Introduction: A Comprehensive Guide to Vertical Farming
Our global population is on the rise, placing a growing strain on traditional agriculture. But what if we could cultivate crops in a way that maximizes yield, minimizes environmental impact, and thrives even in urban landscapes? Enter the realm of vertical farming, a revolutionary approach to agriculture that’s reshaping our vision of food production.
This comprehensive Vertical farming guide dives deep into the world of vertical farming, equipping you with the knowledge to understand its core principles, explore its numerous advantages, and discover the exciting possibilities it holds for the future.

Here’s a taste of what you’ll discover:
- The Essence of Vertical Farming: We’ll unveil the core concept behind vertical farming, providing a clear and concise definition to set the foundation for your understanding.
- A Harvest of Benefits: Delve into the numerous advantages of vertical farming, from increased crop yields and reduced water usage to minimized land footprint and year-round production. We’ll explore how vertical farming addresses key challenges in traditional agriculture.
- The Mechanics of Vertical Mastery: Unravel the fascinating inner workings of vertical farms. We’ll explore how these systems function, from advanced lighting and hydroponic cultivation methods to meticulous environmental control.
- A Spectrum of Techniques and Systems: Discover the diverse approaches to vertical farming, including building-based, containerized, and in-tunnel systems. We’ll delve into the unique features and benefits of each.
- A Glimpse into the Future: We’ll explore the exciting potential of vertical farming, examining how it can revolutionize food security, address resource scarcity, and contribute to a more sustainable food system.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with a comprehensive understanding of vertical farming, its impact on the future of food production, and the potential it holds to reshape our agricultural landscape. So, buckle up and get ready to explore the fascinating world of vertical farming!
What is vertical farming?
As our global population swells, traditional agriculture faces mounting pressure to produce enough food. But what if we could cultivate crops in a way that transcends limitations, minimizes environmental impact, and thrives even in urban landscapes? This is the revolutionary promise of vertical farming, a modern approach to agriculture that’s fundamentally reshaping our vision of food production.
Unveiling the Essence: A Definition of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming isn’t just about planting crops on shelves. It’s a meticulously designed system that maximizes space utilization and optimizes growing conditions. Here’s a clear and concise definition:
Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, creating a controlled indoor environment where factors like lighting, temperature, and nutrients are meticulously managed to ensure optimal plant growth.
Imagine a multi-story building dedicated solely to cultivating plants, maximizing space utilization, and creating ideal growing conditions. This approach is particularly valuable in urban areas with limited land availability, offering a solution for sustainable food production in densely populated regions.
A Harvest of Benefits: Advantages of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming isn’t just about innovation; it offers a multitude of advantages that contribute to a more sustainable and productive future for agriculture. Let’s delve into some of the key benefits:
Increased Crop Yields: By providing optimal growing conditions and eliminating external environmental factors that can harm crops (pests, unpredictable weather), vertical farms can significantly increase yields compared to traditional methods.
Reduced Water Usage: Vertical farms often utilize hydroponics or aeroponics, which require significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. This is a crucial advantage in regions facing water scarcity.
Minimized Land Footprint: Vertical farming defies the limitations of horizontal space. By stacking growing layers, it maximizes production on a smaller footprint, making it ideal for urban areas or regions with limited arable land.
Year-Round Production: Unlike traditional farms susceptible to seasonal variations, vertical farms can operate year-round, providing a consistent and reliable source of fresh produce, regardless of external weather conditions.

Improved Food Quality: The controlled environment in vertical farms minimizes the need for pesticides and herbicides, promoting a more sustainable approach to food production. Additionally, precise control over growing conditions can lead to higher quality, more nutritious crops.
Reduced Environmental Footprint: The controlled environment minimizes reliance on pesticides and fertilizers, leading to reduced environmental pollution. Additionally, the potential for local food production (especially in urban areas) lowers overall carbon emissions associated with transportation.
Beyond Increased Yields: The Potential of Vertical Farming
The potential of vertical farming extends far beyond the benefits listed above. Future advancements in areas like artificial intelligence and automation can further optimize growing conditions and resource utilization. Additionally, research is ongoing to explore the feasibility of cultivating a wider variety of crops in vertical farms, including fruits, vegetables, and even certain grains.
By understanding the core principles and advantages of vertical farming, you’ve gained valuable insight into this transformative approach to agriculture. The following sections will delve deeper into the inner workings of vertical farms, explore the diverse systems and techniques employed, and examine the exciting possibilities this technology holds for the future of food production.
Exploring the Mechanisms of Vertical Farming – How Does it Work?
Vertical farming isn’t just about stacking plants and hoping for the best. It’s a complex dance of technology and controlled environments, working together to create an ideal world for crops to flourish. This section delves into the inner workings of vertical farms, exploring the core mechanisms that make it all possible.
Breakdown of the Vertical Farming System:
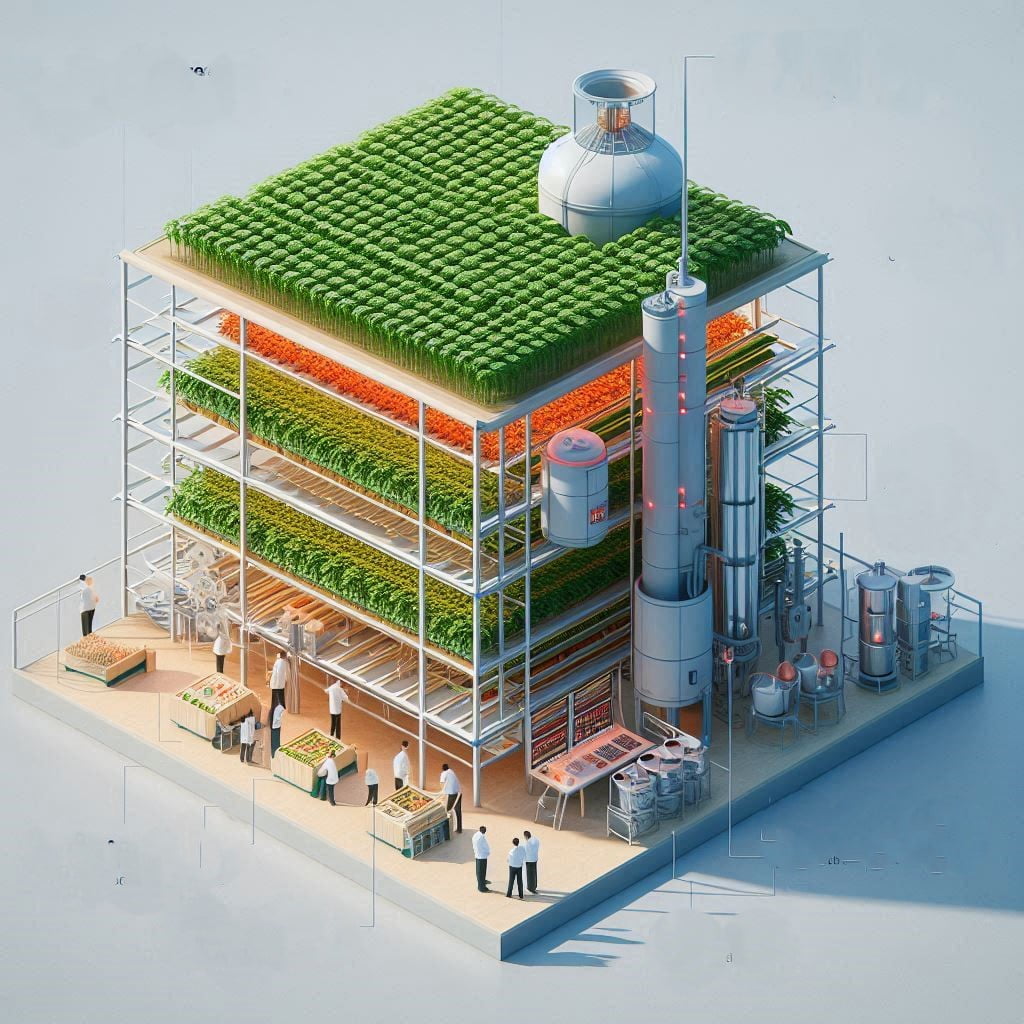
Imagine a multi-layered structure, each level meticulously designed to optimize plant growth. Below is the breakdown of the key components of Vertical Farming:
Lighting Systems: Traditional farms rely on sunlight, but vertical farms create their own sunshine. Advanced LED lighting systems provide the necessary light spectrum for plant growth, ensuring optimal light delivery regardless of external conditions. These systems are highly efficient, converting most of the energy they use into usable light, minimizing wasted energy.

Cultivation Methods: Vertical farms say goodbye to traditional soil-based agriculture. Instead, they often utilize two primary methods:
- Hydroponics: This technique eliminates soil, growing plants with their roots suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution. The solution is precisely formulated to deliver the exact nutrients each plant needs for optimal growth.
- Aquaponics: This innovative system combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics. The waste produced by the fish provides natural nutrients for the plants growing in the hydroponic system, creating a closed-loop ecosystem.
Environmental Control: Unlike traditional farms at the mercy of the elements, vertical farms provide a controlled environment. Advanced systems meticulously manage:
- Temperature: Sensors and automated systems ensure the optimal temperature range for each specific crop is maintained.
- Humidity: Precise control over humidity levels prevents excessive moisture buildup and promotes healthy plant growth.
- Airflow: Proper ventilation ensures adequate air circulation and prevents the spread of disease.
- Nutrient Delivery: Automated systems precisely deliver the exact amount of nutrients required by the plants at each growth stage, maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste.
Types of Vertical Farming Systems:
The beauty of vertical farming lies in its adaptability. While the core principles remain the same, the physical structures can vary depending on factors like available space and desired scale. Here’s a glimpse into the diverse world of vertical farming systems:
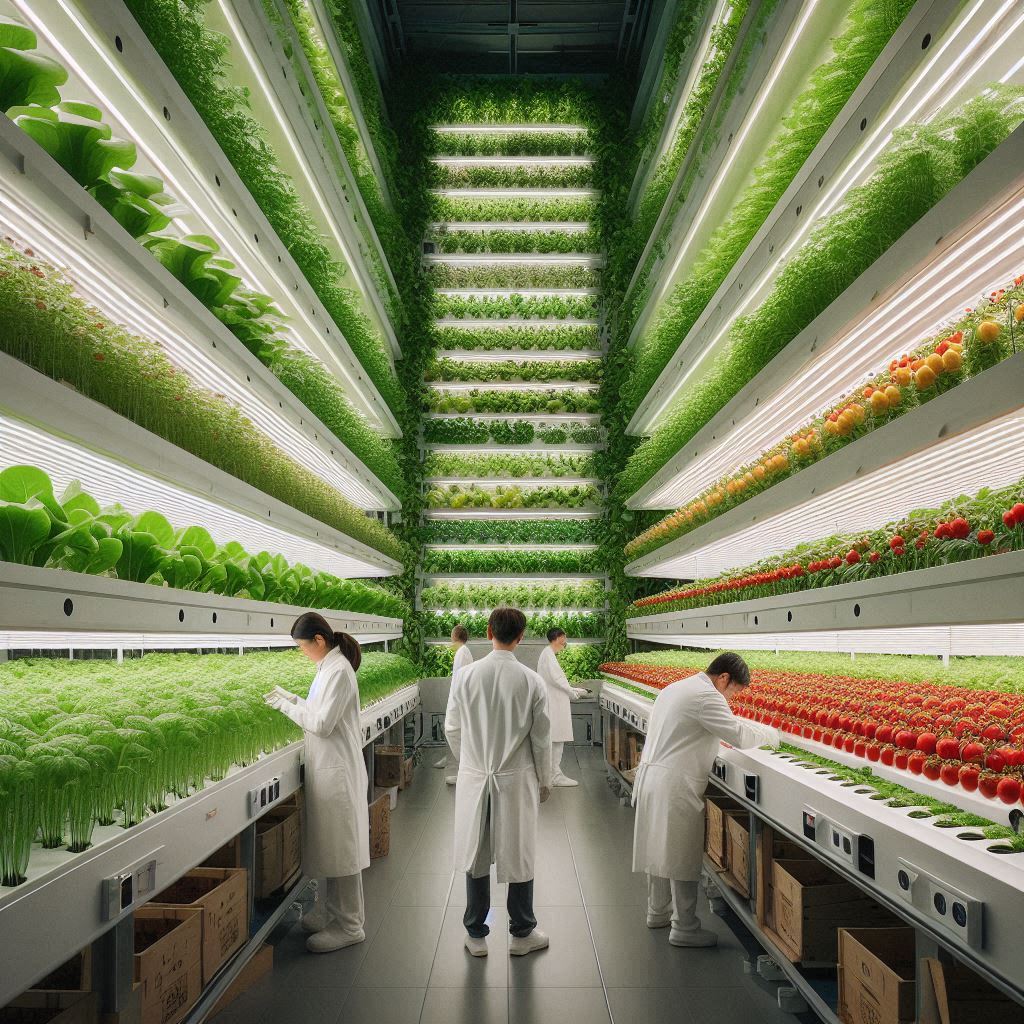
- Building-Based Farms: These large-scale operations utilize specially designed multi-story buildings to maximize growing space. These facilities often house multiple growing layers, each meticulously controlled to cultivate a variety of crops.
- Containerized Farms: Ideal for smaller spaces or urban settings, these compact and mobile units transform repurposed shipping containers into vertical farms. This approach offers a flexible and scalable solution for local food production.
- In-Tunnel Farms: Abandoned mines or specially designed tunnels can be repurposed for vertical cultivation. These underground farms offer a unique and controlled environment for growing crops, potentially utilizing geothermal energy sources for temperature regulation.
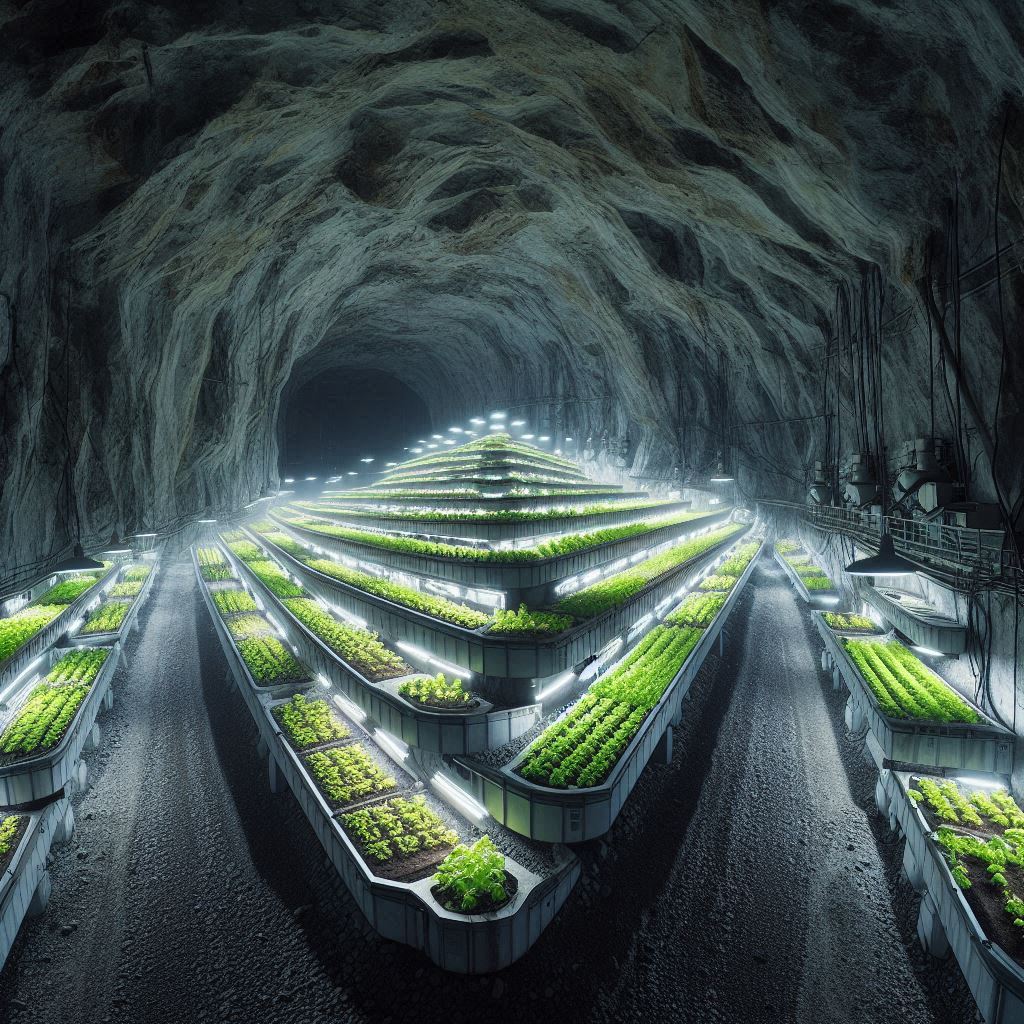

The Symphony of Technology and Nature:
By combining advanced technology with a deep understanding of plant science, vertical farming creates a symphony of controlled environments that optimizes growth and maximizes yield. In the next section, we’ll explore the exciting future of vertical farming and how it has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce food.
Delving Deeper – Vertical Farming Techniques and Systems
The magic of vertical farming lies not just in the concept, but in the intricate details that bring it to life. This section delves deeper into the techniques and systems that power this innovative approach to agriculture.
Optimizing Growth Conditions: A Symphony of Science and Technology
Imagine a conductor meticulously leading an orchestra, ensuring each instrument plays its part in harmony. Vertical farming utilizes a similar approach, with various techniques working together to create optimal growth conditions. Here’s a closer look at some key elements:
- Nutrient Delivery Systems: Gone are the days of scattering fertilizer. Vertical farms often employ automated systems that precisely deliver the exact amount of nutrients required by the plants at each growth stage. These systems can be tailored to the specific needs of each crop variety, maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste.
- Climate Control Strategies: Unlike traditional farms battling unpredictable weather, vertical farms provide a meticulously controlled environment. Advanced sensors and automated systems monitor and adjust factors like temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels to create the ideal climate for each specific crop. This level of control allows for year-round production and minimizes the risk of crop failure due to external factors.
- Automation: Repetitive tasks no longer need to be done manually. Vertical farms leverage automation to streamline processes, from nutrient delivery and climate control to monitoring plant health and harvesting. This frees up human labor for more focused tasks like system optimization and crop innovation.
Spotlight on Vertical Farming Systems: A Glimpse into the Future
The world of vertical farming is brimming with innovation. Let’s explore some prominent players and their unique approaches:
- Plenty: This industry leader utilizes vertical farming technology to cultivate a variety of leafy greens and herbs in controlled environments. Their focus on data-driven insights and automation allows for continuous improvement and optimization of their systems.
- AeroFarms: This company takes a unique approach, utilizing aeroponics – a method where plant roots are misted with a nutrient-rich solution. Their emphasis on vertical farming technology and sustainable practices positions them at the forefront of the industry.
- InFarm: This vertical farming innovator offers modular growing systems that can be adapted to various spaces, making it ideal for urban environments. Their focus on local food production and resource efficiency aligns with the growing demand for sustainable agriculture solutions.
These are just a few examples, and the landscape of vertical farming companies is constantly evolving. As research and development continue, we can expect even more innovative techniques and systems to emerge, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
The Future of Food Production: A Glimpse Beyond
By delving deeper into the techniques and systems employed in vertical farming, we gain a deeper appreciation for its potential. In the next section, we’ll explore how vertical farming can revolutionize the future of food production, addressing challenges like food security, resource scarcity, and environmental sustainability.
A Glimpse into the Future – The Potential of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming isn’t just a futuristic concept; it’s a transformative approach with the potential to revolutionize the way we produce food. This section explores the exciting possibilities vertical farming holds for the future, addressing challenges like food security, resource scarcity, and population growth.
Revolutionizing Food Production: Cultivating a More Sustainable Future
As our global population continues to rise, traditional agriculture faces an uphill battle. Vertical farming offers a compelling solution, with the potential to:
- Enhance Food Security: Vertical farms can be established anywhere, regardless of climate or available land. This allows for local food production, especially in regions facing food insecurity or limited arable land. Imagine urban areas growing their own fresh produce, reducing reliance on long-distance transportation and increasing access to nutritious food.
- Address Population Growth: The ability to grow crops vertically allows for significantly increased yields on a smaller footprint. This is crucial to meet the growing demand for food as the global population climbs towards 10 billion by mid-century.
- Combat Resource Scarcity: Vertical farming is a champion of resource efficiency. Hydroponic and aeroponic techniques use significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. Additionally, controlled environments minimize the need for pesticides and fertilizers, promoting a more sustainable approach.
- Reduce Environmental Impact: Reduced reliance on transportation (due to local production) and minimized use of pesticides contribute to a lower overall environmental footprint for vertical farming. Additionally, advancements in renewable energy sources can further reduce the carbon footprint associated with powering these systems.
- Year-Round Production: Unleash the power of predictable harvests! Vertical farms are not subject to the whims of nature. By controlling the environment, farmers can ensure year-round production of fresh, high-quality crops, regardless of external weather conditions.
Challenges and Opportunities: A Look Ahead
While the potential of vertical farming is undeniable, there are challenges to address:
- Initial Investment Costs: Setting up a vertical farm requires significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure. Ongoing research and development are crucial to bring down these costs and make vertical farming a more accessible option.
- Energy Consumption: Lighting and climate control systems require energy to operate. The key lies in utilizing renewable energy sources and optimizing energy efficiency within the systems themselves.

- Labor and Expertise: Vertical farming requires a skilled workforce with expertise in plant science, engineering, and automation. Developing training programs and fostering collaboration between various disciplines will be crucial.
Future Advancements: Pushing the Boundaries of Possibility
The future of vertical farming is brimming with exciting possibilities:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can play a vital role in optimizing growing conditions, predicting crop yields, and automating processes, leading to even greater efficiency and resource management.
- Integration with Robotics: Robots can be employed for tasks like planting, monitoring plant health, and harvesting, further reducing manual labor requirements and improving precision.
- Expanding Crop Variety: Research is ongoing to explore the feasibility of cultivating a wider range of crops in vertical farms, potentially including fruits, vegetables, and even certain grains.
- Urban Agriculture Revolution: Vertical farming has the potential to transform urban landscapes, creating local food production hubs and promoting a more sustainable food system in cities.
By acknowledging the challenges and embracing ongoing advancements, vertical farming can become a cornerstone of a more secure, sustainable, and efficient food production system for the future.
Conclusion: Cultivating a Brighter Future with Vertical Farming
In this exploration of vertical farming, we’ve unveiled a revolutionary approach to agriculture with the potential to reshape our food system. We’ve delved into the core concept, explored the intricate mechanics at play, and discovered the exciting possibilities it holds for the future.
Key Takeaways: A Sustainable Future on the Rise
- Vertical farming offers a solution for maximizing food production in a space-efficient and environmentally conscious manner.
- By utilizing controlled environments and innovative techniques like hydroponics and aeroponics, vertical farms significantly reduce water usage and minimize reliance on pesticides.
- The ability to grow crops year-round, regardless of external weather conditions, enhances food security and promotes a more stable food supply chain.
- The potential for local food production in urban areas can revolutionize our food system, reducing transportation emissions and fostering a more sustainable approach.
Be Part of the Change
The future of vertical farming is brimming with promise. As research and development continue, we can expect advancements in areas like AI, robotics, and energy efficiency, further pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
We encourage you to delve deeper into this innovative approach. Explore the work of leading vertical farming companies, learn more about the ongoing research, and consider the role vertical farming can play in creating a more sustainable food system for generations to come.
Vertical farming isn’t just about cultivating crops; it’s about cultivating a brighter future. Join the conversation, advocate for sustainable solutions, and be a part of shaping a world where food production is not just efficient, but truly transformative.
Explore our other interesting blogs: