Introduction: The Rise of Airborne Wind Turbine
As the global demand for renewable energy soars, conventional wind turbines face significant limitations. Traditional onshore and offshore wind farms require substantial land, expensive infrastructure, and are constrained by wind patterns that are weaker at lower altitudes. Moreover, they are often impractical in remote regions and offshore deep waters where installation and maintenance costs are prohibitively high.
This is where airborne wind energy (AWE) enters the picture. Airborne wind turbines leverage high-altitude wind power—where wind speeds are stronger and more consistent—to generate electricity more efficiently. These flying turbines, whether in the form of tethered kites, drones, or helium-filled aerostats, can harness energy from kites at altitudes of 300-500 meters or more, delivering greater power output with significantly lower material costs.

Game-Changing Innovation in Airborne Wind Turbines
Several leading companies are pushing AWE technology forward, including:
- Altaeros Energies, developing helium-lifted airborne wind turbines.
- Makani (Google X), which explored kite-based wind power before discontinuing operations in 2020.
- Kitekraft, which is innovating in autonomous drone-based wind energy systems.
Why Now? The Tech Breakthroughs Enabling AWE
While the concept of airborne wind turbines has been explored for decades, recent breakthroughs in AI-driven flight control, lightweight materials, and automation have made these systems commercially viable. AI-powered automation reduces the need for human intervention, and advancements in composite materials have enhanced durability. Additionally, new software-driven optimization models ensure that airborne turbines maximize power generation by dynamically adjusting to wind conditions.
How Do Airborne Wind Turbines Work?
Tethered Flight: The Core of AWE Technology
Unlike traditional wind turbines fixed to the ground, airborne wind turbines float or fly at high altitudes while being tethered to a ground station. These tethers not only keep the system stable but also serve as conduits for transmitting electricity back to the grid. The core working principle relies on capturing wind energy from high altitudes, where airborne wind energy technology benefits from:
- Stronger and more stable winds.
- Higher energy density, allowing for better efficiency.
- Lower material costs since towers and foundations are eliminated.
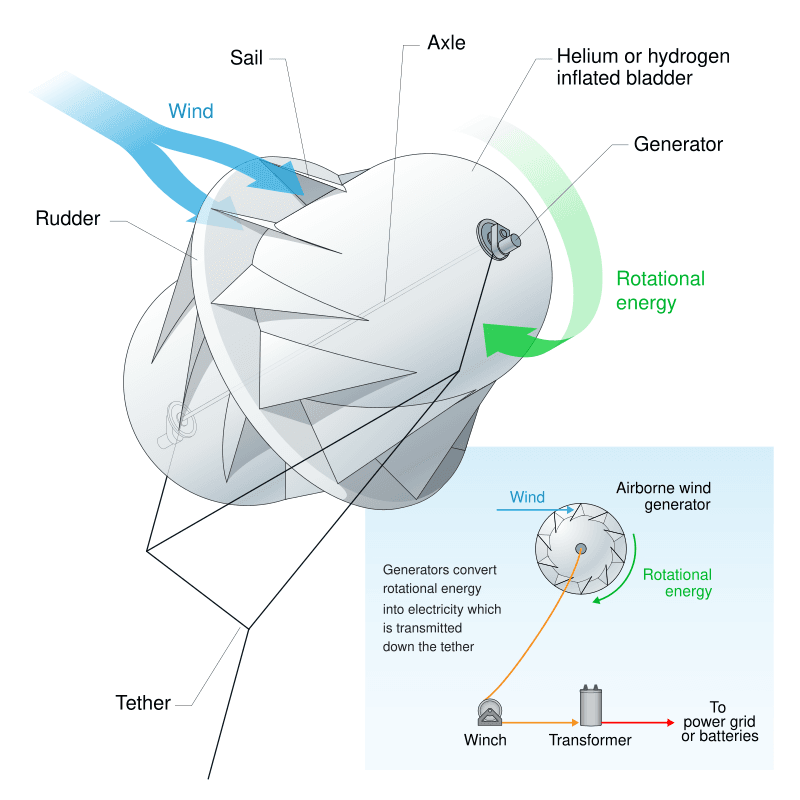
Types of Airborne Wind Turbines
Different AWE designs have emerged, each with unique advantages:
Tethered Balloon-Style Turbines
- Example: Altaeros Energies’ BAT (Buoyant Airborne Turbine).
- Uses helium-filled aerostats with built-in turbines to generate power.
- Can be deployed quickly in remote locations, ideal for disaster relief and off-grid areas.
Kite-Based Wind Energy Systems
- Example: Makani Power’s Kite-Turbines (discontinued but influential).
- Rotors mounted on flying kites generate electricity, which is transmitted via the tether.
- Can operate at altitudes of 300m+, capturing winds more effectively than traditional turbines.
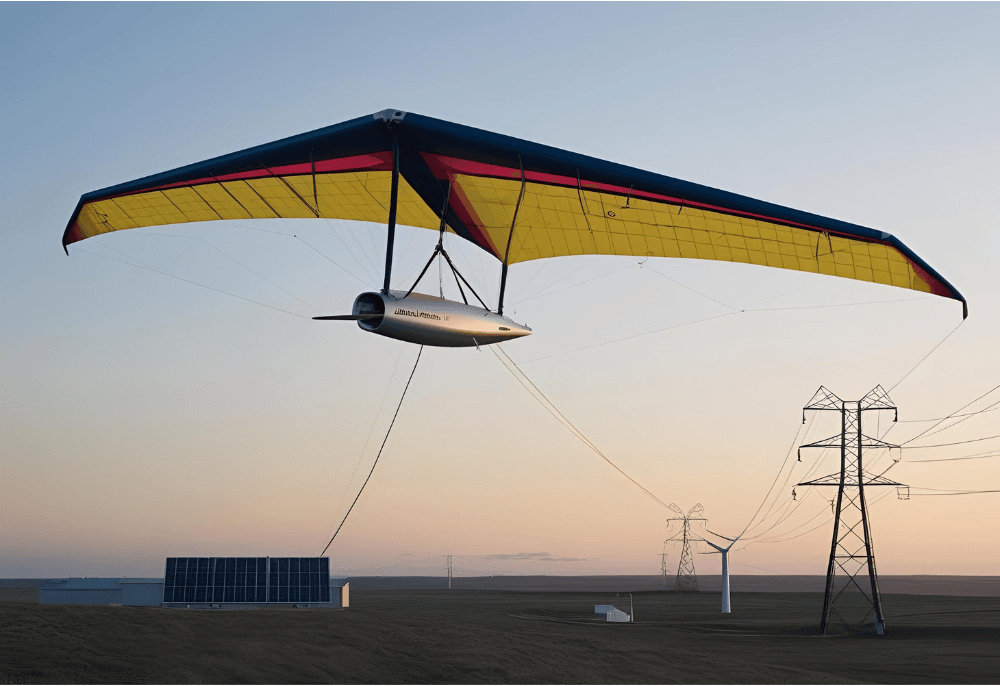
Autonomous Drone Wind Turbines
- Example: Kitekraft’s autonomous wind drones.
- Small, self-flying turbines that hover at high altitudes, adjusting dynamically to wind conditions.
- AI-driven flight controls optimize power generation.
Physics Behind High-Altitude Wind Power
The key advantage of energy from kites and other airborne turbines is their ability to tap into wind streams at 500+ meters, where wind speeds are 2-3 times stronger than near the ground. Higher altitude winds provide 8-10 times more energy than those captured by traditional turbines. As a result, airborne systems can produce more electricity while requiring less infrastructure.
Why Airborne Wind Turbines Are More Efficient
- Access to Stronger Winds: At 500m altitude, winds are more powerful and reliable compared to the 100m height of conventional wind turbines.
- Less Material Usage: No need for massive towers, reducing steel and concrete requirements.
- Lower Installation & Maintenance Costs: Can be deployed in remote areas without major infrastructure investments.
The Future of Airborne Wind Energy
With companies like Altaeros and Kitekraft making rapid progress, airborne wind turbines are expected to play a crucial role in the future of renewable energy. By 2035-2040, AWE could achieve 40% lower costs compared to traditional wind turbines, making them a viable alternative for powering off-grid regions, deep-sea offshore locations, and even military operations.
Airborne wind energy represents a revolutionary shift in wind power technology. By overcoming the limitations of traditional turbines and harnessing high-altitude wind power, AWE has the potential to provide clean, scalable, and cost-effective energy worldwide. As advancements in AI, automation, and material sciences continue to drive innovation, airborne wind turbines could soon become a mainstream component of our renewable energy future.
Advantages of Airborne Wind Turbines Over Traditional Wind Farms
- Access to Stronger, More Consistent Wind Currents
One of the key advantages of airborne wind energy vs. traditional wind turbines is the ability to capture wind at much higher altitudes (300-600 meters). Wind speeds at these heights are:
- 2-3 times stronger than those at conventional wind turbine heights (80-120 meters).
- More consistent and less intermittent, reducing energy fluctuations.
- Able to generate more electricity with smaller systems, making airborne wind power a high-efficiency alternative.
- Lower Material & Infrastructure Costs
Unlike traditional wind farms, airborne wind turbines do not require large towers, deep foundations, or heavy infrastructure. The benefits of airborne wind turbines in this area include:
- Lower steel and concrete usage, cutting down manufacturing costs.
- Easier transportation and deployment in remote locations.
- Reduced maintenance costs since the system is modular and can be repaired on the ground instead of climbing 100-meter-high towers.
- Faster Deployment in Remote & Offshore Locations
One major benefit of airborne wind turbines is their ability to be deployed virtually anywhere, including:
- Offshore areas, where building traditional turbines is expensive.
- Mountainous or inaccessible regions, where normal wind farms are impractical.
- Temporary power needs, such as disaster relief or military operations, due to their fast deployment and portability.
- Lower Environmental Impact
High-altitude wind power is considered an environmentally friendly alternative to ground-based wind farms because:
- No land disruption – airborne systems do not require land clearing, reducing deforestation and habitat destruction.
- Wildlife-friendly – traditional turbines are known to cause bird and bat fatalities, while airborne wind turbines operate at heights where bird activity is lower.
- Minimal noise pollution – unlike traditional turbines, airborne wind energy systems generate power silently.
- Decentralized Power Generation Potential
Unlike large-scale wind farms, airborne wind energy is scalable and flexible, making it ideal for:
- Islands and remote communities that lack connection to the main power grid.
- Disaster relief operations, where quick, temporary power sources are needed.
- Military applications, where mobile and adaptable power solutions are critical.
With high-altitude wind power efficiency improving rapidly, airborne wind turbines have the potential to outperform traditional wind energy systems in multiple areas.
Challenges & Limitations of Airborne Wind Power
- Technical & Engineering Hurdles
Despite their advantages, airborne wind turbines face engineering challenges that must be solved for large-scale adoption. The biggest airborne wind turbine disadvantages include:
- Durability of tethers – high winds and extreme weather conditions put stress on the tethering system, leading to wear and tear.
- Autonomous flight stability – these systems rely on AI-driven flight control to remain airborne and adjust to wind changes. Crashes or malfunctions can cause significant downtime.
- Regulatory & Airspace Issues
One of the biggest limitations of airborne wind energy is airspace regulation and aviation safety. Key concerns include:
- Interference with aviation routes – airborne wind turbines operate in controlled airspace, which could lead to conflicts with aircraft and drones.
- Government restrictions – many countries have strict regulations on flying structures, making commercial deployment difficult.
- Energy Transmission Difficulties
One of the most overlooked high-altitude wind power challenges is how to efficiently transfer energy from airborne systems to the ground.
- Longer transmission distances require advanced power cables that minimize energy loss.
- Grid integration challenges – many airborne wind energy projects are still in testing phases, making it difficult to assess long-term reliability.
- Weather Dependency
While high-altitude wind power efficiency is high, extreme weather conditions pose a challenge:
- Turbulence and storm risks – hurricanes, thunderstorms, and high turbulence can damage airborne systems.
- Seasonal wind variations – some locations experience inconsistent wind speeds at different times of the year.
The Road Ahead for Airborne Wind Energy
Although airborne wind energy has some challenges, ongoing advancements in AI, automation, and materials are making these systems more reliable and commercially viable. Many companies are working on solutions to overcome the current airborne wind turbine disadvantages, making it an exciting field to watch in the coming years.
Top Companies Developing Airborne Wind Energy Technology
Leading Players & Their Innovations
The airborne wind energy sector is rapidly growing, with several key players pioneering innovative solutions:
- Altaeros Energies – Specializes in floating wind turbine technology, particularly for remote and off-grid applications. Their Buoyant Airborne Turbine (BAT) is designed to reach stronger, steadier winds at higher altitudes.
- Kitekraft – Develops AI-powered kite-based wind energy systems, integrating automation for increased efficiency.
- SkySails Power – Uses large-scale airborne wind kites to harness energy from high-altitude winds, reducing material costs compared to traditional turbines.
- Ampyx Power – Focuses on autonomous airborne wind energy technology, using fixed-wing drones tethered to the ground for energy generation.
- Makani (formerly Google X, now discontinued) – Developed one of the most advanced kite-based wind energy systems, contributing significantly to research in the field.
Other key players in the broader airborne wind energy industry include GE Power, Siemens AG, and Vestas Wind Systems, which are exploring high-altitude wind solutions alongside traditional wind turbine technology.
Cost & Efficiency Analysis: Is Airborne Wind Power Viable?
Installation Costs vs. Traditional Wind Turbines
- Traditional wind turbines require large foundations, extensive infrastructure, and expensive materials, driving up costs.
- Airborne wind turbines eliminate the need for tall towers and heavy machinery, reducing material and installation costs significantly.
Projected Energy Output & Efficiency
- High-altitude wind power is more consistent and stronger than ground-level winds, leading to higher capacity factors.
- While traditional wind farms operate at around 35-45% efficiency, airborne wind energy systems have the potential to reach 50-60% efficiency due to stronger, uninterrupted winds.
Return on Investment (ROI) & Commercial Viability
- Current airborne wind technology is still in early commercial stages, but with ongoing AI and automation advancements, ROI is expected to improve.
- Companies like Kitekraft and SkySails Power aim to achieve cost parity with conventional wind turbines within the next decade.
Government Support & Market Outlook
- Governments worldwide are increasing subsidies and providing funding for airborne wind technology development.
- The market for airborne wind energy is projected to grow significantly between 2025 and 2030, driven by increased interest in decentralized renewable energy solutions.
Future of Airborne Wind Energy: What’s Next?
Advancements in AI & Automation
The future of airborne wind energy is increasingly being shaped by artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. Advanced control algorithms and machine learning models are helping to optimize wind tracking, flight stability, and autonomous landing and takeoff systems. These improvements will significantly reduce operational costs and improve efficiency, making airborne wind turbines more commercially viable. Companies such as Ampyx Power and Skysails Power are investing in AI-driven automation to refine their airborne wind systems.
Grid Integration for Large-Scale Adoption
One of the key challenges for airborne wind energy is integrating it into national and regional grids. Researchers and industry leaders are working on improved energy transmission methods, such as lightweight superconducting cables and high-efficiency conversion systems, to ensure that airborne wind farms can deliver power seamlessly. Grid compatibility will be crucial for the technology to move from experimental projects to mainstream renewable energy sources.
Replacing Fossil Fuels & Supporting Off-Grid Electrification
Airborne wind turbines hold great promise for reducing reliance on fossil fuels, particularly in regions with limited access to traditional wind farms or solar power. Their mobility and scalability make them ideal for off-grid electrification in remote areas, islands, and disaster-prone regions. According to the World Economic Forum, airborne wind systems could provide clean energy solutions for refugee camps and emergency zones, offering rapid deployment and minimal infrastructure requirements.
Projected Commercialization Timeline
Currently, airborne wind energy is still in the demonstration and early deployment phase. While some companies, such as Kite Power Systems and Makani, have developed large-scale prototypes, full commercial viability is expected within the next two decades. Analysts predict that airborne wind farms could become cost-competitive with conventional wind and solar power by 2040, thanks to continued improvements in automation, materials, and regulatory frameworks.
Conclusion: Can Airborne Wind Energy Power the Future?
Airborne wind energy offers several advantages over traditional wind power:
- Higher energy yields due to stronger, more consistent high-altitude winds.
- Lower material and infrastructure costs, eliminating the need for massive towers.
- Flexibility and rapid deployment, making it suitable for remote locations and disaster relief.
- Reduced environmental impact, as it minimizes land use and avoids disruption to wildlife.
Challenges to Overcome
For airborne wind energy to become a mainstream renewable source, several challenges must be addressed:
- Engineering and durability issues, particularly the reliability of tethered flight systems.
- Regulatory and safety concerns, including airspace conflicts and aviation risks.
- Grid integration and energy storage, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
Final Thoughts on Its Role in the Energy Mix
While airborne wind turbines are not expected to fully replace traditional wind and solar energy, they are likely to play a crucial role in diversifying the renewable energy landscape. With continued innovation, strategic investment, and supportive policies, airborne wind energy has the potential to become a significant contributor to global clean energy efforts in the coming decades.
Related Reads You Might Find Interesting
📌 Hydrogen vs. Electric: The Future of Clean Energy
📌 Advanced Energy Storage: Cutting-Edge Battery Technologies
📌 Electricity-Generating Slime: The Next Renewable Energy Breakthrough?
📌 Tidal Energy: Harnessing Ocean Power