Introduction: The Rise of AI in Mental Health Care
In a world where mental health concerns are escalating and access to licensed professionals remains limited, a new wave of support has emerged: AI therapists.
Once a concept limited to science fiction, AI-driven mental health tools are now real, widely used, and steadily growing in sophistication. Platforms like Woebot, Wysa, and Replika are redefining the therapeutic experience—offering users instant, round-the-clock conversations powered by artificial intelligence.
But this innovation sparks an important, and at times uncomfortable, question:
👉 Can AI therapists genuinely grasp human emotions—and could they one day surpass the capabilities of human therapists?
While traditional therapy involves deep emotional understanding, empathy, and lived experience, AI offers consistency, scale, and accessibility unmatched by any human. Imagine millions of people receiving emotional support simultaneously, without wait times or costs.
The stakes are high. As AI therapists become more deeply embedded in healthcare ecosystems, schools, and even corporate wellness programs, we must critically evaluate their capabilities, benefits, limitations, and ethical implications.
In this blog, we’ll break down:
- What AI therapists really are
- Whether they actually “work”
- How they compare to human therapists
- Where the future is heading in AI-powered emotional care
By blending current tech, real-world applications, and future predictions, this article explores how AI is revolutionizing mental health—and whether we’re ready for that revolution.
Do AI Therapists Exist? What Are They, Really?
Let’s start with clarity:
Do AI therapists exist? Yes.
Are there AI therapists equivalent to human professionals? Not exactly.
✅ What Is an AI Therapist?
An AI therapist is a software program that uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to simulate human-like conversations focused on emotional support, wellness, and behavioral therapy.
They are designed to:
- Listen and respond in a human-like way
- Provide evidence-based therapeutic techniques (e.g., CBT)
- Monitor mood, suggest coping strategies, and encourage self-reflection
But here’s the catch: AI therapists are not licensed clinicians. They don’t diagnose, prescribe, or replace complex therapy. Instead, they act as digital mental health assistants, offering real-time, judgment-free support that is especially helpful in moments of stress, anxiety, or loneliness.
💬 Examples of AI Therapy Tools Available Today
Several AI-powered therapy platforms are already in active use:
- Woebot – Developed by Stanford researchers, it’s one of the most respected AI therapy bots. It uses CBT principles and provides daily check-ins to manage thoughts, behaviors, and emotions.
- Wysa – A mental wellness app combining AI chatbot interaction with access to real human therapists. Wysa tracks moods and suggests interventions like mindfulness or guided journaling.
- Replika – Originally a social AI companion, Replika has evolved into an emotional wellness assistant. While not therapy-focused, it provides empathetic conversations and support, especially for loneliness and self-exploration.
⚖️ How AI Therapists Differ From Human Therapists
| Feature | AI Therapist (e.g., Woebot) | Human Therapist |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | 24/7 Instant Access | Scheduled Sessions Only |
| Cost | Often Free or Low Cost | Expensive for Many |
| Emotional Depth | Simulated Empathy | Real Emotional Intuition |
| Training + Experience | Algorithm Trained on Data | Years of Clinical Education + Practice |
| Suitability | Everyday Stress, Self-help | Deep Trauma, Crisis, Long-Term Therapy |
AI therapists are best suited for providing low-intensity mental health support, particularly for individuals who are:
- New to therapy
- Facing emotional challenges but not clinical disorders
- In remote or underserved areas with limited access to professionals
They do not replace human therapists when it comes to complex trauma, suicidal ideation, or psychiatric disorders—but they fill an important gap in the mental health care ecosystem.
🤔 Are There AI Therapists With Human-Like Intelligence?
As of now, AI therapists do not possess consciousness or emotional awareness. Their ability to “understand” emotions is based on statistical patterns, not lived experience.
However, with advances in large language models, emotion recognition algorithms, and contextual AI, the line is beginning to blur.
The question isn’t just do AI therapists exist?—it’s becoming:
How soon before they understand us better than we understand ourselves?
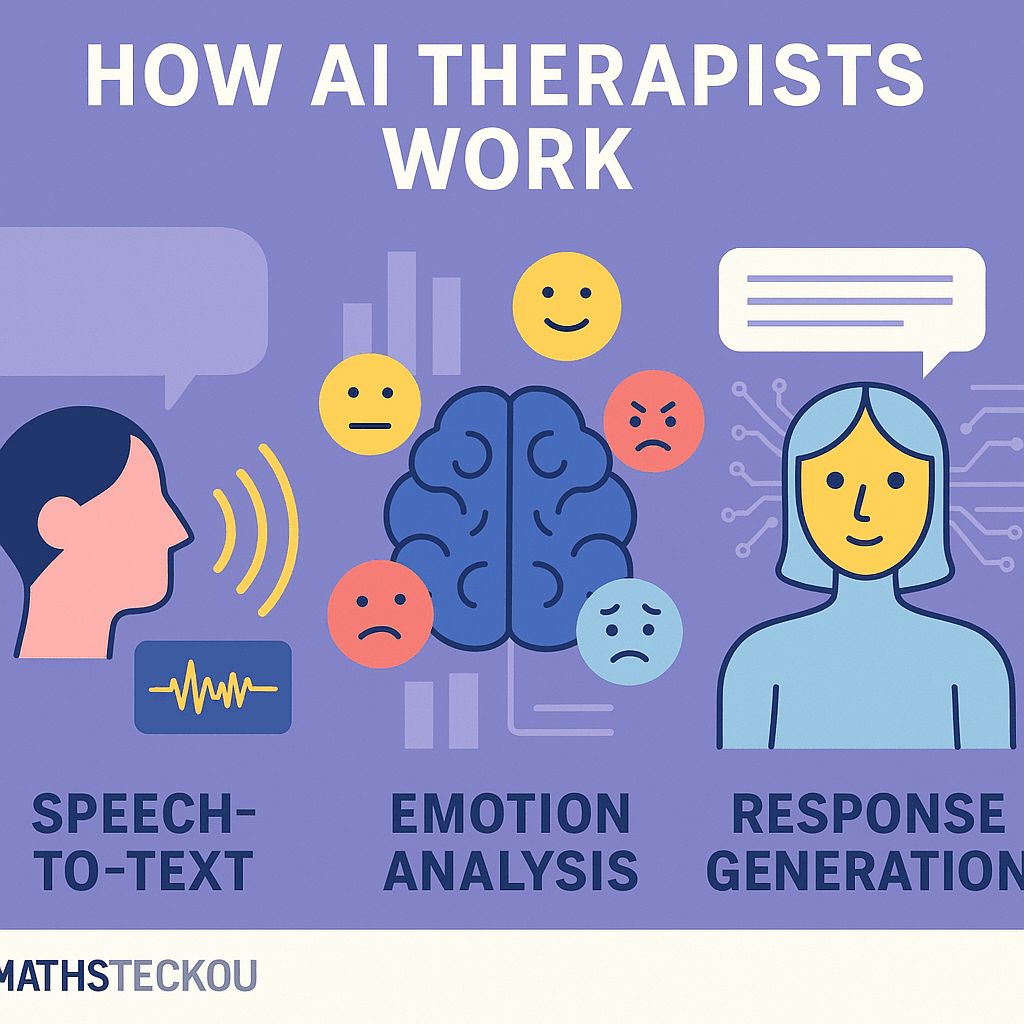
How AI Therapists Work: The Technology Behind the Talk
Ever chatted with an AI therapist like Woebot or Wysa and wondered, How does this machine seem to “get” me? The secret lies in combining Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning, and behavioral analytics to drive meaningful insights and responses.
Let’s break down the key technologies that power AI therapists and make them feel so conversational—and sometimes, even comforting.
🧠 Natural Language Processing (NLP): Understanding Human Language
At the core of every AI therapist is NLP—the ability to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a contextual and emotionally intelligent way.
- Text tokenization: Breaks down your input into words and phrases.
- Syntax parsing: Understands grammar and sentence structure.
- Emotion recognition: Detects underlying emotions based on word choice, tone, and typing patterns.
For instance, if you say “I feel stuck and hopeless,” the system flags this as a low-emotion sentiment and tailors its response to be supportive, perhaps offering a CBT-based tool to reframe the thought.
💬 Conversational AI: Real-Time Dialogue Simulation
This is what makes AI therapists feel “human.” They’re designed to mimic natural human conversation, offering follow-up questions, empathetic replies, and even occasional humor to build rapport.
- Pre-trained on millions of mental health dialogues
- Leverages contextual memory to recall and reference previous parts of the conversation, creating a more coherent and personalized dialogue.
- Can escalate or de-escalate tone depending on user mood
The goal is to create an interaction that feels natural, even if it’s entirely machine-generated.
📈 Behavioral Pattern Tracking: Learning From You Over Time
AI therapists don’t just listen—they learn.
Over repeated interactions, the system collects data on:
- Mood fluctuations
- Recurring concerns
- User engagement patterns
This enables personalized insights, such as:
“You’ve mentioned feeling anxious about work three times this week. Would you like to explore what’s causing this?”
This continuous learning helps the AI become a better support tool tailored to your needs—making users often ask: Do AI therapists work better over time? For many, the answer is yes.
🔍 Supporting Technologies: The Real Engine
| Technology | Role in AI Therapy |
|---|---|
| Sentiment Analysis | Gauges emotional tone from text |
| NLP Models (e.g., GPT) | Enables fluid and logical language generation |
| Behavioral Analytics | Tracks usage trends and adapts conversation paths |
| Reinforcement Learning | Improves responses based on feedback loops |
These technologies combine to create an AI therapist experience that’s fast, scalable, and surprisingly intuitive—but still, not quite human.
Are AI Therapists Good? Measuring Effectiveness
AI therapists may be available 24/7 and speak in reassuring tones—but are they actually helpful?
Let’s examine the growing body of research, user testimonials, and expert reviews that attempt to answer the question:
👉 Do AI therapists work—and are they any good?
📊 What the Data Says: Studies and User Feedback
- A Stanford University study on Woebot users showed significant reductions in anxiety and depression symptoms after just two weeks of usage.
- Wysa reported that 70% of users felt better after a single session with its AI chatbot.
- Replika’s emotionally intelligent AI has seen strong user engagement, particularly among individuals experiencing loneliness, by delivering interactions that feel remarkably companion-like.
While not a substitute for clinical therapy, many users report feeling heard, supported, and even emotionally connected—surprising outcomes from code and algorithms.
✅ The Pros: Why Users Are Turning to AI Therapists
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| 24/7 Availability | Support at any time—no need to book appointments. |
| Low/No Cost | Many platforms are free or offer affordable premium plans. |
| No Stigma | Users can open up without fear of judgment or social labeling. |
| Accessibility | Helpful for people in rural areas or countries lacking mental health access. |
AI therapists offer immediate emotional support, which is a game-changer in a world where waitlists for human therapists often stretch for weeks or months.
❌ The Cons: Where AI Falls Short
Despite promising outcomes, AI therapists do not replace human therapists—especially in complex mental health cases.
| Limitation | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Lack of Deep Empathy | AI can simulate emotion but doesn't truly "feel" or "understand" you. |
| No Legal Licensing | Cannot legally diagnose or treat clinical mental health disorders. |
| Misses Context | May not fully grasp personal history, culture, or subtle emotional cues. |
| Risk of Overreliance | Users might avoid real help thinking AI is enough. |
🤖 AI vs Human Therapists: A Comparison
| Criteria | AI Therapist | Human Therapist |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | 24/7 | Limited by schedule |
| Empathy | Simulated | Authentic emotional intelligence |
| Cost | Low to free | High (insurance or out-of-pocket) |
| Personalization | Based on interaction history | Based on holistic understanding |
| Complexity Handling | Limited | Trained to handle trauma, disorders |
🧠 Final Verdict: Are AI Therapists Good?
Yes, with limits.
For managing everyday stress, mood tracking, and emotional wellness, AI therapists do work—and for many, they’re a powerful starting point.
But for deep healing, trauma recovery, or psychiatric care, they’re still just the first step in a larger mental health journey.
Real-World Case Studies: AI Therapy in Action
AI therapists are no longer just a futuristic concept—they’re already making real-world impact. From mental health support apps to corporate wellness platforms, AI therapists are helping millions manage their emotional well-being.
Let’s dive into some notable platforms leading the charge in AI-based therapy—and what real users and researchers are saying about them.
🤖 Woebot: A Clinically Validated Mental Health Chatbot
Developed by Stanford researchers, Woebot uses cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) principles to offer daily mental health check-ins and emotional coaching.
- Clinical Backing: A study in the JMIR Mental Health Journal found that Woebot significantly reduced symptoms of depression in just two weeks.
- How It Works: Through friendly, daily conversations, Woebot helps users reframe negative thoughts using evidence-based techniques.
- User Sentiment: Most users praise its non-judgmental tone, humor, and privacy as reasons they feel comfortable opening up.
💬 Wysa: An AI-Backed Emotional Support Coach
Wysa blends AI conversation with the option to connect with human therapists.
- Personalized Tools: Offers mindfulness exercises, mood tracking, CBT activities, and anxiety-reduction guides.
- Corporate Adoption: Major companies like Accenture and Aetna are using Wysa in employee wellness programs.
- Global Reach: Used in over 65 countries with millions of downloads, showing the growing trust in AI therapists worldwide.
❤️ Replika: An AI Companion with Emotional Intelligence
Unlike traditional therapy apps, Replika is designed to be a digital companion, learning from your interactions and offering emotional conversations.
- Unique Approach: Users can form “relationships” with their AI, from friends to romantic partners.
- Emotional Connectivity: Uses deep learning to mimic emotional expression, creating a sense of intimacy.
- Controversial But Popular: While some users find comfort in Replika’s companionship, experts caution against over-attachment to synthetic relationships.
🧪 Clinical Research & Adoption Trends
| Platform | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Woebot | Clinically validated to reduce depression and anxiety symptoms |
| Wysa | 93% of users found it helpful in self-management, according to internal data |
| Replika | High engagement, but mixed reviews on emotional dependence |
AI therapists are also seeing adoption in:
- Hospitals and telehealth platforms for initial screenings
- Schools and universities as a low-cost mental health resource
- HR wellness programs to reduce workplace stress
These real-world examples demonstrate that AI therapists are already making a measurable impact—even if they’re not perfect.
Emotional Intelligence in Machines: Can AI Truly Understand Feelings?
One of the biggest debates in the rise of AI therapists is this:
Can a machine truly understand how you feel—or is it just pretending?
This question lies at the heart of emotional AI, also known as affective computing—the technology that gives machines the ability to simulate empathy and detect emotional states.
🧠 Emotion Recognition Algorithms: How AI Detects Feelings
Today’s AI therapists use advanced emotion detection systems that analyze:
- Text-based sentiment (e.g., sadness, anger, hope)
- Tone and typing behavior
- Repeated patterns in conversations
Tools like sentiment analysis and NLP engines classify emotional cues in real time, allowing the AI to adjust tone, suggest coping tools, or escalate responses when needed.
For example:
If you type: “I’m exhausted and don’t see a way out,”
The AI may classify it as a high-risk input and respond with grounding exercises or refer you to crisis resources.
🤖 Synthetic Empathy: Real Support or an Illusion?
AI doesn’t feel emotions—it recognizes patterns and generates appropriate responses.
But can this simulation of care still be meaningful?
- Many users report feeling heard by AI therapists, even knowing it’s not human.
- Some prefer AI for its neutrality, consistency, and non-judgmental nature.
- Still, others say it lacks nuance, especially in delicate emotional situations like grief or trauma.
🧬 The Psychology of Bonding with Machines
Humans are wired to form emotional connections—even with machines. This is known as anthropomorphism, where we attribute human traits to non-human agents.
- Studies show that users of Replika and Wysa often describe their AI as a friend, a safe space, or a confidant.
- These emotional bonds can reduce loneliness, especially for people who struggle with social interaction.
However, critics warn that over-reliance on emotionally intelligent AI could blur the lines between real and artificial connection, potentially leading to:
- Isolation from real-world relationships
- Avoidance of professional help
- Emotional dependence on software
❤️ Human Connection vs. Machine Understanding
| Trait | AI Therapist | Human Therapist |
|---|---|---|
| Emotion Recognition | Pattern-based, reactive | Intuitive, empathetic, deeply nuanced |
| Empathy | Simulated via programming | Genuine and emotionally resonant |
| Trust-Building | Based on consistency | Based on shared understanding and rapport |
| Adaptive Emotional Depth | Limited to pre-programmed responses | Deeply responsive to complex emotions |
🔍 Final Thought: Can Machines Understand Feelings?
AI therapists are advancing rapidly in emotional intelligence, but they still operate within coded boundaries. They don’t feel—but they can respond in ways that feel real.
For many users, this is enough. For others, it’s a reminder that technology should augment, not replace, genuine human empathy.
Ethical Questions and Privacy Concerns
With the rise of AI in mental health care, we are entering uncharted territory—not just in terms of technological innovation, but also in the realm of ethics and privacy. As AI therapists begin to play an increasingly significant role in providing emotional support and therapy, several important questions arise.
🔐 What Happens to Your Therapy Conversations?
AI therapists, like Woebot, Wysa, and Replika, store and process users’ emotional data, conversation logs, and other sensitive information. This data collection can significantly enhance the AI’s ability to tailor responses and track progress—but it also raises significant privacy concerns.
- Data Usage: While companies often state that user conversations are anonymized and only used for improvement, the question remains: how secure is this data in the long run? Who controls it, and how might it be shared or sold in the future?
- User Rights: Do users have the right to request the deletion of their data or to know exactly what is being collected?
These questions are critical because mental health data is some of the most personal and sensitive information a person can share. Without stringent protections, users risk exposure to potential misuse.
🔒 Are AI Therapy Platforms Secure and Transparent?
Despite advances in security protocols, data breaches are a real threat. Companies providing AI therapy services must be fully transparent about the security measures they implement to protect users’ mental health information. This includes:
- End-to-end encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
- Well-defined privacy guidelines that transparently explain how user data is gathered, managed, and utilized.
- User consent—ensuring that users understand how their data will be processed and for what purpose.
However, even with the most robust systems, data security remains an ongoing concern. AI platforms that store and analyze sensitive emotional data must continue to evolve their security measures.
🧠 Over-Reliance on AI for Serious Mental Health Conditions
One of the potential risks of AI-based therapy is the over-reliance on these systems for serious mental health conditions. While AI can be highly effective for managing mild to moderate symptoms (e.g., stress, anxiety, mood tracking), it cannot replace the deep emotional understanding or clinical expertise that human therapists provide for conditions such as:
- Severe depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Complex personality disorders
AI systems may lack the nuanced judgment to detect when someone needs immediate, in-person care. Without proper human oversight, there’s a risk that AI therapists might be used as a substitute rather than a complementary tool, leaving some people without the professional help they truly need.
⚖️ The Need for Regulation and Ethical Boundaries in AI Mental Health
As the AI-driven therapy industry continues to grow, ethical guidelines and regulatory standards are essential for protecting both users and developers. Governments, tech companies, and mental health professionals need to collaborate on establishing clear regulations:
- Transparency in AI functions and capabilities.
- Ethical boundaries to ensure AI does not manipulate or take advantage of vulnerable users.
- Accountability structures for any potential harm caused by inaccurate or biased AI recommendations.
The AI in mental health space must evolve in tandem with these ethical frameworks to build trust and ensure these tools are safe, effective, and fair.
The Future of AI Therapy: Partnership, Not Replacement
As we look toward the future of AI therapists, we begin to imagine a model where human therapists and AI work together—each complementing the other’s strengths. Instead of AI therapists replacing human intervention, the future may hold a synergistic relationship where both can co-exist and collaborate.
🤝 AI as a Co-Pilot for Human Therapists
In this future model, AI could serve as a co-pilot to human therapists, providing essential support in areas like:
- Mood tracking: AI can continuously monitor and track a patient’s emotional and psychological state between sessions, offering real-time insights for therapists to work with.
- Progress reports: AI could help generate data-driven reports that highlight trends and improvements, making therapist evaluations more precise.
- Automated check-ins: AI systems can conduct brief check-ins between therapy sessions to track progress and remind patients of coping strategies, ensuring that clients don’t fall through the cracks.
By handling routine tasks and analyzing background data, AI could free up human therapists to concentrate on delivering deeper emotional support and nuanced care.
🧠 AI Advancements: What’s Next?
Looking further ahead to 2050, AI therapists could be much more advanced, incorporating:
- Voice tone analysis: Understanding tone of voice in addition to text, allowing AI to detect emotional nuances and tailor responses with even more accuracy.
- Virtual reality integration: Imagine AI therapy that takes place in immersive virtual environments, where users can confront their issues in simulated, safe spaces.
- Deeper personality modeling: AI could assess personality traits, life events, and emotional triggers, adapting responses to create highly personalized treatment.
These developments could radically improve the effectiveness and reach of virtual therapy sessions, allowing more people to benefit from personalized mental health care at scale.
🌍 AI in Underserved Regions: Bridging the Mental Health Gap
Perhaps the most promising aspect of AI therapists is their ability to scale. In areas where access to mental health professionals is limited—whether due to geographical location, economic barriers, or cultural stigma—AI therapists could offer an affordable, scalable solution.
For example:
- Global access: AI platforms can be accessed anywhere, anytime, offering instant support to those who would otherwise have limited resources.
- Cost-effective care: By reducing the need for extensive infrastructure or in-person consultations, AI platforms could provide affordable mental health care to the masses.
AI has the potential to be a game-changer in reducing global mental health disparities.
Conclusion: Can a Machine Really Care?
As we reach the end of this exploration into AI therapists, it’s clear that while they hold tremendous promise, they are still a far cry from replacing human care. AI can help manage emotional well-being, offer accessible support, and improve mental health care in underserved regions, but can it truly “care”?
The Strengths of AI Therapists:
- 24/7 availability and accessibility
- Scalable solutions for mental health crises
- Non-judgmental support and reduced stigma
The Limitations:
- Lack of human empathy and the ability to understand complex emotional nuances
- Risk of over-reliance, leaving patients without necessary human intervention
- Privacy and ethical concerns
Looking ahead, the future of mental health therapy may not be about AI replacing humans, but rather about AI making it easier for more people to access care. AI and humans can work together, with machines acting as tools to augment and support traditional therapy. But the ultimate question remains: Can a machine ever truly understand the human heart? Can it really care?
Want to explore more mind-bending ideas at the intersection of AI and emotion? Don’t miss these fascinating reads:
-
AI Dream Interpretation – Can artificial intelligence really decode what your subconscious is trying to say?
-
Emotion AI: Can Robots Truly Feel or Just Fake It? – Dive into whether machines can genuinely experience emotions or are just expert imitators.
-
Smart Mirrors That Diagnose You – Discover how your bathroom mirror might soon act as your personal health assistant.
-
Augmented Reality in Healthcare – See how AR is reshaping surgery, therapy, and patient care in ways we never imagined.