Introduction: The Rise of Home Fuel Cells
As the demand for clean and efficient energy solutions grows, home fuel cells are emerging as a game-changer in residential energy. A home fuel cell generator provides continuous, on-site electricity by converting chemical energy from hydrogen or natural gas into electrical power, offering homeowners a sustainable and independent energy source.
With increasing concerns over climate change and rising electricity costs, home fuel cell installation costs are becoming more competitive, making this technology an attractive alternative to traditional grid power. By generating power efficiently with minimal emissions, home fuel cell generators contribute to sustainable home power while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.

The adoption of residential fuel cell energy has been steadily increasing, with countries like Japan and Germany leading the way in deploying hydrogen fuel cells for homes. Companies are developing more affordable and scalable solutions, positioning fuel cells as the future of home energy. As this technology continues to evolve, homeowners can expect greater energy independence, improved home energy efficiency, and a significant reduction in carbon footprints.
How Home Fuel Cells Work
How Fuel Cells Generate Electricity for Homes
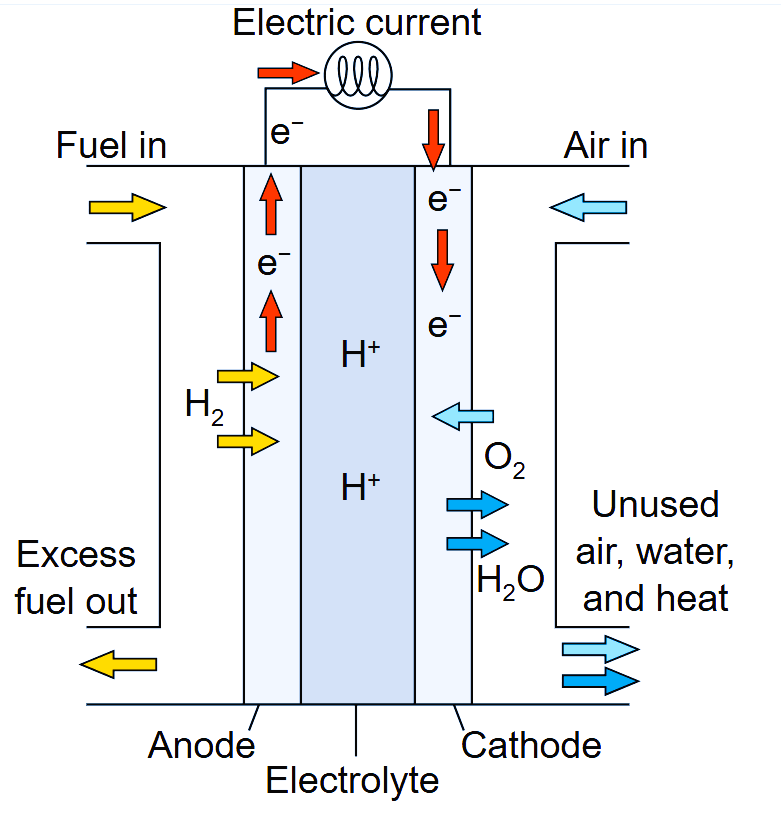
A home fuel cell operates similarly to a battery but relies on a continuous fuel supply—typically hydrogen—to generate electricity. The core principle involves a chemical reaction where hydrogen and oxygen interact, producing electricity, heat, and water as byproducts. Unlike conventional batteries, fuel cells do not run down or require recharging as long as they have a fuel supply, making them an excellent option for sustainable home power solutions.
Key Components of a Home Fuel Cell
- Anode (Negative Electrode): This is where hydrogen gas is introduced. A catalyst (often platinum) helps split the hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons.
- Electrolyte: This special membrane allows only protons to pass through to the cathode while blocking electrons, forcing them through an external circuit, generating usable electricity.
- Cathode (Positive Electrode): Oxygen from the air reacts with the hydrogen protons and electrons at the cathode, forming water and heat as byproducts.
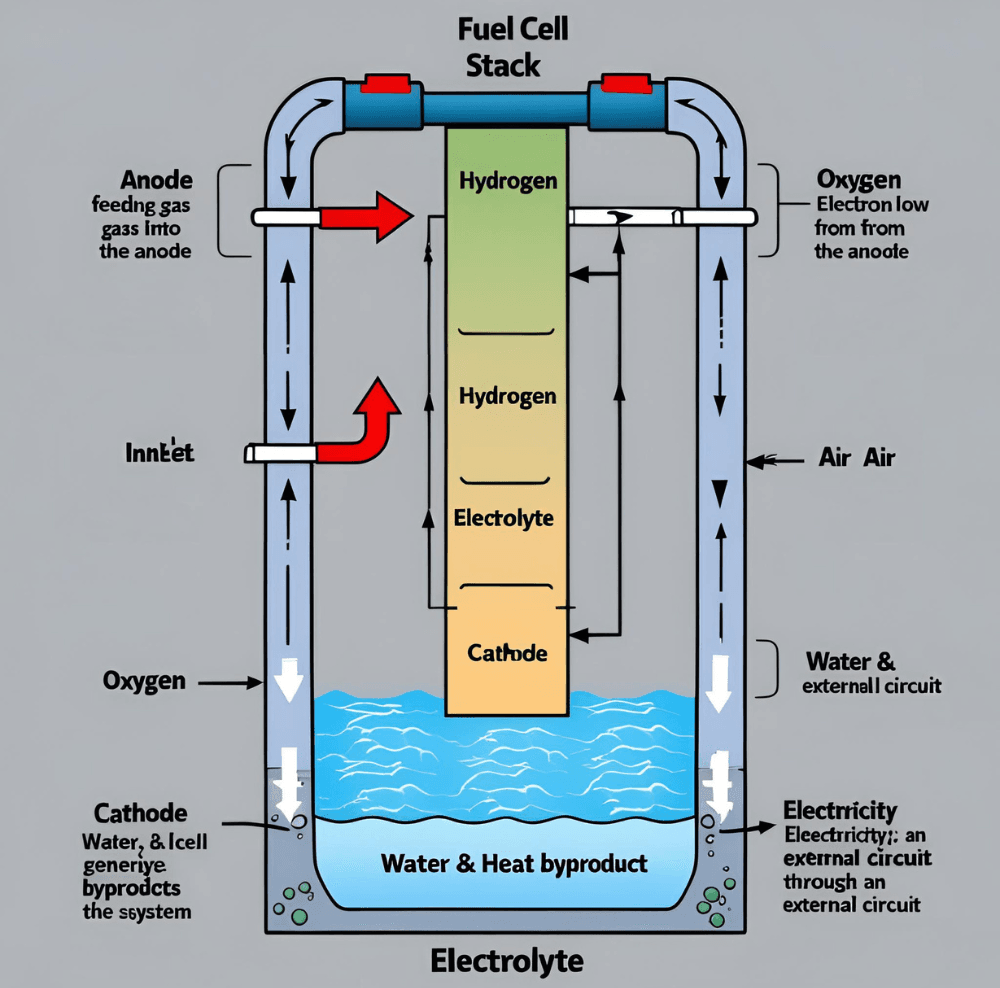
The Role of Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Home Energy Efficiency
Fuel cells can be highly efficient, with solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and molten carbonate fuel cells (MCFCs) reaching up to 85% efficiency when used in a combined heat and power (CHP) system. This means that in addition to generating electricity, excess heat can be captured for residential heating and hot water, significantly improving home energy efficiency. Compared to traditional combustion-based power generation, hydrogen fuel cell for home use produces zero carbon emissions when using pure hydrogen, making it a key technology in the future of home energy.
Types of Home Fuel Cell Generators
Home fuel cell generators come in different types, each offering unique benefits in terms of efficiency, durability, and fuel sources. The two most commonly used fuel cell types for residential energy solutions are Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC) and Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC). Additionally, the debate between hydrogen vs. natural gas fuel cells is essential when considering sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC) – Ideal for Homes
PEMFCs use hydrogen as a fuel source, generating electricity through an electrochemical reaction. They operate at relatively low temperatures (60-100°C), making them well-suited for residential applications where rapid startup times and compact designs are needed.
Key Advantages:
- Fast startup time: PEMFCs can quickly begin generating power, making them suitable for backup and primary residential energy.
- High power density: These fuel cells provide efficient energy output despite their small size.
- Clean energy production: The only by-product is water, ensuring zero carbon emissions when using pure hydrogen.
Challenges:
- Hydrogen storage: Storing hydrogen safely can be complex and expensive.
- Platinum catalyst cost: PEMFCs require platinum catalysts, increasing installation and maintenance costs.
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) – High Efficiency for Continuous Use
SOFCs are high-temperature fuel cells that operate between 500-1,000°C, using a solid ceramic electrolyte. They can run on hydrogen, natural gas, biogas, and other hydrocarbon fuels, offering greater flexibility.
Key Advantages:
- Higher efficiency: SOFCs can achieve up to 60% efficiency in electricity generation and over 85% when combined with heat generation.
- Fuel flexibility: Unlike PEMFCs, SOFCs can use multiple fuel types, including natural gas and biofuels.
- Longer lifespan: With fewer moving parts and solid-state construction, SOFCs generally last longer than PEMFCs.
Challenges:
- Long startup time: SOFCs take longer to reach operational temperatures, making them less suitable for on-demand backup power.
- High operating temperatures: These systems require advanced insulation and cooling systems, adding to installation complexity.
Comparing Hydrogen vs. Natural Gas Fuel Cells
A major consideration for home fuel cell adoption is the fuel source. Both hydrogen and natural gas fuel cells have distinct benefits:
- Hydrogen fuel cells offer zero-emission energy, making them the most sustainable choice. However, hydrogen production and storage remain costly and infrastructure is limited.
- Natural gas fuel cells are more accessible and can integrate with existing gas pipelines. However, they produce some carbon emissions, making them less eco-friendly than pure hydrogen solutions.
Benefits of Home Fuel Cells
High Efficiency & Sustainability
Home fuel cells provide greater efficiency than conventional fossil-fuel-based electricity generation. Unlike combustion-based power, fuel cells convert chemical energy directly into electricity with minimal energy loss, leading to higher energy efficiency and lower operational costs.
Lower Carbon Footprint
Fuel cells significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particularly when using hydrogen. Even natural gas-powered fuel cells produce far fewer emissions than coal or oil-based energy sources, making them a valuable transition technology toward a sustainable home power solution.
Off-Grid Power & Reliability
One of the greatest advantages of home fuel cells is their ability to provide reliable, off-grid energy. This is particularly useful for homes in remote locations or areas with unstable power grids.
- Resilience: Fuel cells can function as backup power sources in case of grid failures.
- Lower dependency on external utilities: Homeowners can reduce reliance on centralized electricity networks.
- Cost Savings: While the home fuel cell installation cost can be high, long-term operational savings and potential government incentives can make them cost-effective.
Installation & Costs: Is It Worth It?
Home Fuel Cell Installation Process
Installing a home fuel cell involves several steps, from site assessment to final integration. The process typically starts with an energy audit to determine the household’s power needs. A professional then installs the fuel cell system, which includes the stack (where the electrochemical reaction occurs), fuel supply (hydrogen or natural gas), and inverters to convert the generated power for home use. The installation process varies depending on whether the system is grid-tied or designed for off-grid use. Homeowners should also ensure compliance with local building codes and utility regulations.
Cost Breakdown & Incentives
The home fuel cell installation cost depends on the system type and size. Small residential systems range from $10,000 to $25,000, while larger setups can cost over $50,000. Operating costs include hydrogen fuel (if not generated on-site), maintenance, and potential infrastructure upgrades.
However, various government incentives and tax credits can significantly reduce costs. In the U.S., the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and state-level rebates may cover up to 30% of the installation cost. Homeowners using fuel cells powered by renewable hydrogen can also qualify for additional green energy subsidies, making fuel cells a viable option for sustainable home power.
ROI and Long-Term Savings
While the upfront home fuel cell generator price is high, the return on investment (ROI) is promising for long-term users. Fuel cells boast efficiencies of up to 60%, meaning lower electricity bills. With an expected lifespan of 10-20 years, they can provide significant energy savings. Compared to traditional power sources, fuel cells offer a stable energy cost, reducing reliance on fluctuating grid electricity prices.
Comparing Home Fuel Cells to Other Renewable Energy Sources
Home Fuel Cells vs. Solar Panels
Solar panels and hydrogen fuel cells for home use are both clean energy solutions, but they differ in function. Solar panels generate electricity during daylight hours and require batteries for energy storage, whereas fuel cells produce power on demand, 24/7. While solar has lower upfront costs ($10,000–$30,000 for a typical system) and benefits from decreasing battery storage costs, fuel cells excel in consistent power output, making them ideal for locations with limited sunlight or unreliable grid connections.
Fuel Cells vs. Traditional Backup Generators
Fuel cells and backup generators both provide power in emergencies, but they have key differences:
- Efficiency: Fuel cells can reach 60% efficiency, while traditional gas generators are closer to 30%.
- Environmental Impact: Generators burn fossil fuels, emitting CO₂ and requiring regular refueling. Fuel cells are cleaner, especially when using green hydrogen.
- Operating Costs: Although generators have lower upfront costs (starting at $1,500-$10,000), they require ongoing fuel and maintenance, making them less cost-effective in the long run. Fuel cells, while expensive initially, have lower long-term maintenance and fuel costs, making them a sustainable home power solution.
In summary, home fuel cells are an excellent investment for homeowners seeking a reliable, eco-friendly energy source. While solar panels remain a great alternative, fuel cells outperform in efficiency and consistent power delivery, making them ideal for off-grid and high-energy-demand homes.
Future of Home Fuel Cells
The Role of Hydrogen in Home Energy
Hydrogen fuel cells are set to play a key role in the future of home energy, particularly as nations move toward reducing carbon emissions and achieving net-zero energy goals. Governments and industries are investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, including hydrogen production and distribution networks, making it more accessible for residential use. Green hydrogen, produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, is becoming a significant focus, ensuring that hydrogen fuel cells contribute to truly sustainable home power solutions.
Advancements in Fuel Cell Technology for Homes
Technological advancements are rapidly improving fuel cell efficiency, making them more viable for residential applications. Researchers are working on better catalyst materials, improved electrolyte membranes, and more durable fuel cell stacks. These innovations are reducing costs and increasing the energy density of home fuel cell generators. Companies like Panasonic, Plug Power, and Doosan Fuel Cell are actively investing in R&D to improve the lifespan and efficiency of fuel cells, which is crucial for their long-term adoption in homes.
Market Growth & Adoption Trends
The global hydrogen fuel cell market is projected to experience significant growth through 2030, with Europe and Asia-Pacific leading in adoption. Expanding government incentives, infrastructure development, and collaborations between major corporations and startups are driving market growth. In particular, the residential sector is seeing increasing interest due to the need for reliable, clean, and efficient home energy solutions.
Conclusion: Should You Invest in a Home Fuel Cell?
Recap of Benefits and Costs
Home fuel cells offer numerous advantages, including high energy efficiency, sustainability, and reliable power generation. While initial installation costs remain high, government incentives and advancements in technology are making them more accessible.
Future Outlook for Residential Fuel Cell Energy
As hydrogen infrastructure expands and production costs decrease, home fuel cells will become an increasingly attractive option for homeowners. The push for sustainable energy and regulatory policies supporting hydrogen adoption further indicate strong future growth.
For homeowners considering a transition to sustainable home power, exploring available incentives and emerging fuel cell technologies is a great starting point. As adoption grows, options for home fuel cells will become more affordable and efficient, making them a practical choice for the future of home energy.
Discover More on Sustainable Energy Solutions:
If home fuel cells sparked your interest, don’t miss these groundbreaking articles:
🔹 Micro Algae Biofuel: A Renewable Energy Revolution
🔹 Microbial Fuel Cells as Off-Grid Energy Solutions
🔹 Molten Salt Reactors: The Future of Nuclear Energy
🔹 Advanced Energy Storage: Innovations Shaping the Future
Explore the next frontier in clean energy! ⚡🌱