Introduction: Why More Homes Are Turning to Solar Energy
As electricity bills continue to climb and concerns about climate change grow, homeowners are actively seeking cleaner and more affordable alternatives to traditional power sources. This shift in mindset has made Residential Solar Plant one of the most attractive solutions worldwide. Whether it’s in urban apartments or suburban homes, solar is becoming the go-to option for those looking to cut costs and reduce their carbon footprint.
One of the biggest benefits of a home solar system is its dual impact—on both the environment and your wallet. Not only does it allow families to produce their own electricity using sunlight, but it also dramatically reduces monthly utility bills. With smart net metering policies and government incentives, the payback period for home solar installations has become shorter than ever.
📊 Did you know? Residential solar installations have surged globally—with India witnessing a 30% year-over-year growth in 2023, and the USA crossing 4 million home solar installations as of early 2024.
The transition to Rooftop solar for home is no longer just about saving money—it’s a proactive choice for energy independence and sustainability. With the many benefits of home solar systems now widely understood, it’s clear why more and more homeowners are making the switch.
What Is a Residential Solar Plant for Homes?
A solar power system for homes is essentially a compact energy plant mounted right on your rooftop. Its job? To convert free sunlight into usable electricity for your daily needs—powering everything from lights and fans to refrigerators and washing machines.
To understand the home solar system working mechanism, here’s a simple explanation: Solar panels absorb sunlight and generate Direct Current (DC) electricity. This DC power is then converted into Alternating Current (AC) by an inverter, which your household appliances use. The process is seamless, silent, and doesn’t require daily intervention.
There are three types of rooftop solar systems for homes:
- Grid-tied systems: These are connected to the utility grid and are ideal for homes with consistent electricity supply. Excess power generated is sent back to the grid via net metering.
- Off-grid systems: These operate independently and use batteries for storage, perfect for remote or rural homes.
- Hybrid systems: A mix of both—connected to the grid but also equipped with a battery backup.
The typical capacity for a rooftop solar system for home use ranges from 1 kW to 10 kW, depending on your electricity consumption and available roof space. A 1 kW system can generate around 4 units/day—enough to offset essential household loads.
In summary, knowing how a home solar system works helps you understand its value proposition. With the right setup, your roof can become a mini power plant—delivering clean, reliable energy for decades.
How Solar Powers Your Home: Step-by-Step
Understanding how solar panels work for home use is key to appreciating the simplicity and brilliance of this renewable energy solution. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how sunlight becomes electricity in your house:
- Solar panels absorb sunlight during daylight hours using photovoltaic (PV) cells made of semiconductor materials like silicon.
- These cells generate DC (Direct Current) electricity, which flows through connected circuits.
- A solar inverter then converts this DC power into AC (Alternating Current), the standard form of electricity used in homes.
- The resulting AC electricity powers your home appliances—from fans and lights to TVs and refrigerators.
- If your system includes net metering, extra solar electricity flows into the grid, earning you credits on your bill.
This clean and silent process ensures your household runs smoothly without relying solely on the power grid. The entire solar electricity flow is automatic and intelligently managed by the system’s components.
Once you understand how Residential Solar Plant applications, the system seems less like a high-tech mystery and more like a smart investment that pays off every sunny day.
What Makes Your Roof Suitable for Solar?
Before going solar, it’s essential to evaluate whether your roof is ready. A proper site assessment ensures that your rooftop Residential Solar Plant for house purposes will be effective and long-lasting. Several key factors determine suitability:
- Direction: In India, south-facing roofs receive maximum sunlight throughout the year. In the USA, west-facing rooftops often perform best due to afternoon sun exposure.
- Sunlight hours: Your roof should get at least 6–8 hours of shade-free sunlight daily to make solar panel installation for home efficient.
- Type of roof: RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) rooftops are ideal for anchoring the mounting structures that support solar panels.
- Space requirement: You need roughly 100 square feet of roof space per 1 kW of solar capacity. So, a typical 3 kW system needs 300 sq. ft. of usable area.
📝 Is My Roof Solar-Ready? — Quick Checklist:
- Does your roof get sunlight most of the day?
- Is the surface strong and spacious enough?
- Are there tall trees or structures casting shadows?
- Do you own the roof or have permission for installation?
By answering these questions, homeowners can confidently evaluate if a rooftop solar for house is a viable option. A professional solar panel installation for home always includes a detailed roof assessment, but understanding these basics helps you plan better and ask the right questions.
Key Components of a Home Solar System
To understand how a home solar setup works, it’s important to break down its main components. Each part plays a crucial role in converting sunlight into usable energy.
Solar Panels
The heart of your system, these panels capture sunlight. Common solar panel types for homes include:
- Monocrystalline: High efficiency, sleek look, best for limited roof space.
- Polycrystalline: More affordable, slightly lower efficiency.
- Bifacial panels: Capture sunlight from both sides, suitable for reflective rooftops.
Choosing the right solar panel types for homes depends on your budget, roof space, and aesthetic preferences.
Inverter
Converts DC from the panels into AC power. The two main options for the best inverter for home solar:
- String inverter: Cost-effective and easy to maintain, but performance can drop if one panel is shaded.
- Microinverters: Installed on each panel; maximize output even in partial shade—ideal for complex rooftops.
When selecting the best inverter for Residential Solar Plant, consider roof orientation, shading, and budget.
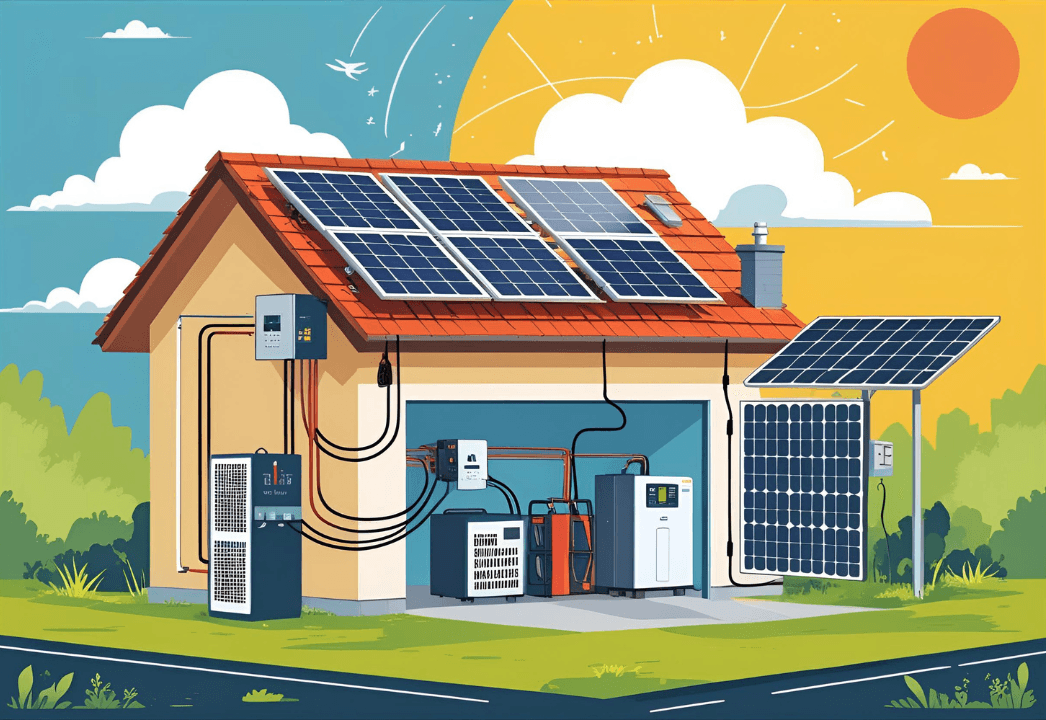
Mounting Structure
Provides sturdy support and correct tilt for your solar panels. Should be corrosion-resistant and windproof.
Net Meter
A bi-directional meter that records both power consumed and power exported back to the grid.
Battery (Optional)
For backup or off-grid systems. Batteries store unused solar energy for night or power outages.
Smart Monitoring Apps
Help track real-time performance, daily generation, and savings through your phone or PC.
Each of these components ensures that your system runs safely, efficiently, and gives you maximum return from your home solar installation.
Cost and Savings for Homeowners
One of the biggest reasons homeowners switch to solar is the long-term financial benefit. Here’s a breakdown of the solar system cost for home in India and the USA, and how much you can save:
System Cost
- India: ₹60,000–₹80,000 per kW (including installation, inverter, structure, and wiring)
- USA: $2.5–$3.5 per Watt (i.e., $2,500–$3,500 per kW on average)
Savings
Homeowners can expect solar panel electricity savings of up to 80–90% on electricity bills after installation. The more electricity rates rise, the more you save.
Payback Period
With the current cost and subsidies, the average payback is 4–6 years. After this, the system keeps generating free electricity for two more decades.
System Lifespan
Modern solar systems last 25+ years with minimal maintenance. Inverters may need replacement after 10–12 years.
Government Incentives
- India: Central Financial Assistance (CFA) offers up to ₹18,000/kW for residential systems, reducing the upfront solar system cost for home India.
- USA: The Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) covers 30% of system cost, making solar highly affordable.
📌 Suggested Table Layout:
| System Size | Cost (India) | Cost (USA) | Avg. Monthly Savings | Payback Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 kW | ₹1.2–1.6 L | $5,000–7,000 | ₹2,000 / $50 | 5–6 years |
| 3 kW | ₹1.8–2.4 L | $7,500–10,000 | ₹3,000 / $75 | 4–5 years |
| 5 kW | ₹3–4 L | $12,500–17,500 | ₹5,000 / $125 | 4–6 years |
With the combined effect of incentives, rising grid tariffs, and low maintenance, solar panel electricity savings make it one of the best long-term investments for homeowners.
Net Metering Simplified
For those installing a solar system connected to the utility grid, net metering is a key concept to understand. It’s the mechanism that allows you to export unused solar electricity and get credited for it.
What Is Net Metering?
Net metering for homeowners is a billing arrangement where any excess electricity your solar system generates is sent back to the grid and deducted from your electricity bill.
How Net Metering Works
- During the day, your system may produce more electricity than your home consumes.
- This extra power flows into the grid through a bi-directional meter that tracks both import (grid to home) and export (home to grid).
- At night or during cloudy days, you draw power from the grid as usual.
The net consumption is the difference between import and export, and your bill is calculated accordingly.
📌 Example:
A 5 kW system might export around 200–250 units per month. If your monthly usage is 400 units, and you export 200, you only pay for 200 units.
Policies in India vs USA
- In India, net metering rules vary by state. Some states offer 1:1 credit while others apply time-based tariffs or caps.
- In the USA, net metering is widely available, but policies vary by state and utility. Some states offer full retail credit, others use wholesale rates.
Understanding how net metering works can help homeowners maximize returns and reduce payback time. In short, net metering for homeowners ensures that no sunlight goes to waste.
Installation Process & Timeline
Installing a solar plant for your home is a streamlined process that can be completed in just a few days when done by a professional EPC (Engineering, Procurement, Construction) provider. Here’s how the residential solar installation steps typically unfold:
📍 Step-by-Step Installation Process:
- Site Assessment: An expert visits your home to evaluate roof space, orientation, and shading. This helps determine feasibility for rooftop installation.
- Load Calculation: Based on your monthly electricity bill, the required system size (kW) is calculated to meet your power needs.
- Documentation & Approvals: In India, DISCOM approval and government paperwork (for net metering and subsidies) are initiated. In the USA, utility permissions and interconnection agreements are managed.
- System Installation: The solar plant installation process involves mounting structures, panels, inverter setup, and wiring — typically completed within 3–5 days.
- Net Meter Integration: After setup, a bi-directional meter is installed to enable net metering. Post-inspection, the system is officially turned on.
📌 Timeline Overview:
| Day | Activity |
|---|---|
| 0 | Site visit and load analysis |
| 1–2 | Documentation and subsidy filing |
| 3–5 | Physical installation |
| 6–7 | Net meter connection & system go-live |
By following this structured process, residential solar installation steps are kept smooth, efficient, and hassle-free for homeowners.
Common FAQs for First-Time Solar Buyers
Considering solar for your home? Here are the most common questions homeowners ask before switching:
❓ What if it’s cloudy or rainy?
Solar panels still generate power under cloudy skies, though at reduced efficiency (typically 10–25%). Net metering ensures your prior grid exports cover such days.
❓ Can solar run air conditioners or heavy appliances?
Yes, solar can power air conditioners, geysers, refrigerators, and other heavy loads — provided your system is appropriately sized. For example, a 3–5 kW system can comfortably support 1–2 ACs along with other appliances.
❓ Do I need a battery?
A solar panel with battery backup is useful for power outages or off-grid homes. However, most urban homes with grid access prefer grid-tied systems due to lower cost and ease of use.
❓ What if I move to another home?
You can either transfer your solar plant (if feasible) or sell it along with the property — increasing its resale value due to lower energy bills for the buyer.
❓ Is maintenance a concern?
Solar panels require minimal maintenance — usually just annual cleaning and occasional inverter checkups. Most systems come with warranties of 25 years (panels) and 5–10 years (inverters).
So, is solar worth it for homes? Absolutely — especially with falling prices, low maintenance, and rising electricity tariffs.
Conclusion
Going solar is no longer a futuristic idea — it’s a smart, proven investment for today’s homeowner.
- You get solar panel electricity savings of up to 90% on your monthly bills.
- You contribute to green energy and reduce your carbon footprint.
- You benefit from government subsidies, attractive financing, and rising property value.
Whether you’re in India or the USA, the combined impact of policy support and technology advancement makes this the perfect time to install a Residential Solar Plant.
📞 Ready to start?
Contact a trusted solar expert for a free site evaluation or check your solar eligibility online.
Let the sun work for you — both financially and environmentally.
Related Reads You’ll Love:
If you’re curious about the broader world of solar energy and smart solutions beyond homes, be sure to check out these insightful posts:
-
Beginner’s Guide to Solar System for Factories and Industrial Rooftop Installations – Learn how large-scale solar can transform industries and reduce power bills.
-
DualSun Hybrid Solar Panels – Discover panels that generate both electricity and hot water from the same surface.
-
AuREUS Solar Panels are Changing Renewable Energy – Explore how this bio-based innovation harvests light even on cloudy days.
-
SolarWindow: Revolutionising Smart Building Technology – See how transparent solar windows could power the skyscrapers of tomorrow.