Introduction to Nano Radio Technology
What is a Nano Radio?
A nano radio is an ultra-miniature radio receiver that operates at the nanoscale, utilizing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene to detect, amplify, and demodulate radio signals. Unlike conventional radios that rely on silicon-based circuits, nano radios function using a single carbon nanotube, making them incredibly compact, energy-efficient, and ideal for nanoscale communication systems.
The History and Development of Nano Radios
This technology emerged from groundbreaking research at UC Berkeley, where scientists first demonstrated how a carbon nanotube could act as both an antenna and an amplifier for radio signals. Since then, advancements in nanoelectronics and molecular engineering have pushed Atomic-scale Radios toward practical applications, from ultra-low-power wireless sensors to medical implants and secure communications.
How Nano Radios Work at the Nanoscale
The carbon nanotube in a Atomic-scale Radio acts as a mechanical resonator. When an external radio frequency (RF) wave hits the nanotube, it causes mechanical vibrations that modulate an electrical signal. Unlike traditional radios that require multiple components for signal processing, a nano receiver can directly demodulate signals, enabling extreme miniaturization and efficiency.
Nano radios have the potential to revolutionize telecommunications, medical diagnostics, and smart IoT networks, paving the way for a future where ultra-small, energy-efficient receivers facilitate real-time wireless communication at the atomic scale.
How Nano Radios Work
Fundamental Physics Behind Nano-Scale Radio Wave Detection
Atomic-scale Radios operate on the principles of nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), where mechanical vibrations at the atomic scale interact with electromagnetic waves. Unlike conventional radios that use circuits to process signals, a nano receiver relies on physical oscillations induced by radio frequency (RF) waves. When an RF signal hits a carbon nanotube, it vibrates at a frequency corresponding to the incoming signal, converting it into an electrical response.
Role of Carbon Nanotubes and Quantum Mechanics in Nano Receiver Technology
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are the core component of a Atomic-scale Radio Device due to their exceptional electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and quantum properties. Their ability to act as an antenna, tuner, and demodulator in a single structure eliminates the need for bulky electronic components.
Key quantum mechanical effects that enhance nano radios:
- Ballistic transport: Electrons travel through CNTs with minimal resistance, improving efficiency.
- Quantum confinement: The nanotube’s diameter determines its resonance frequency, allowing precise tuning of radio signals.
- Nanoscale mechanical oscillations: Unlike traditional circuits, nano receivers use mechanical motion to modulate signals, reducing energy consumption.
Differences Between Conventional and Nano Receivers
| Feature | Conventional Radio Receiver | Nano Radio Receiver |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Millimeter to centimeter scale | Nanometer-scale |
| Signal Processing | Uses capacitors, transistors, and circuits | Directly demodulates signals via nanotube vibration |
| Power Consumption | Requires external power | Operates at ultra-low power levels |
| Tuning Mechanism | Electronic tuning via capacitors | Mechanical tuning via nanotube resonance |
Nano radios represent a breakthrough in wireless communication, offering miniaturization, energy efficiency, and novel quantum-based signal processing. These advances position nano receivers as a key technology for next-gen IoT devices, biomedical implants, and ultra-secure quantum networks.
Key Applications of Nano Radio Technology
Medical Diagnostics & Implantable Devices
Nano radios have the potential to revolutionize bioelectronics by enabling wireless communication within the human body. Their nanoscale size makes them ideal for implantable medical devices, such as:
- Smart biosensors that monitor glucose levels or detect early signs of disease.
- Wireless neural implants for brain-computer interfaces and prosthetics.
- Targeted drug delivery systems that respond to remote commands.
Because nano receivers require minimal power, they can function inside the body without frequent battery replacements.
IoT & Smart Sensors
The Internet of Things (IoT) benefits from ultra-low-power nano radios, allowing seamless integration into smart homes, industrial automation, and environmental monitoring systems. Atomic-scale Radio Devices enhance:
- Smart agriculture by enabling real-time soil and crop monitoring.
- Industrial automation with sensors in factories and supply chains.
- Energy-efficient smart homes, where nano-scale sensors regulate lighting, temperature, and security.
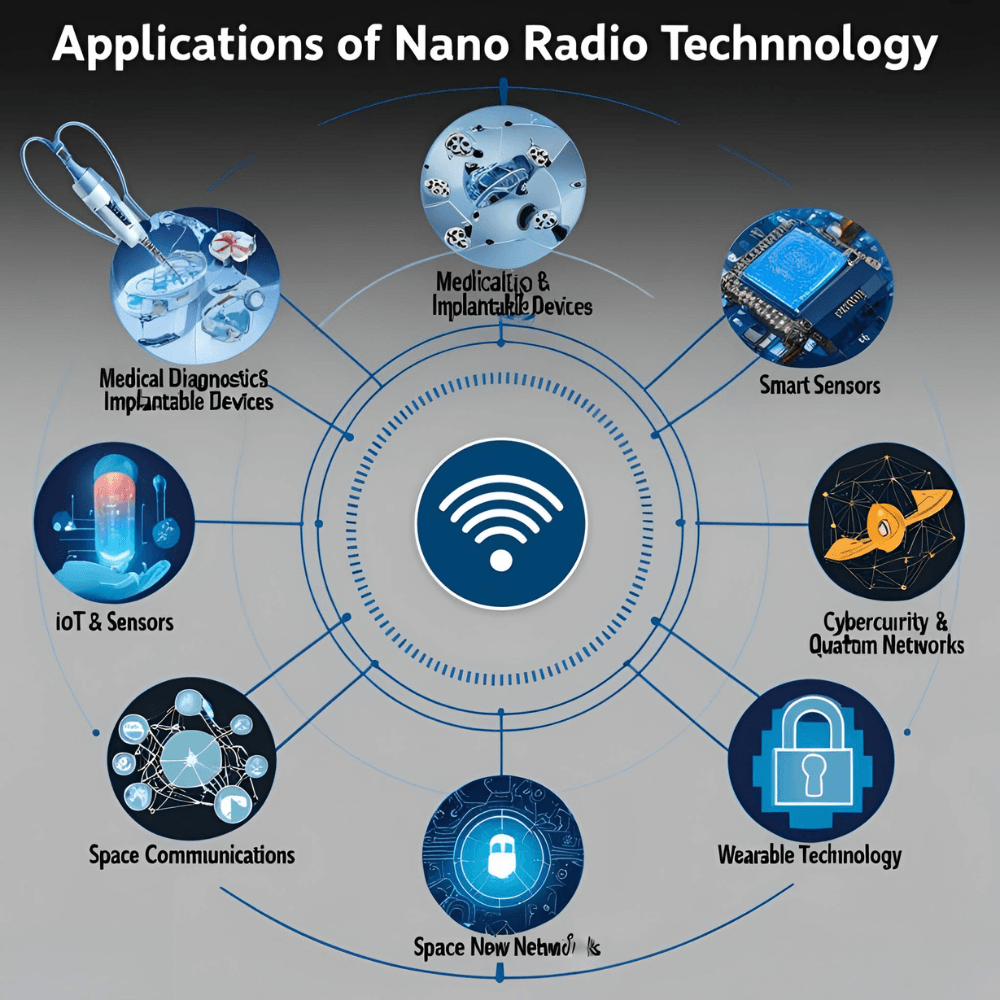
Space Communications
Nano radios could play a crucial role in deep space exploration by offering lightweight, energy-efficient communication systems for interstellar probes. Their small size enables:
- Reduced payload weight for satellites and spacecraft.
- Low-power operation, essential for long-term deep space missions.
- Quantum communication advancements, allowing secure, long-distance data transfer.
Cybersecurity & Quantum Networks
Nano-scale radio waves hold promise for secure communications and encrypted data transfer in emerging quantum networks. They can be applied in:
- Quantum cryptography, where nano radios enable tamper-proof communication.
- Stealth communications, using ultra-miniature devices for military and intelligence operations.
- Secure IoT networks, preventing cyberattacks on connected devices.
Wearable Technology
Nano radios are set to transform next-generation wearable devices, including:
- Smartwatches with ultra-efficient, always-on connectivity.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) headsets with ultra-low-latency communication.
- Smart textiles, embedding nano receivers into clothing for health tracking.
By enabling miniaturized, energy-efficient wireless communication, nano radio applications will shape the future of healthcare, IoT, space technology, cybersecurity, and wearable devices.
The Role of Nano Receivers in Next-Gen Wireless Networks
Enhancing Wireless Communication Efficiency
Nano receivers redefine wireless communication by enabling miniaturized, ultra-low-power signal processing. These nanoscale devices:
- Reduce energy consumption by eliminating bulky components.
- Improve signal precision using quantum effects for better frequency selectivity.
- Enhance integration into IoT, medical implants, and next-gen connectivity.
Use in 5G and 6G Networks
With 5G and upcoming 6G networks, nano radios offer:
- Faster data transmission via high-frequency signal processing.
- Lower latency, crucial for real-time AI and IoT applications.
- Massive device interconnectivity, allowing seamless communication between billions of sensors.
Challenges at Nano Scales
Despite their advantages, nano receivers face hurdles such as:
- Signal stability issues due to atomic-scale vibrations.
- Limited range, requiring signal repeaters.
- Interference at high frequencies, impacting efficiency in crowded networks.
Nano Radios vs. Traditional Radios: Key Differences
| Feature | Traditional Radios | Nano Radios |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Centimeter-scale | Nanometer-scale |
| Power Consumption | High | Ultra-low |
| Efficiency | Energy-intensive | Highly efficient |
| Tuning Mechanism | Electronic circuits | Mechanical resonance |
| Environmental Suitability | Limited extreme environment usage | Operates in space, bioelectronics, and nanoscale IoT |
Superior Performance in Extreme Environments
Atomic-scale Radio Devices excel in harsh conditions such as:
- Space missions, where their small size reduces payload weight.
- Medical implants, offering seamless bioelectronic integration.
- Military applications, with stealth communication capabilities.
Nano radios could eventually replace large-scale antennas, making wireless systems smaller, more efficient, and sustainable in 6G, AI, and IoT ecosystems.
Challenges & Future Prospects of Nano Radios
Technical Limitations of Nano Radios
Despite their revolutionary potential, nano radios face several technical barriers:
- Sensitivity Issues – Nano receivers must detect extremely weak signals, making them susceptible to external noise and interference.
- Energy Harvesting Challenges – Since they operate at the nanoscale, they require ultra-low-power sources like ambient electromagnetic energy, which limits their functionality.
- Miniaturization Trade-Offs – Reducing size often leads to weaker signal reception and range limitations.
Advancements in Material Science
To overcome these limitations, researchers are leveraging nanomaterials like:
- Graphene-based antennas for ultra-sensitive signal detection.
- Carbon nanotube transistors for improved energy efficiency.
- Molecular-scale components to enhance frequency selectivity and reduce interference.
Predictions for Commercialization
Nano radios are expected to enter mainstream markets within the next decade, particularly in:
- Biomedical devices for wireless health monitoring.
- IoT and smart cities, powering ultra-efficient sensor networks.
- Next-gen wireless communication, including 6G and beyond.
Conclusion: Are Nano Radios the Future of Wireless Communication?
Summary of Nano Radio Advantages
Atomic-scale Radio Devices offer unprecedented miniaturization, energy efficiency, and integration across multiple industries. Their ability to function at the nanoscale makes them ideal for medical implants, secure communications, and space exploration.
Revolutionizing Key Industries
- Medical & Bioelectronics – Wireless implants, biosensors, and neural interfaces.
- IoT & Smart Environments – Seamless connectivity with minimal power usage.
- Space & Quantum Communications – Enabling deep-space missions and next-gen secure networks.
Nano radios represent a paradigm shift in wireless technology, merging quantum mechanics with real-world applications. As material science advances and technical hurdles are overcome, nano receivers will play a crucial role in the future of computing, healthcare, and global connectivity.
Explore More on Radio and Radar Technologies
Curious about the evolution of communication and detection systems? Check out these related articles:
🔹 Invention of the Radio – Discover how early radio technology shaped modern wireless communication.
🔹 How Does Sonar Work? – Learn about sonar systems and their applications in underwater exploration.
🔹 The Invention of Radar – A deep dive into how radar technology revolutionized military and aviation systems.
🔹 Quantum Radar Technology – Explore the future of radar with quantum advancements for enhanced detection.