNC machines. - Net Metering (if applicable)
When production exceeds consumption (like on weekends or holidays), surplus electricity is exported to the grid. The net meter records these units, helping you earn credits on your electricity bill.
📌 Example Scenario:
Imagine a CNC workshop with three machines and 120 kW connected load. After installing a 100 kW solar system, it now operates at 60–70% solar utilization during peak sunlight hours, significantly reducing grid reliance and cutting down monthly bills by over ₹60,000 ($720).
Costs and Savings Explained
If you’re considering setting up a large-scale solar system for your factory, understanding the costs and returns is key to making an informed decision.
💰 Installation Cost Overview
- In India, the average cost of setting up large-scale solar systems (100 kW and above) ranges between ₹35–₹45 per watt, depending on material quality, site complexity, and vendor.
- In the USA, costs range from $0.70 to $1.00 per watt, influenced by regional labor rates, incentives, and utility policies.
📈 Payback Period and ROI
- Typical payback period: 2–4 years
- Annual ROI: 15–25% based on load profile and solar irradiance
- Long-term benefit: Free electricity for 20+ years after payback
📌 Sample Savings Table:
| Plant Size | India (₹) | USA ($) | Payback | Yearly Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 kW | ₹40L | $90K | 3 yrs | ₹13L / $16K |
| 250 kW | ₹1 Cr | $210K | 2.5 yrs | ₹33L / $38K |
| 500 kW | ₹2 Cr | $400K | 2 yrs | ₹65L / $75K |
📌 Pro Tip: Solar is a capital-heavy investment upfront, but once recovered, the free energy and tax incentives make it an unmatched long-term asset.
Financing Options for Industrial Solar Plants
Worried about upfront costs? Here’s how to install a solar system for factories without straining your finances.
✅ 1. CAPEX Model (Capital Expenditure)
Paying the full amount upfront gives you complete ownership—every saving and incentive benefits your business directly.
💼 2. RESCO/OPEX Model (Operating Expenditure)
A third-party owns the system, and you pay only for the electricity you use. Ideal for companies that want zero capital investment.
🔒 3. Power Purchase Agreement (PPA)
You sign a long-term agreement (10–25 years) to buy solar electricity at a pre-fixed rate, which is often lower than grid tariffs.
🎯 Available Incentives
India:
- Central Financial Assistance (CFA) under MNRE
- The system must comply with ALMM (Approved List of Models and Manufacturers) guidelines.
USA:
- Eligible for a 30% Investment Tax Credit (ITC) as per the Inflation Reduction Act.
Best-Suited Industries for Industrial Rooftop Solar
Not all industries are solar-ready — but these ones can benefit immediately from installing a solar system for factories.
🏭 Industries that Benefit the Most
- Textile & Apparel Units
High daytime energy loads make them ideal for solar offsetting. - Auto Component Manufacturing
Consistent usage patterns help achieve quicker ROI. - Cold Storage & Logistics Hubs
Perfect for warehouse solar installations — continuous cooling and lighting loads demand uninterrupted power. - Pharmaceuticals & Chemical Plants
If your area suffers frequent outages, solar not only keeps the power on but also lowers your energy bills - Educational & Research Campuses
High electricity usage during day + rooftop space = perfect solar opportunity.
📌 Bonus Insight: Many warehouse solar installations now combine solar with battery storage to handle night-time or blackout usage.
Installation Timeline & Process
Smooth execution is crucial when setting up a large-scale solar system. The process is designed to minimize downtime for factories and ensure timely returns.
📌 Timeline Breakdown:
| Step | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Site Visit & Feasibility Study | Evaluate rooftop strength, sun hours, and shadow analysis |
| Week 2–3 | System Design & Engineering | Layout planning, load calculations, inverter sizing |
| Week 4 | Regulatory Approvals | DISCOM net metering, CEIG inspection, state-level permissions |
| Week 5–8 | Installation & Commissioning | Panel mounting, wiring, inverter setup, testing |
Whether you’re planning rooftop solar or setting up a large-scale solar system on industrial land, timelines may vary based on project size and location. Faster commissioning means quicker ROI—one of the key reasons businesses prefer turnkey providers for setting up large-scale solar systems.
FAQs: Industrial Solar for Beginners
New to solar? Here are answers to the most frequently asked questions about rooftop solar for manufacturing units:
Q: Do I need a battery backup?
A: Not if you’re going for an on-grid system. Rooftop solar for manufacturing units typically uses net metering to offset power usage in real time.
Q: What if I relocate my factory?
A: Your rooftop solar for manufacturing units can be dismantled and moved, though reinstallation costs apply.
Q: Is my rooftop strong enough?
A: Most industrial buildings can support solar panels, but a structural audit is mandatory before installing rooftop solar for manufacturing units.
Q: Can my factory run 100% on solar?
A: Depends on roof size and daily load. While complete offset is rare, 40–80% coverage is typical for rooftop solar for manufacturing units.
Conclusion
A solar system for factories is not just an energy upgrade—it’s a long-term strategic investment. From lowering operational costs to meeting ESG benchmarks, solar adoption is accelerating across industries.
Whether it’s a CNC machine shop or a warehouse solar installation, solar offers:
- Savings of up to 70% on power bills
- Low maintenance and high lifespan
- Better utilization of unused rooftop assets
- Faster ROI, especially for energy-intensive industries
✅ A warehouse solar installation can slash energy costs in logistics hubs by over 60%, while a solar system for factories gives production units predictable power at low cost.
👉 Call to Action:
Book your free solar site audit today. Want a custom ROI estimate for your warehouse solar installation or factory? Let our experts guide you!
Ready to explore the next wave of solar innovations?
After understanding how industrial rooftop solar systems work, we highly recommend diving into these breakthrough technologies:
- DualSun Hybrid Solar Panels: Discover how DualSun is redefining efficiency by combining solar electricity and water heating in one powerful panel.
- AuREUS Solar Panels are Changing Renewable Energy: See how this award-winning solar tech captures UV rays—even without direct sunlight—to generate electricity from windows and walls.
- SolarWindow: Revolutionising Smart Building Technology: Explore how transparent solar coatings are turning glass surfaces into power-generating assets for commercial buildings.